Cybercrime impacts folks from all walks of life, however it hits small companies the toughest. Whereas cyberattacks on giant corporations and authorities companies get a majority of the information protection, small companies (broadly talking, organizations with lower than 500 staff) are typically extra susceptible to cybercriminals and endure extra proportionally from the outcomes of cyberattacks. A scarcity of skilled safety operations workers, underinvestment in cybersecurity, and smaller info expertise budgets total are contributing components to this degree of vulnerability. And when they’re hit by cyberattacks, the expense of restoration could even power many small companies to shut.
Small companies will not be a small matter. In response to the World Financial institution, greater than 90% of the world’s companies are small- and medium-sized organizations, they usually account for greater than 50% of employment worldwide. In america, small and medium companies account for over 40% of total financial exercise. (On this report, we’ll use the phrases small- and medium-sized companies or organizations interchangeably, reflecting their similarity in our information.)
In 2023, over 75% of buyer incident response circumstances dealt with by Sophos’ X-Ops Incident Response service had been for small companies. Information collected from these circumstances, along with telemetry collected from clients of our small- and medium-sized enterprise safety software program, offers us additional distinctive perception into the threats which are focusing on these organizations every day.
Based mostly on that information and Sophos menace analysis, we see that ransomware continues to have the best affect on smaller organizations. However different threats additionally pose an existential menace to small companies:
- Information theft is the main target of most malware focusing on small and medium companies—password stealers, keyboard loggers, and different spyware and adware made up almost half of malware detections. Credential theft by phishing and malware can expose small companies’ information on cloud platforms and repair suppliers, and community breaches can be utilized to focus on their clients as nicely
- Attackers have stepped up using web-based malware distribution—by malvertising or malicious SEO (“search engine optimization poisoning”)—to beat difficulties created by the blocking of malicious macros in paperwork, along with utilizing disk photos to overwhelm malware detection instruments
- Unprotected units linked to organizations’ networks—together with unmanaged computer systems with out safety software program put in, improperly configured computer systems and methods working software program fallen out of help by producers—are a main level of entry for all sorts of cybercrime assaults on small companies
- Attackers have turned more and more to abuse of drivers—both susceptible drivers from respectable corporations or malicious drivers which have been signed with stolen or fraudulently obtained certificates—to evade and disable malware defenses on managed methods
- Electronic mail assaults have begun to maneuver away from easy social engineering towards extra lively engagement with targets over electronic mail, utilizing a thread of emails and responses to make their lures extra convincing
- Assaults on cellular system customers, together with social engineering-based scams tied to the abuse of third-party companies and social media platforms, have grown exponentially, affecting people and small companies. These vary from enterprise electronic mail and cloud service compromise to pig butchering (shā zhū pán (殺豬盤)) scams.
A phrase about our information
The information utilized in our evaluation comes from the next sources:
- Buyer experiences—detection telemetry from Sophos safety software program working on clients’ networks, which provides a broad view of threats encountered, and analyzed inside SophosLabs (on this report, known as the Labs dataset);
- Managed Detection and Response (MDR) incident information, gathered in the middle of escalations pushed by detection of malicious exercise on MDR clients’ networks (on this report, known as the MDR dataset);
- Incident Response crew information, drawn from incidents on buyer networks for enterprise of 500 staff or fewer the place there was little or no managed detection and response safety in place (on this report, known as the IR dataset).
For a deeper take a look at information drawn strictly from the circumstances dealt with by our external-facing IR crew (together with circumstances involving clients with greater than 500 staff), please see our sister publication, the Energetic Adversary Report (AAR). The conclusions on this report are based mostly, except in any other case acknowledged, on the mixed datasets with applicable normalization.
Information is the prime goal
The best cybersecurity problem going through small companies—and organizations of all sizes—is information safety. Greater than 90% of assaults reported by our clients contain information or credential theft in a method or one other, whether or not the tactic is a ransomware assault, information extortion, unauthorized distant entry, or just information theft.
Enterprise electronic mail compromise (BEC), during which electronic mail accounts are taken over by a cybercriminal for the aim of fraud or different malicious functions, is a considerable downside within the small-to-medium enterprise set. We don’t at the moment cowl BEC in our sister publication, the Energetic Adversary Report, however the authors of the AAR estimate that in 2023, enterprise electronic mail compromises had been recognized by our Incident Response crew extra typically than every other kind of incident, save ransomware.
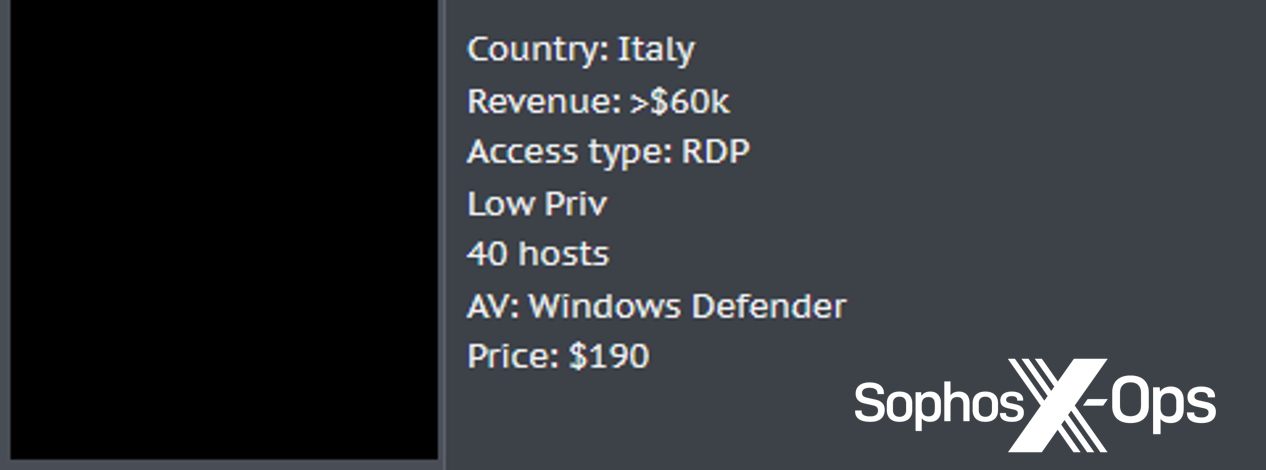
Stolen credentials, together with browser cookies, can be utilized for enterprise electronic mail compromise, entry to third-party companies akin to cloud-based finance methods, and entry to inner assets that may be exploited for fraud or different financial achieve. They will also be offered by “entry brokers” to anybody who cares to use them; Sophos has tracked affords on underground boards claiming to supply entry to quite a lot of small and medium companies’ networks.
