Carding — the underground enterprise of stealing, promoting and swiping stolen fee card information — has lengthy been the dominion of Russia-based hackers. Fortunately, the broad deployment of safer chip-based fee playing cards in the USA has weakened the carding market. However a flurry of innovation from cybercrime teams in China is respiration new life into the carding trade, by turning phished card information into cell wallets that can be utilized on-line and at important avenue shops.
A picture from one Chinese language phishing group’s Telegram channel exhibits varied toll highway phish kits obtainable.
In case you personal a cell phone, the probabilities are glorious that sooner or later prior to now two years it has obtained at the very least one phishing message that spoofs the U.S. Postal Service to supposedly gather some excellent supply charge, or an SMS that pretends to be an area toll highway operator warning of a delinquent toll charge.
These messages are being despatched via refined phishing kits bought by a number of cybercriminals primarily based in mainland China. And they aren’t conventional SMS phishing or “smishing” messages, as they bypass the cell networks totally. Relatively, the missives are despatched via the Apple iMessage service and thru RCS, the functionally equal know-how on Google telephones.
Individuals who enter their fee card information at considered one of these websites will likely be informed their monetary establishment must confirm the small transaction by sending a one-time passcode to the client’s cell gadget. In actuality, that code will likely be despatched by the sufferer’s monetary establishment to confirm that the person certainly needs to hyperlink their card info to a cell pockets.
If the sufferer then gives that one-time code, the phishers will hyperlink the cardboard information to a brand new cell pockets from Apple or Google, loading the pockets onto a cell phone that the scammers management.
CARDING REINVENTED
Ford Merrill works in safety analysis at SecAlliance, a CSIS Safety Group firm. Merrill has been learning the evolution of a number of China-based smishing gangs, and located that the majority of them characteristic useful and informative video tutorials of their gross sales accounts on Telegram. These movies present the thieves are loading a number of stolen digital wallets on a single cell gadget, after which promoting these telephones in bulk for lots of of {dollars} apiece.
“Who says carding is lifeless?,” stated Merrill, who introduced about his findings on the M3AAWG safety convention in Lisbon earlier at present. “That is one of the best magazine stripe cloning gadget ever. This menace actor is saying you want to purchase at the very least 10 telephones, and so they’ll air ship them to you.”
One promotional video exhibits stacks of milk crates stuffed filled with telephones on the market. A better inspection reveals that every telephone is affixed with a handwritten notation that sometimes references the date its cell wallets have been added, the variety of wallets on the gadget, and the initials of the vendor.
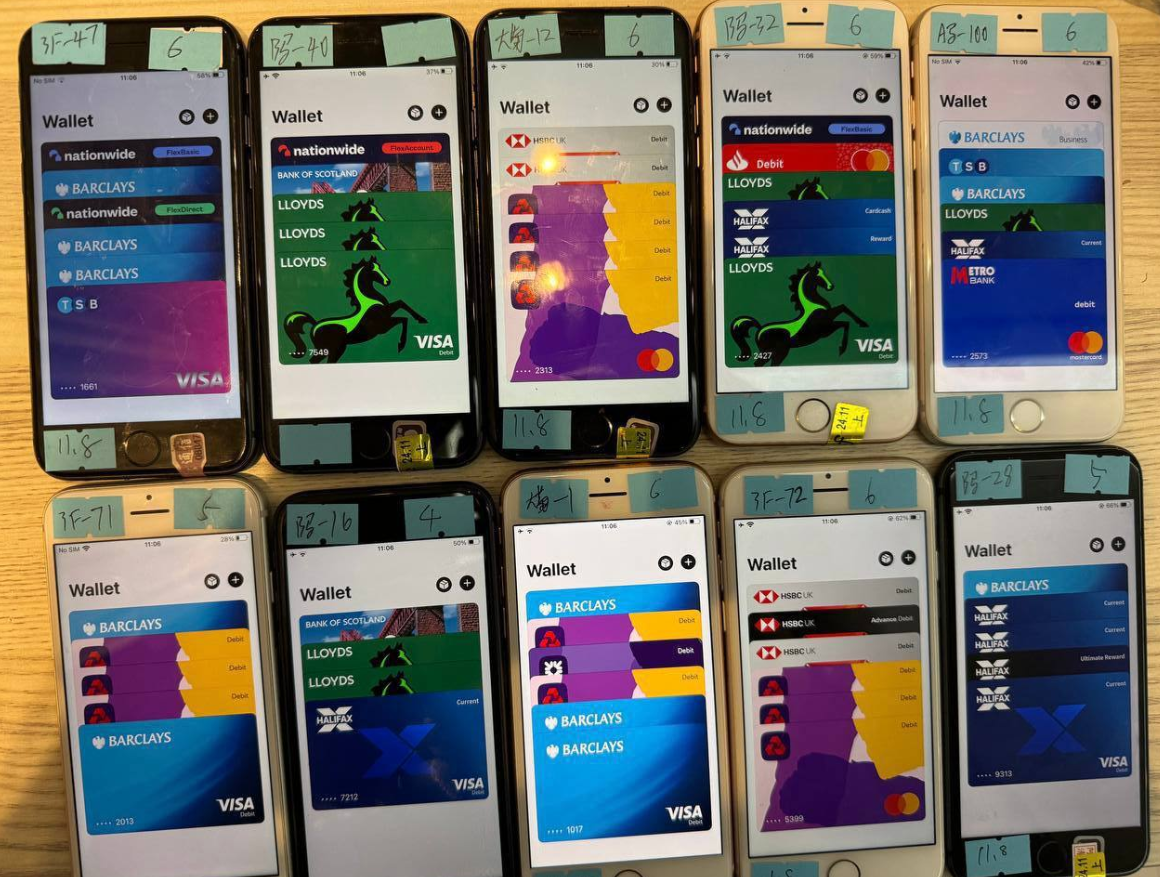
