Briefly: The pristine night time skies above certainly one of Earth’s premier astronomical observatories are in jeopardy, and astronomers are sounding the alarm. A large $10 billion renewable power complicated proposed just some miles from the European Southern Observatory’s Very Massive Telescope in Chile may severely disrupt observations with elevated mild air pollution.
European Southern Observatory Director Normal Xavier Barcons instructed House.com that astronomers count on the challenge to brighten the sky by as much as 10 p.c across the observatory. Such a rise can be sufficient to decrease the Very Massive Telescope’s standing because the world’s premier observatory, lowering it to merely an “common” facility.
That modest 10-percent spike packs a much bigger punch than it appears. Barcons warned that elevated mild may stop commentary of as much as 30 p.c of the faintest galaxies at present seen.
The VLT’s unimaginable sensitivity has allowed groundbreaking discoveries like the primary direct picture of an exoplanet and the disclosing of the cosmic net construction. Nonetheless, it might lose this functionality have been the skies to develop into brighter.
The power complicated in query is the INNA Renewables Park, deliberate by US power large AES. It might span over 7,400 acres in Chile’s Atacama Desert and have photo voltaic farms, wind farms, and hydrogen manufacturing amenities. Sadly, the challenge may additionally leak as a lot mild into the night time sky as a metropolis of 20,000 individuals, primarily based on ESO estimates.
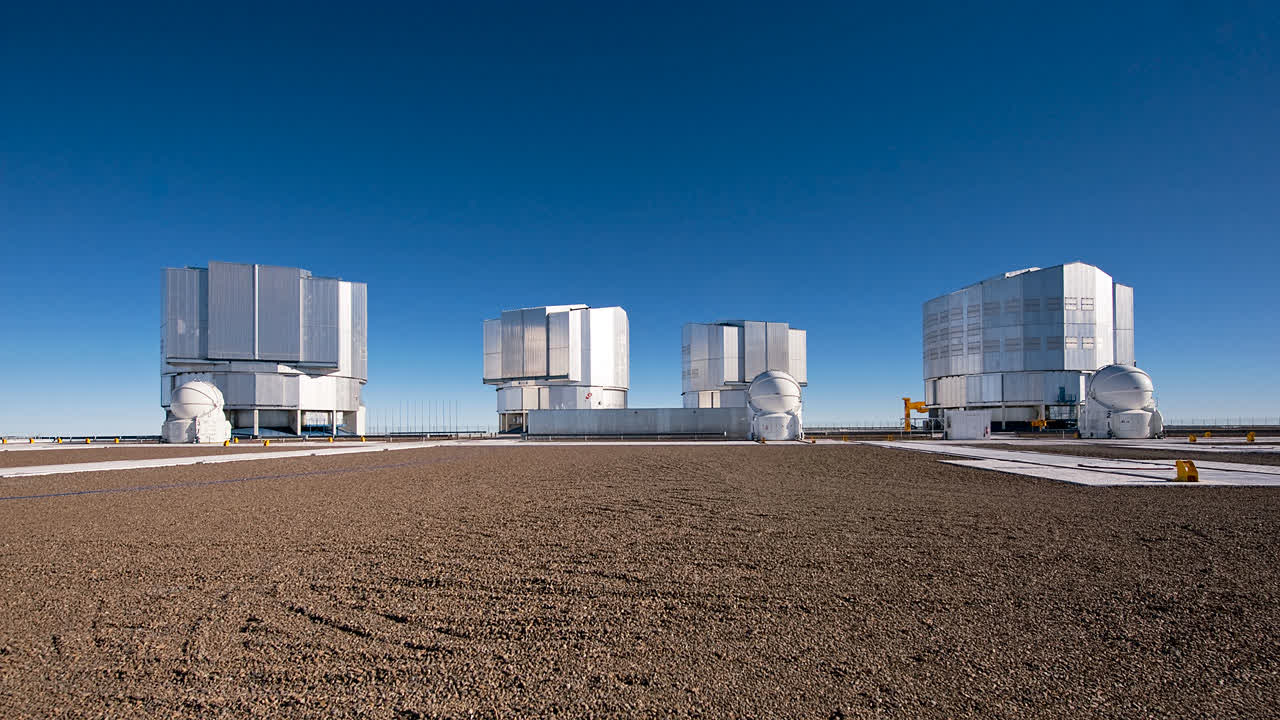

The park spells potential bother for the ESO’s $840 million telescope. It would additionally have an effect on its upcoming $1.5 billion Extraordinarily Massive Telescope on Mount Armazones. Each have been rigorously located within the Atacama’s distant areas to make the most of a few of the darkest night time skies on the planet. The ESO and 16 member nations selected this web site after an intensive international seek for ideally suited commentary situations.
Barcons clarified that the ESO will not be against the ability; it’s simply its proximity. He argues that AES ought to construct the power complicated additional away from the observatory. Mocing it 50km (31 miles) additional away would resolve the issue. The ESO can be calling for stricter authorized protections of the Chilean night time sky, particularly across the observatories within the Atacama Desert.
In keeping with AES Chile, the challenge remains to be in its early phases and pending remaining approval. In December, it submitted an environmental examine stating that “group engagement is a prime precedence.”
Picture credit score: ESO