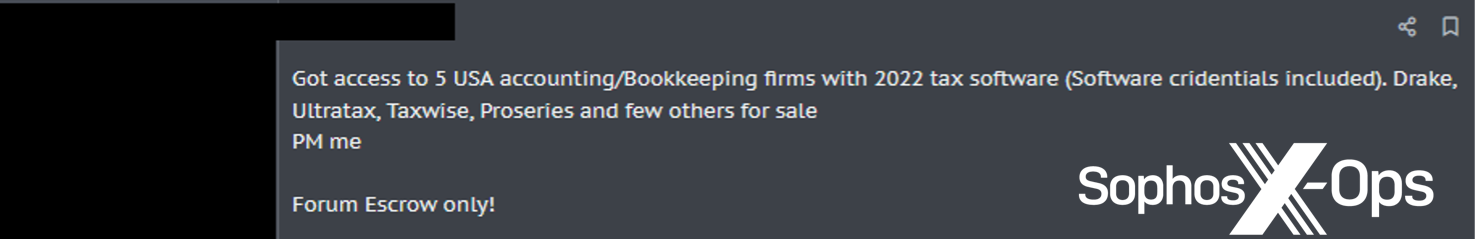
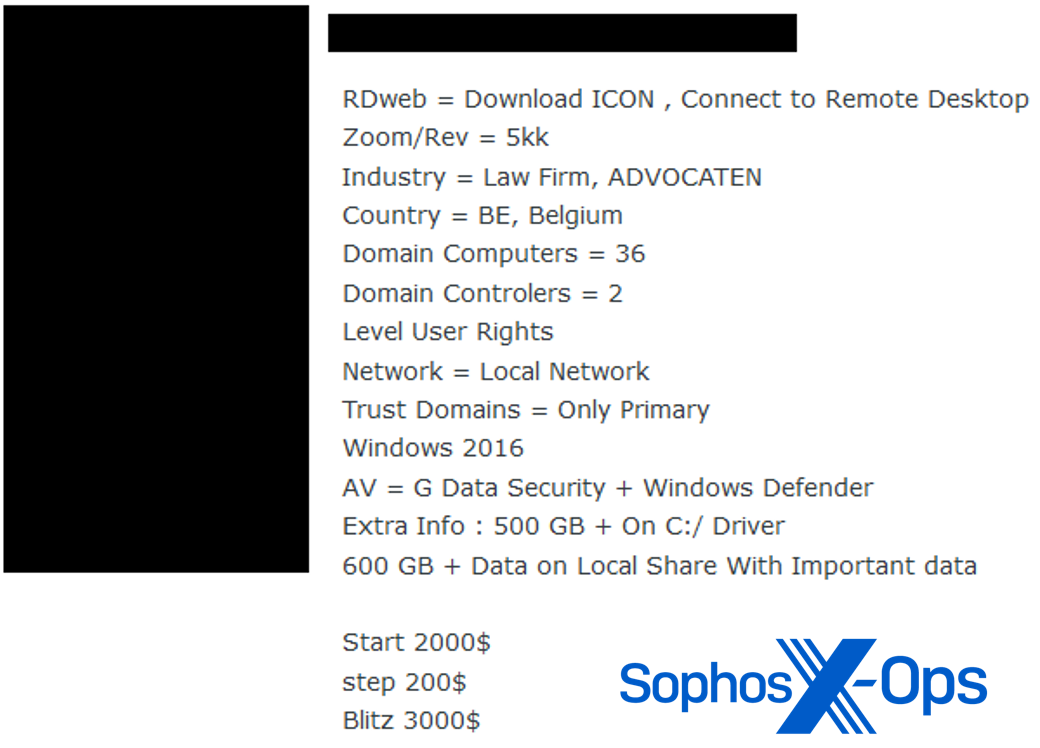
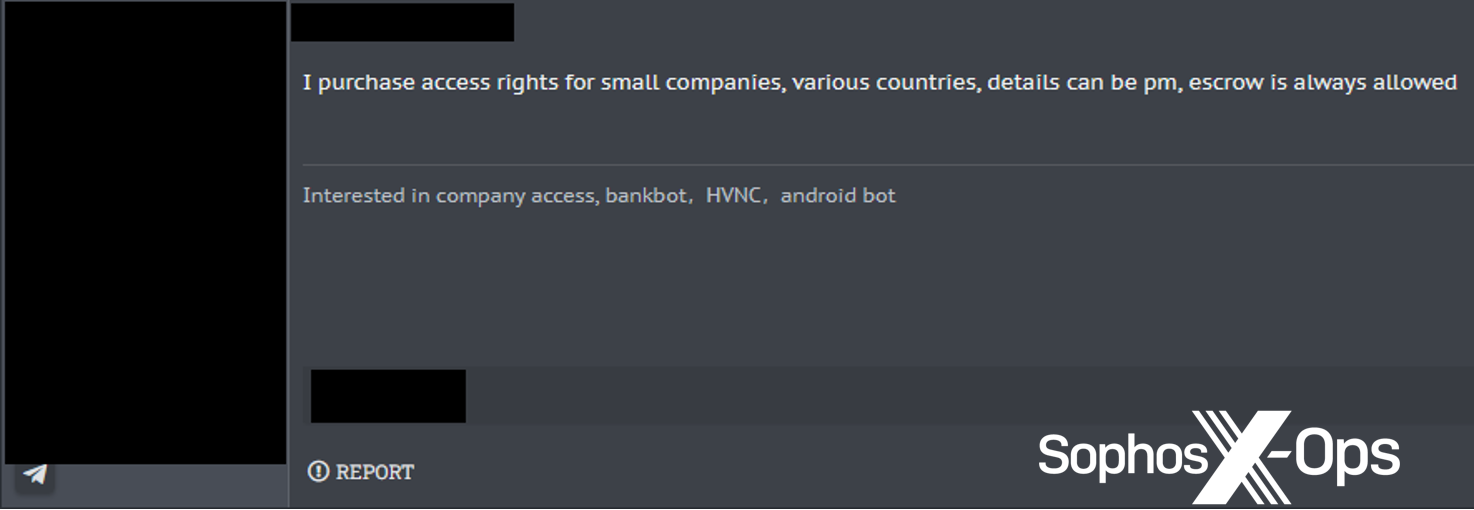
Determine 3: A cybercriminal providing to buy entry to small corporations
By class, almost half of malware detected in 2023 focused the information of its supposed victims. The vast majority of that’s malware we’ve categorised particularly as “stealers”—malware that grabs credentials, browser cookies, keystrokes, and different information that may be both was money as offered entry or used for additional exploitation.
Due to the modular nature of malware, nonetheless, it’s troublesome to utterly categorize malware by performance—almost all malware has the power to steal some type of information from focused methods. These detections additionally don’t embrace different credential theft strategies, akin to phishing by way of electronic mail, textual content message, and different social engineering assaults. After which there are different targets, akin to macOS and cellular units, the place malware, doubtlessly undesirable functions, and social engineering assaults goal customers’ information—particularly of the monetary sort.