A picture from the Telegram channel for a well-liked Chinese language smishing package vendor exhibits 10 cell phones on the market, every loaded with 4-6 digital wallets from completely different UK monetary establishments.
Merrill stated one frequent means prison teams in China are cashing out with these stolen cell wallets includes organising pretend e-commerce companies on Stripe or Zelle and operating transactions via these entities — typically for quantities totaling between $100 and $500.
Merrill stated that when these phishing teams first started working in earnest two years in the past, they’d wait between 60 to 90 days earlier than promoting the telephones or utilizing them for fraud. However nowadays that ready interval is extra like simply seven to 10 days, he stated.
“After they first put in this, the actors have been very affected person,” he stated. “These days, they solely wait like 10 days earlier than [the wallets] are hit onerous and quick.”
GHOST TAP
Criminals can also money out cell wallets by acquiring actual point-of-sale terminals and utilizing tap-to-pay on telephone after telephone. However additionally they provide a extra cutting-edge cell fraud know-how: Merrill discovered that at the very least one of many Chinese language phishing teams sells an Android app referred to as “ZNFC” that may relay a sound NFC transaction to anyplace on this planet. The person merely waves their telephone at an area fee terminal that accepts Apple or Google pay, and the app relays an NFC transaction over the Web from a telephone in China.
“The software program can work from anyplace on this planet,” Merrill stated. “These guys present the software program for $500 a month, and it may possibly relay each NFC enabled tap-to-pay in addition to any digital pockets. The even have 24-hour help.”
The rise of so-called “ghost faucet” cell software program was first documented in November 2024 by safety specialists at ThreatFabric. Andy Chandler, the corporate’s chief industrial officer, stated their researchers have since recognized a variety of prison teams from completely different areas of the world latching on to this scheme.
Chandler stated these embrace organized crime gangs in Europe which might be utilizing comparable cell pockets and NFC assaults to take cash out of ATMs made to work with smartphones.
“Nobody is speaking about it, however we’re now seeing ten completely different methodologies utilizing the identical modus operandi, and none of them are doing it the identical,” Chandler stated. “That is a lot greater than the banks are ready to say.”
A November 2024 story within the Singapore every day The Straits Instances reported authorities there arrested three overseas males who have been recruited of their residence international locations by way of social messaging platforms, and given ghost faucet apps with which to buy costly objects from retailers, together with cell phones, jewellery, and gold bars.
“Since Nov 4, at the very least 10 victims who had fallen for e-commerce scams have reported unauthorised transactions totaling greater than $100,000 on their bank cards for purchases reminiscent of digital merchandise, like iPhones and chargers, and jewellery in Singapore,” The Straits Instances wrote, noting that in one other case with an identical modus operandi, the police arrested a Malaysian man and girl on Nov 8.