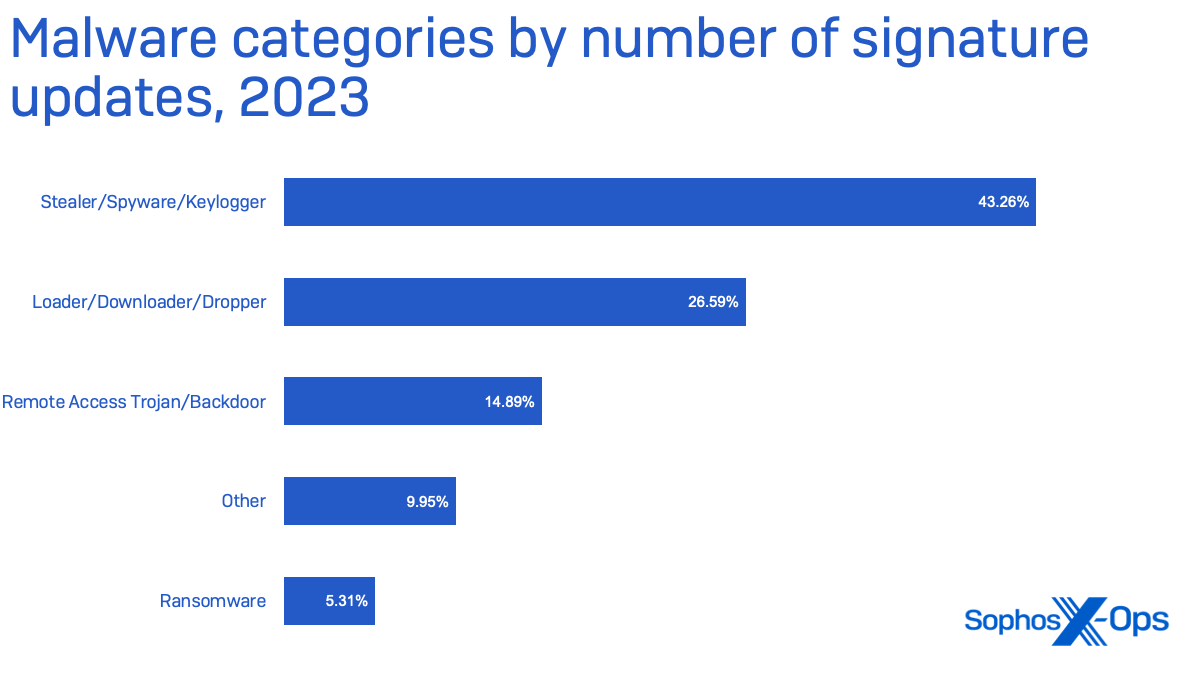
Practically 10% of malware detected falls outdoors of the 4 main classes proven above. This “different” class consists of malware that targets browsers to inject ads, redirect search outcomes to earn money for clicks, or in any other case modifies or collects information for the revenue of the malware developer, amongst different issues.
Some stealers are very particular of their focusing on. Discord “token” stealers, supposed to steal Discord messaging service credentials, are sometimes leveraged to ship different malware by chat servers or by way of Discord’s content material supply community. However different main stealers—Strela, Raccoon Stealer, and the venerable RedLine stealer household—are way more aggressive of their focusing on, accumulating password shops from the working system and functions in addition to browser cookies and different credential information. Raccoon Stealer has additionally deployed cryptocurrency “clippers” which swap crypto pockets addresses copied to the clipboard with a pockets tackle managed by the malware operator.
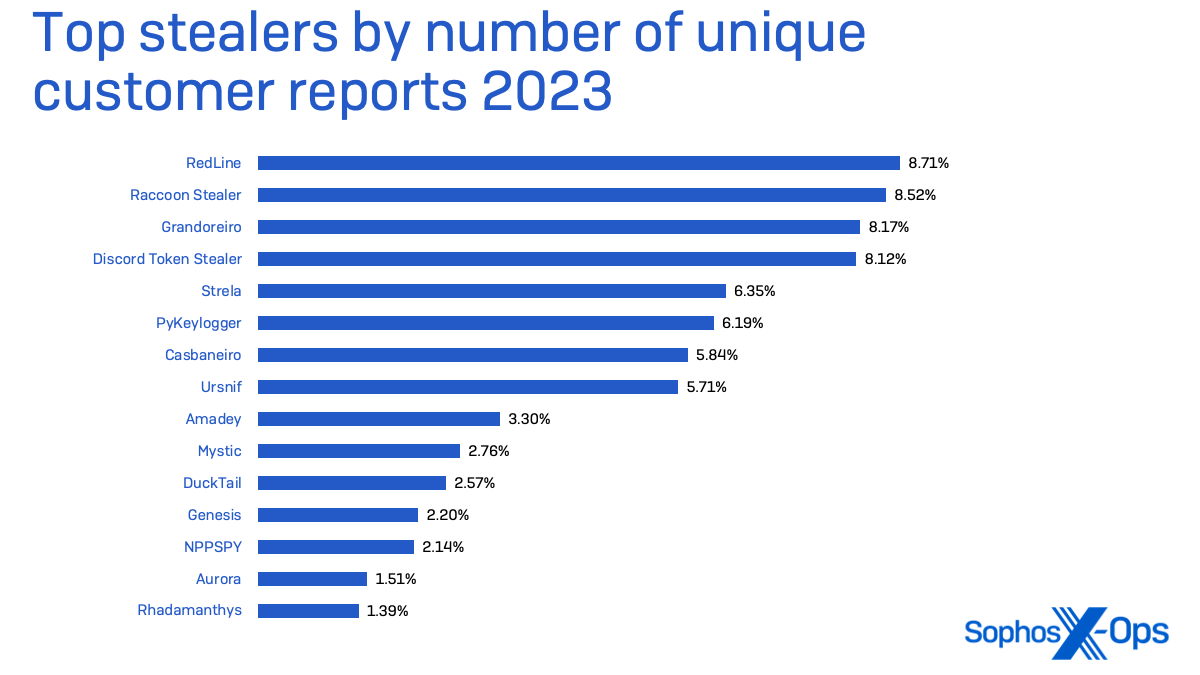
Sophos has seen a rise within the variety of information-stealing malware focusing on macOS, and we imagine that pattern will proceed. These stealers—a few of that are offered in underground boards and Telegram channels for as much as $3,000— can accumulate system information, browser information, and cryptowallets.
Ransomware stays a prime menace for small companies
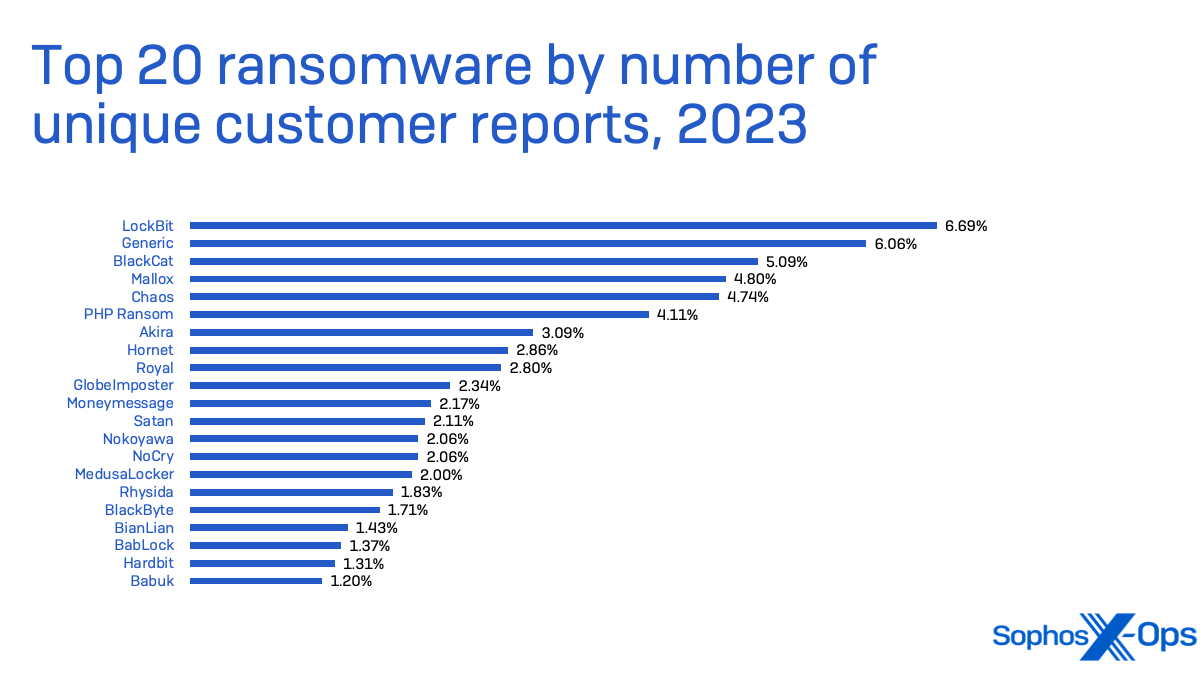
Whereas ransomware makes up a comparatively small proportion of total malware detections, it nonetheless packs the most important punch when it comes to affect. Ransomware impacts all sizes of companies throughout all sectors, however now we have seen it hit small- and medium-sized enterprises probably the most continuously. In 2021, the Institute for Safety and Expertise’s Ransomware Job Pressure discovered that 70% of ransomware assaults focused small companies. Whereas the general variety of ransomware assaults has assorted yr over yr, that proportion bears out in our personal metrics.
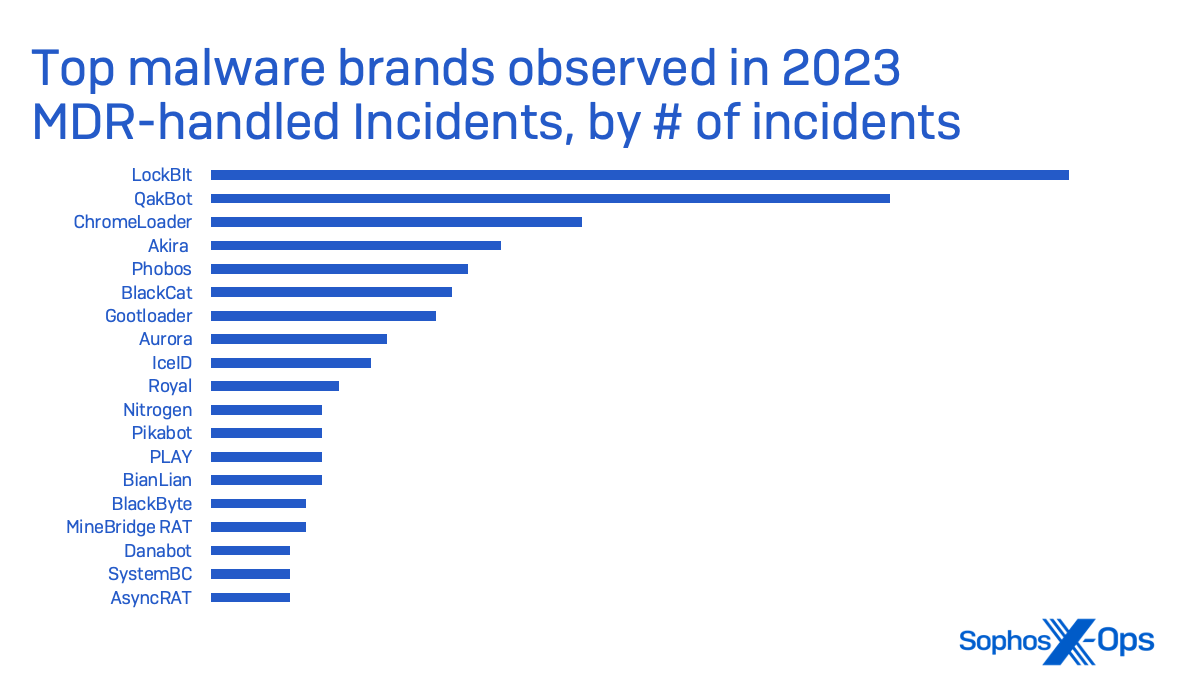
LockBit ransomware was the highest menace in small enterprise safety circumstances taken on by Sophos Incident Response in 2023. LockBit is a ransomware-as-a-service, delivered by quite a lot of associates, and was probably the most deployed ransomware of 2022 based on Determine 7.