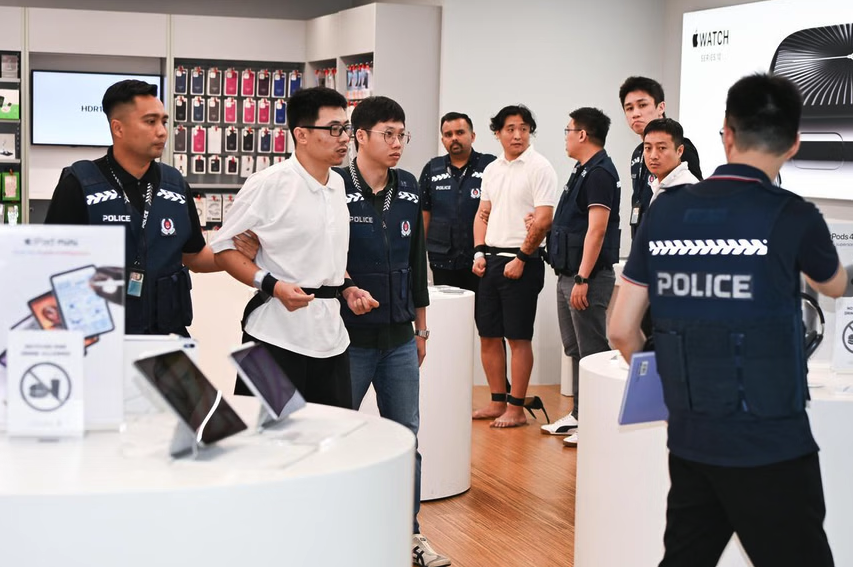

Three people charged with utilizing ghost faucet software program at an electronics retailer in Singapore. Picture: The Straits Instances.
ADVANCED PHISHING TECHNIQUES
Based on Merrill, the phishing pages that spoof the USPS and varied toll highway operators are powered by a number of improvements designed to maximise the extraction of sufferer information.
For instance, a would-be smishing sufferer may enter their private and monetary info, however then determine the entire thing is rip-off earlier than truly submitting the info. On this case, something typed into the info fields of the phishing web page will likely be captured in actual time, no matter whether or not the customer truly clicks the “submit” button.
Merrill stated individuals who submit fee card information to those phishing websites typically are then informed their card can’t be processed, and urged to make use of a unique card. This system, he stated, generally permits the phishers to steal multiple cell pockets per sufferer.
Many phishing web sites expose sufferer information by storing the stolen info instantly on the phishing area. However Merrill stated these Chinese language phishing kits will ahead all sufferer information to a back-end database operated by the phishing package distributors. That means, even when the smishing websites get taken down for fraud, the stolen information remains to be secure and safe.
One other vital innovation is the usage of mass-created Apple and Google person accounts via which these phishers ship their spam messages. One of many Chinese language phishing teams posted photographs on their Telegram gross sales channels displaying how these robotic Apple and Google accounts are loaded onto Apple and Google telephones, and organized snugly subsequent to one another in an expansive, multi-tiered rack that sits instantly in entrance of the phishing service operator.

The ashtray says: You’ve been phishing all evening.
In different phrases, the smishing web sites are powered by actual human operators so long as new messages are being despatched. Merrill stated the criminals seem to ship only some dozen messages at a time, doubtless as a result of finishing the rip-off takes handbook work by the human operators in China. In spite of everything, most one-time codes used for cell pockets provisioning are usually solely good for a couple of minutes earlier than they expire.
Notably, not one of the phishing websites spoofing the toll operators or postal providers will load in an everyday Net browser; they are going to solely render in the event that they detect {that a} customer is coming from a cell gadget.
“One of many causes they need you to be on a cell gadget is they need you to be on the identical gadget that’s going to obtain the one-time code,” Merrill stated. “In addition they wish to decrease the probabilities you’ll depart. And in the event that they wish to get that cell tokenization and seize your one-time code, they want a reside operator.”
Merrill discovered the Chinese language phishing kits characteristic one other innovation that makes it easy for purchasers to show stolen card particulars right into a cell pockets: They programmatically take the cardboard information equipped by the phishing sufferer and convert it right into a digital picture of an actual fee card that matches that sufferer’s monetary establishment. That means, trying to enroll a stolen card into Apple Pay, for instance, turns into as straightforward as scanning the fabricated card picture with an iPhone.