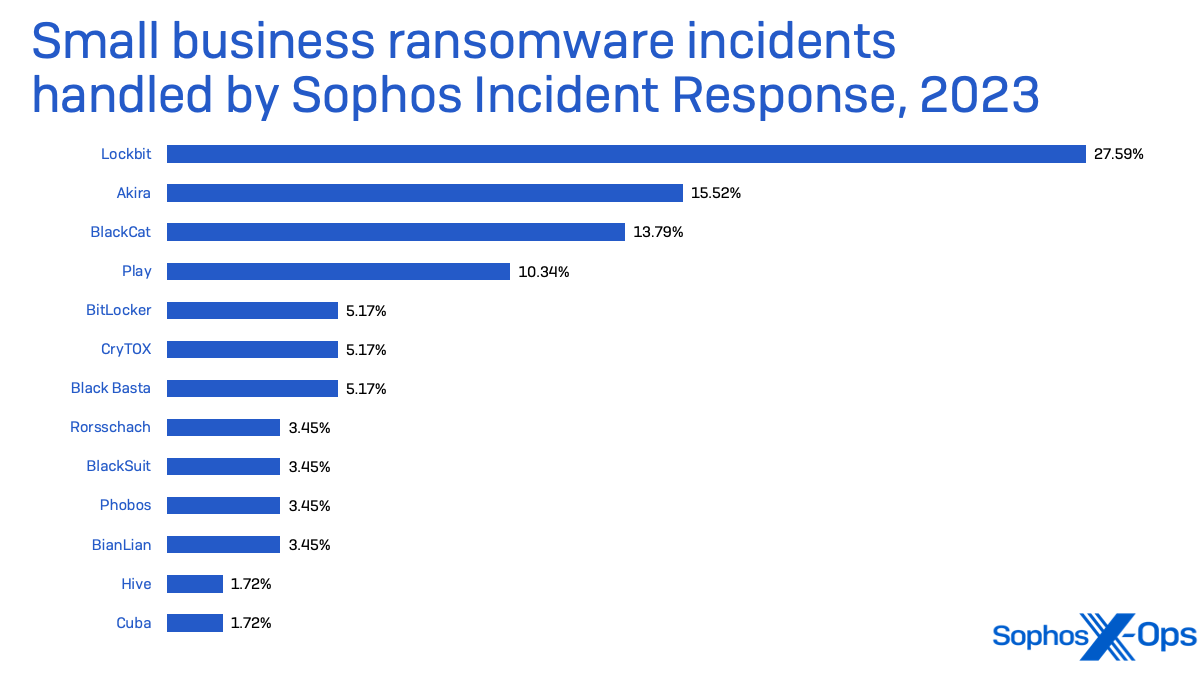
LockBit was the malware noticed probably the most by Sophos’ Managed Detection and Response (MDR) group (which incorporates the Incident Response crew and its information)—with almost 3 times the variety of incidents during which ransomware deployment was tried than its nearest peer, Akira.
As 2023 progressed, we noticed a rise in using distant execution of ransomware—utilizing an unmanaged system on organizations’ networks to aim to encrypt recordsdata on different methods by community file entry.
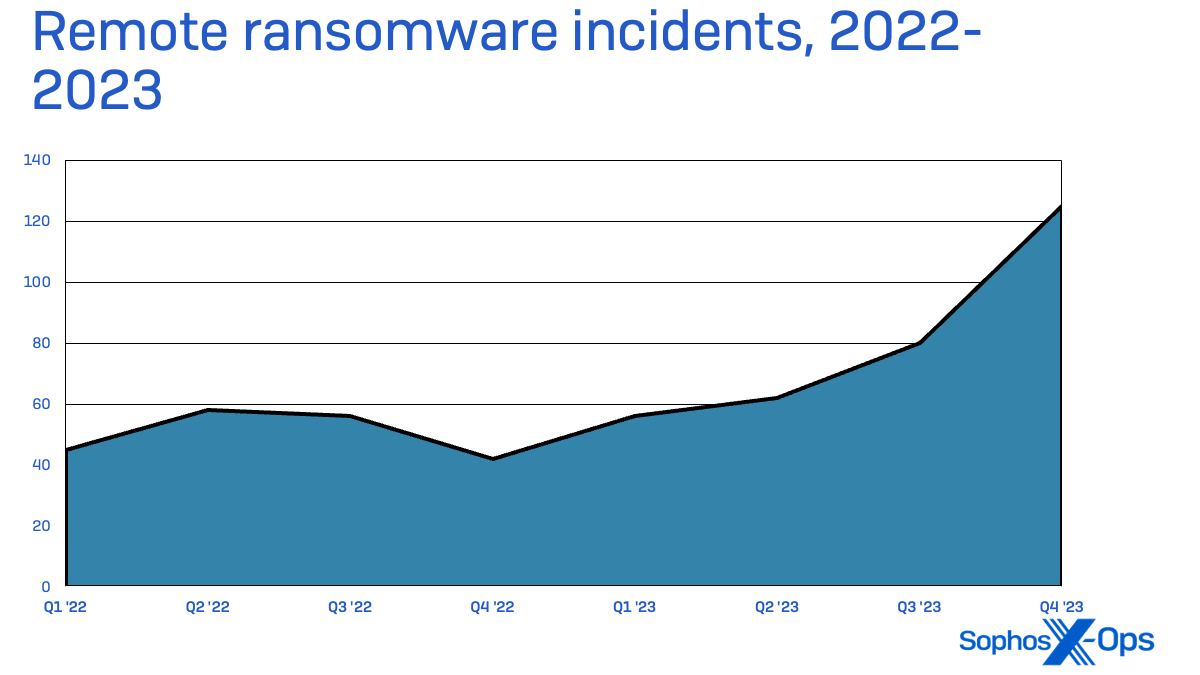
These kinds of assaults are capable of achieve footholds by exploitation of unprotected servers, private units, and community home equipment that hook up with organizations’ Home windows-based networks. Protection in depth can stop these assaults from taking whole organizations offline, however they’ll nonetheless go away organizations susceptible to information loss and theft.
Home windows methods aren’t the one ones focused by ransomware. More and more, ransomware and different malware builders are utilizing cross-platform languages to construct variations for macOS and Linux working methods and supported {hardware} platforms. In February of 2023, a Linux variant of Cl0p ransomware was found to have been utilized in a December 2022 assault; since then, Sophos has noticed leaked variations of LockBit ransomware focusing on macOS on Apple’s personal processor and Linux on a number of {hardware} platforms.
Cybercrime as a service
The malware world continues to be dominated by what we’ve known as “Malware as a Service” (MaaS)—using malware supply frameworks offered by cybercriminals by underground marketplaces to different cybercriminals. However a mixture of enhancements in platform safety and takedown operations by business and legislation enforcement have had some affect on the form of the MaaS panorama.
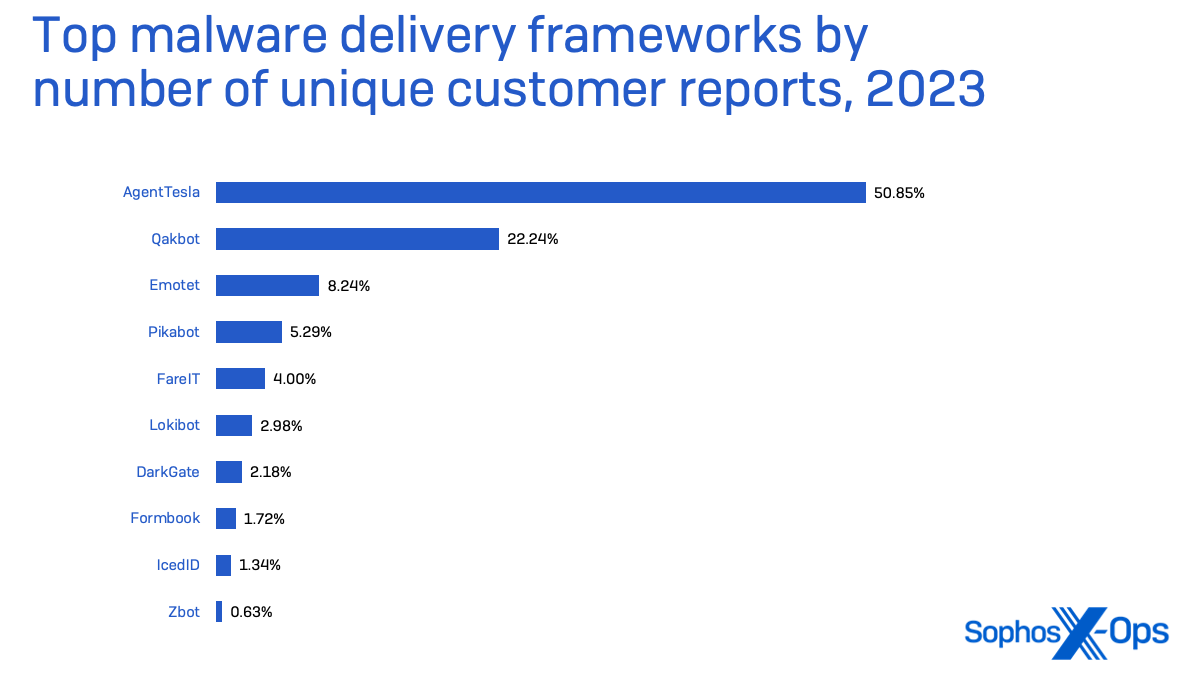
After a decade of dominance within the malware supply enterprise, Emotet has receded since being taken down by Europol and Eurojust in January 2021. So, to a lesser diploma, have Qakbot and Trickbot, after being disrupted by legislation enforcement in August 2023. Whereas Qakbot has returned in some restricted type, it has been largely supplanted by its would-be successors, Pikabot and DarkGate.
None of this has impacted the venerable distant entry trojan AgentTesla, which has moved to the highest of the MaaS market. It was the malware most frequently detected by endpoint safety in 2023 total in endpoint (except for generic malicious .LNK recordsdata and obfuscated malware), and made up 51% of the malware supply framework detections in our telemetry final yr.
Discovering a special supply route
Malware assaults require some type of preliminary entry. Sometimes, that entails one of many following:
- Phishing emails
- Malicious electronic mail attachments
- Exploits of vulnerabilities in working methods and functions
- Pretend software program updates
- Exploitation and abuse of Distant Desktop Protocol
- Credential theft
MaaS operators have up to now been largely reliant on malicious electronic mail attachments for that preliminary foothold. However adjustments to the default safety of the Microsoft Workplace platform have had an affect on the MaaS market. As Microsoft has rolled out adjustments to Workplace functions that block by default Visible Primary for Purposes (VBA) macros in paperwork downloaded from the Web, it has turn into tougher for MaaS operators to make use of their favored technique of spreading malware.
That has led to some adjustments within the varieties of file attachments attackers use—attackers have moved to PDF file attachments virtually solely. Nonetheless, there have been some notable exceptions. In early 2023, Qakbot operators turned to utilizing malicious OneNote paperwork to get round adjustments being pushed out to Excel and Phrase, concealing throughout the doc hyperlinks to script recordsdata that had been activated when the goal clicked on a button throughout the OneNote pocket book file.
In 2021, we famous that “malware-as-a-service” choices such because the RaccoonStealer backdoor had begun to rely closely on internet supply, typically utilizing SEO (search engine optimization) methods to idiot targets into downloading their malware. In 2022, we noticed “search engine optimization poisoning” used as a part of a SolarMarker info stealer marketing campaign. These strategies are on the rise once more, and the actors behind them have grown extra subtle.
We noticed a number of notable campaigns utilizing malicious online advertising and search engine optimization poisoning to focus on victims. One in all these was by an exercise group utilizing malware we dubbed “Nitrogen”; the group used Google and Bing ads tied to particular key phrases to lure targets into downloading a software program installer from a pretend web site, utilizing a respectable software program developer’s model id. The identical malvertising method has been utilized in reference to quite a lot of different preliminary entry malware, together with the Pikabot botnet agent, IcedID info stealer, and Gozi backdoor malware households.
Within the case of Nitrogen, the advertisements focused IT generalists, providing downloads together with well-known distant desktop software program for end-user help and safe file switch utilities. The installers carried what was marketed, however additionally they delivered a malicious Python payload that, when launched by the installer, pulled down a Meterpreter distant shell and Cobalt Strike beacons. Based mostly on different researchers’ findings, this was seemingly step one in a BlackCat ransomware assault.
“Twin use” instruments
Cobalt Strike, the well-worn “adversary simulation and purple crew operations” software program package, continues for use by precise adversaries in addition to respectable safety testing organizations. However it’s not at all the one commercially developed software program utilized by attackers—and it’s now not the most typical.
Distant desktop instruments, file compression instruments, widespread file switch software program, different utilities, and open-source safety testing instruments are generally utilized by attackers for a similar cause that they’re utilized by small and medium enterprises—to make their jobs simpler.