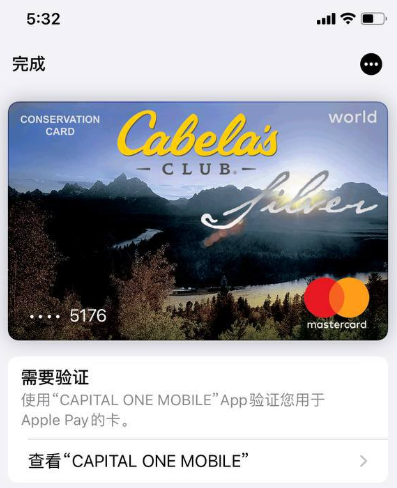
An advert from a Chinese language SMS phishing group’s Telegram channel displaying how the service converts stolen card information into a picture of the stolen card.
“The telephone isn’t sensible sufficient to know whether or not it’s an actual card or simply a picture,” Merrill stated. “So it scans the cardboard into Apple Pay, which says okay we have to confirm that you simply’re the proprietor of the cardboard by sending a one-time code.”
PROFITS
How worthwhile are these cell phishing kits? The perfect guess up to now comes from information gathered by different safety researchers who’ve been monitoring these superior Chinese language phishing distributors.
In August 2023, the safety agency Resecurity found a vulnerability in a single common Chinese language phish package vendor’s platform that uncovered the non-public and monetary information of phishing victims. Resecurity dubbed the group the Smishing Triad, and located the gang had harvested 108,044 fee playing cards throughout 31 phishing domains (3,485 playing cards per area).
In August 2024, safety researcher Grant Smith gave a presentation on the DEFCON safety convention about monitoring down the Smishing Triad after scammers spoofing the U.S. Postal Service duped his spouse. By figuring out a unique vulnerability within the gang’s phishing package, Smith stated he was capable of see that individuals entered 438,669 distinctive bank cards in 1,133 phishing domains (387 playing cards per area).
Primarily based on his analysis, Merrill stated it’s cheap to anticipate between $100 and $500 in losses on every card that’s became a cell pockets. Merrill stated they noticed practically 33,000 distinctive domains tied to those Chinese language smishing teams through the yr between the publication of Resecurity’s analysis and Smith’s DEFCON speak.
Utilizing a median variety of 1,935 playing cards per area and a conservative lack of $250 per card, that comes out to about $15 billion in fraudulent fees over a yr.
Merrill was reluctant to say whether or not he’d recognized further safety vulnerabilities in any of the phishing kits bought by the Chinese language teams, noting that the phishers shortly mounted the vulnerabilities that have been detailed publicly by Resecurity and Smith.
FIGHTING BACK
Adoption of touchless funds took off in the USA after the Coronavirus pandemic emerged, and plenty of monetary establishments in the USA have been desperate to make it easy for purchasers to hyperlink fee playing cards to cell wallets. Thus, the authentication requirement for doing so defaulted to sending the client a one-time code by way of SMS.
Specialists say the continued reliance on one-time codes for onboarding cell wallets has fostered this new wave of carding. KrebsOnSecurity interviewed a safety government from a big European monetary establishment who spoke on situation of anonymity as a result of they weren’t licensed to talk to the press.
That skilled stated the lag between the phishing of sufferer card information and its eventual use for fraud has left many monetary establishments struggling to correlate the causes of their losses.
“That’s a part of why the trade as an entire has been caught abruptly,” the skilled stated. “Lots of people are asking, how that is doable now that we’ve tokenized a plaintext course of. We’ve by no means seen the amount of sending and other people responding that we’re seeing with these phishers.”
To enhance the safety of digital pockets provisioning, some banks in Europe and Asia require clients to log in to the financial institution’s cell app earlier than they will hyperlink a digital pockets to their gadget.
Addressing the ghost faucet menace might require updates to contactless fee terminals, to raised determine NFC transactions which might be being relayed from one other gadget. However specialists say it’s unrealistic to anticipate retailers will likely be keen to switch current fee terminals earlier than their anticipated lifespans expire.
And naturally Apple and Google have an elevated position to play as effectively, provided that their accounts are being created en masse and used to blast out these smishing messages. Each corporations may simply inform which of their units instantly have 7-10 completely different cell wallets added from 7-10 completely different folks world wide. They may additionally suggest that monetary establishments use safer authentication strategies for cell pockets provisioning.
Neither Apple nor Google responded to requests for touch upon this story.