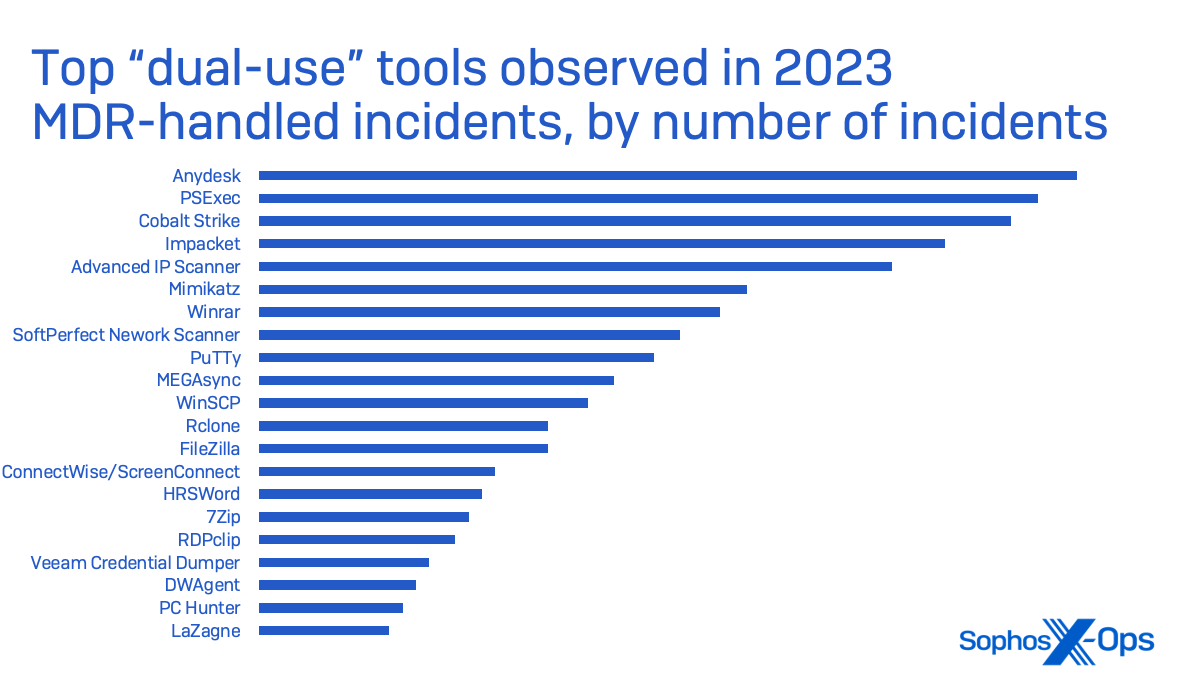
Sophos MDR has noticed these utilities, which we discuss with as “dual-use instruments”, abused as a part of the post-exploitation course of by attackers:
- Discovery: Superior IP Scanner, NetScan, PCHunter, HRSword
- Persistence: Anydesk, ScreenConnect, DWAgent
- Credential Entry: Mimikatz, Veeam Credential Dumper, LaZagne
- Lateral Motion: PsExec, Impacket, PuTTy
- Information Assortment & Exfil: FileZilla, winscp, megasync, Rclone, WinRar, 7zip
AnyDesk and PsExec had been each seen in additional incidents by Sophos MDR than was Cobalt Strike, as seen beneath:
Zero-day assaults and nonzero-day assaults
In Could 2023, Progress Software program reported vulnerabilities within the firm’s broadly used safe managed file switch platform, MOVEit—together with one which had been exploited by a minimum of one set of malicious actors. Subsequently the corporate would reveal a number of extra vulnerabilities and challenge a number of patches to repair them.
The assaults had been attributed to actors related to the Cl0p ransomware ring. The attackers used the vulnerability to deploy internet shells on the public-facing internet interfaces to MOVEit Switch servers—internet shells that in some circumstances endured after the vulnerabilities had been patched by Progress clients.
MOVEit was simply one in all quite a lot of “zero day” vulnerabilities that challenged defenders in 2023. GoAnywhere, one other managed file switch system, disclosed a vulnerability in February that one other CL0p-affiliated group tried to use. And a distant code execution vulnerability within the PaperCut MF and NG print server software program merchandise was exploited by the Bl00dy ransomware gang in March and April after being reported to the builders in January.
In some circumstances, these vulnerabilities merely can’t be patched. For instance, a vulnerability in Barracuda Electronic mail Safety Gateway home equipment, present in June, was so extreme that it couldn’t be patched and required full substitute of bodily or digital home equipment. A Chinese language menace group continued to use the susceptible home equipment all through the remainder of 2023.
Vulnerabilities in software program and units don’t should be new to be leveraged by attackers. Risk actors continuously search out software program that has fallen out of help, akin to older community firewalls and internet server software program, to focus on— figuring out that no patch will likely be coming.
Provide chain assaults and digitally signed malware
Small companies additionally should be involved concerning the safety of the companies they rely on to handle their enterprise—and their IT infrastructure. Provide chain assaults will not be only for nation-state actors; we’ve seen assaults towards managed service suppliers turn into an everlasting a part of the ransomware playbook.
In 2023, Sophos MDR responded to 5 circumstances during which small enterprise clients had been attacked by an exploit of a service supplier’s distant monitoring and administration (RMM) software program. The attackers used the NetSolutions RMM agent working on the focused organizations’ computer systems to create new administrative accounts on the focused networks, after which deployed industrial distant desktop, community exploration and software program deployment instruments. In two of the circumstances, the attackers efficiently deployed LockBit ransomware.
It’s onerous to defend towards assaults that leverage trusted software program, particularly when that software program offers attackers the power to disable endpoint safety. Small companies and the service suppliers who help them have to be vigilant to alerts that endpoint safety has been turned off on methods on their networks, as a result of this can be an indication that an attacker has gained privileged entry by a provide chain vulnerability—or by different software program that initially look could seem respectable.
For instance, in 2023, we noticed quite a lot of cases of attackers utilizing susceptible kernel drivers from older software program that also had legitimate digital signatures, and of deliberately created malicious software program that used fraudulently obtained digital signatures—together with malicious kernel drivers digitally signed by Microsoft’s Home windows {Hardware} Compatibility Writer (WHCP) program—to evade detection by safety instruments and run code that disables malware safety.
Kernel drivers function at a really low degree throughout the working system, and are usually loaded earlier than different software program in the course of the working system’s start-up. That implies that they execute in lots of circumstances earlier than safety software program can begin up. Digital signatures act as a license to drive, so to talk—in all variations of Home windows since Home windows 10 model 1607, kernel drivers have to have a sound digital signature or Home windows working methods with Safe Boot enabled gained’t load them.
In December 2022, Sophos notified Microsoft of the invention of malicious kernel drivers that carried Microsoft-signed certificates. As a result of these drivers had Microsoft-signed certificates, they had been by default accepted as benign software program, permitting them to be put in—after which disable endpoint protections on methods that they had been put in on. Microsoft issued a safety advisory, after which in July 2023 revoked a number of malicious drivers’ certificates that had been obtained by WHCP.
Drivers don’t should be malicious to get exploited. We’ve seen a number of circumstances of drivers and different libraries from older and even present variations of software program merchandise leveraged by attackers to “facet load” malware into system reminiscence.
We’ve additionally seen Microsoft’s personal drivers utilized in assaults. A susceptible model of a driver for Microsoft’s Course of Explorer utility has been used a number of instances by ransomware operators in efforts to disable endpoint safety merchandise; in April 2023, we reported on a software dubbed “AuKill” that used this driver in a number of assaults in makes an attempt to deploy Medusa Locker and LockBit ransomware.
Typically we get fortunate and catch susceptible drivers earlier than they are often exploited. In July, Sophos behavioral guidelines had been triggered by exercise from a driver for one more firm’s safety product. The alert was triggered by a buyer’s personal attacker simulation check, however our investigation of the occasion uncovered three vulnerabilities that we reported to the software program vendor and had been subsequently patched.
Spammers push social engineering boundaries
Electronic mail could seem to be an old-school communication technique in an period of encrypted end-to-end cellular chats, however spammers didn’t appear to note (or care) about that. Whereas the normal BEC technique of merely posing as an worker and asking one other worker to ship reward playing cards persists, spammers have gotten way more inventive.
Previously yr, Sophos’ messaging safety crew got here throughout a slew of latest social engineering methods and methods designed to evade typical electronic mail controls. Messages during which the attacker emails an attachment or hyperlink out of the blue at the moment are passé: The more practical spammers usually tend to strike up a dialog first, then transfer in for the kill in observe up emails.
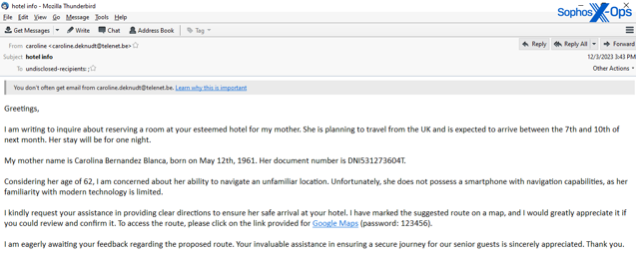
We noticed this system in assaults during which spammers posing as supply service staff referred to as enterprise clients on the cellphone and requested them to open a weaponized electronic mail. We additionally noticed spammers initially electronic mail a solicitation for enterprise or criticism, in assaults focusing on a wide range of industries in 2023, adopted by a hyperlink to obtain a disguised, weaponized file after the enterprise responded to the primary electronic mail.
Typical spam prevention entails processes inspecting message content material and making selections based mostly on that content material. Spammers experimented with a wide range of strategies of changing any textual content content material of their messages with embedded photos: Typically the photographs seemed to be a written message, whereas others experimented with using QR codes or photos that seem like invoices (with phone numbers the attackers immediate victims to name) as a strategy to evade detection.
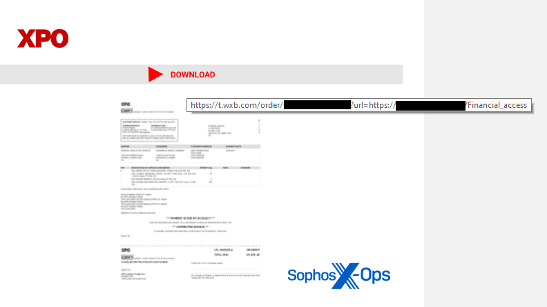
Malicious attachments even pushed boundaries, with weaponized PDFs making one thing of a comeback, linking to malicious scripts or websites, generally utilizing embedded QR codes. The Qakbot malware household expansively abused Microsoft’s OneNote doc format, the pocket book (or .one file), to ship payloads earlier than being shut down later within the yr in a coordinated takedown. Attackers additionally latched onto the MSIX file format – a sort of archive file format utilized by Microsoft to distribute apps by the Home windows App Retailer – as a method of bypassing detection.

And attackers abused Microsoft’s companies as nicely: By the yr’s finish, about 15% of the full spam Sophos blocked had been despatched utilizing electronic mail accounts created in Microsoft’s business-oriented onmicrosoft.com messaging system.
Cell malware and social engineering threats
Small companies rely closely on cellular units as a part of both authorised or ad-hoc info methods. Textual content messages, messaging and communications functions, and apps connecting to cloud companies—together with cellular level of sale functions—are mission-critical methods for distributed small enterprises. Cybercriminals know that, and proceed to seek out methods to focus on cellular system customers to achieve entry to information or to defraud.
Adware and “bankers” are a gaggle of Android malware of specific concern, and which we imagine will proceed to be a menace. Adware is used to reap information on the cellphone—and generally will even subscribe the system’s consumer to premium-rate companies for direct financial achieve. They harvest private information, together with SMS messages and name logs from the affected system, which is then offered to fraudsters or used for blackmail—or each. There have been a number of circumstances the place victims have taken their very own lives on account of threats from spyware and adware operators.
These malicious cellular functions are distributed in quite a lot of methods. They might masquerade as respectable functions on the Google Play app retailer or third-party app retailer websites—typically as cellular lending functions. They’re additionally unfold by hyperlinks despatched by way of textual content messages.
Bankers are malware that focus on monetary functions, together with cryptocurrency wallets, to reap account information to achieve entry to funds—utilizing accessibility permissions to achieve entry to delicate information on the cellphone.
Then there’s the phenomenon of “pig butchering,” or sha zhu pan. We started monitoring pretend functions on each the iOS and Android platform tied to a type of rip-off we first known as “CryptoRom” in early 2021; since then, the scams have turn into more and more extra subtle.
The crime rings that function these scams— continuously operated out of scamming compounds staffed with individuals who have primarily been kidnapped by organized crime—have taken billions of {dollars} from victims worldwide, and infrequently concentrate on folks tied to small companies. In 2023, a small financial institution in Kansas failed and was seized by the FDIC after the financial institution CEO despatched over $12 million from deposits to scammers in an effort to get well funds he had misplaced reportedly in one in all these scams. This tragic instance reveals how a rip-off normally related to a person’s private life can have ramifications and affect on small companies.
Sha zhu pan scammers lure victims by social media websites, relationship apps, different apps and neighborhood platforms, and even “inadvertent” SMS messages. They have a tendency to focus on people who’re in search of a romantic connection or friendship. After shifting the goal to a safe messaging app akin to WhatsApp or Telegram, they achieve their belief and introduce a money-making concept that they declare to have inside information about—and that normally entails cryptocurrency.
Over the previous yr, we’ve seen the pretend functions utilized by these scams making their method into the Google Play and iOS App shops. They evade retailer safety overview by presenting as a benign app till the overview course of is over, after which change distant content material to show it right into a pretend crypto buying and selling app. Any crypto deposited by these apps is instantly pocketed by the scammers.
Lately, we’ve additionally seen these scams undertake a tactic from one other kind of crypto rip-off that requires no pretend apps—as an alternative, they use the “Web3” performance of cellular crypto pockets apps to immediately faucet into wallets created by the victims. We now have recognized a whole bunch of domains related to these “DeFi (Decentralized Finance) mining” variants of sha zhu pan, and as with the pretend apps we establish, we proceed to report them and work to get them taken down.
Conclusions
Small companies face no scarcity of threats, and the sophistication of these threats is usually on par with these used to assault giant enterprises and governments. Whereas the amount of cash that may be stolen is lower than obtainable from a bigger group, the criminals are pleased to steal what you’ve and make up for it in quantity.
Prison syndicates are relying on smaller corporations to be much less well-defended and to not have deployed fashionable, subtle instruments to guard their customers and property. The important thing to efficiently defending towards these threats is to show their assumptions incorrect: Educate your workers, deploy multifactor authentication on all externally going through property, patch servers and community home equipment with the utmost precedence and think about migrating troublesome to handle property like Microsoft Change servers to SaaS electronic mail platforms.
The first distinction in our expertise between the businesses that had been impacted probably the most by cyberattacks and people who suffered the least is time to reply. Having safety specialists to watch and reply 24/7 is desk stakes for an efficient protection in 2024. Staying protected isn’t unattainable; it simply takes complete planning and layered defenses to purchase you time to reply and reduce damages.










