KrebsOnSecurity turns 13 years outdated at present. That’s a loopy very long time for an unbiased media outlet lately, however then once more I’m sure to maintain doing this so long as they maintain letting me. Heck, I’ve been doing this so lengthy I briefly forgot which birthday this was!
Because of your readership and assist, I used to be capable of spend extra time in 2022 on some deep, meaty investigative tales — the actually satisfying type with the potential to have an effect on constructive change. A few of that work is highlighted within the 2022 12 months in Overview assessment under.
Till not too long ago, I used to be pretty lively on Twitter, often tweeting to greater than 350,000 followers about vital safety information and tales right here. For a wide range of causes, I’ll now not be sharing these updates on Twitter. I appear to be doing most of that exercise now on Mastodon, which seems to have absorbed a lot of the infosec refugees from Twitter, and in any case is proving to be a much more helpful, civil and constructive place to submit such issues. I will even proceed to submit on LinkedIn about new tales in 2023.
Right here’s a have a look at among the extra notable cybercrime tales from the previous 12 months, as coated by KrebsOnSecurity and elsewhere. A number of sturdy themes emerged from 2022’s crop of breaches, together with the concentrating on or impersonating of workers to achieve entry to inside firm instruments; a number of intrusions on the identical sufferer firm; and less-than-forthcoming statements from sufferer corporations about what truly transpired.
JANUARY
You simply knew 2022 was going to be The 12 months of Crypto Grift when two of the world’s hottest antivirus makers — Norton and Avira — kicked issues off by putting in cryptocurrency mining applications on buyer computer systems. This daring about-face dumbfounded many longtime Norton customers as a result of antivirus corporations had spent years broadly classifying all cryptomining applications as malware.
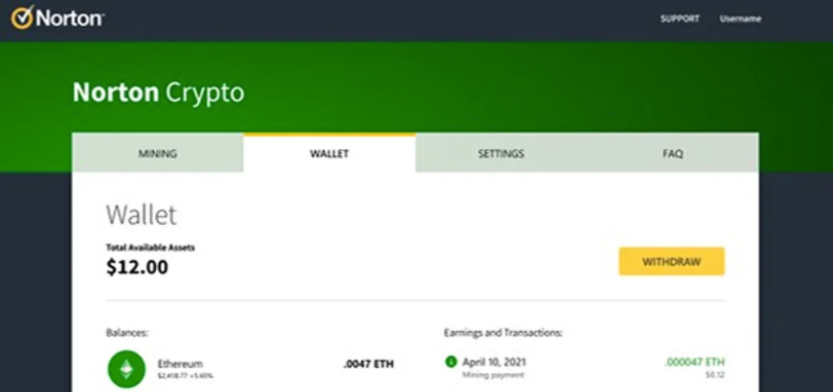
All of the sudden, a whole bunch of hundreds of thousands of customers — lots of them sufficiently old to have purchased antivirus from Peter Norton himself again within the day — had been being inspired to begin caring about and investing in crypto. Huge Yellow and Avira weren’t the one established manufacturers cashing in on crypto hype as a approach to attraction to a broader viewers: The venerable electronics retailer RadioShack wasted no time in saying plans to launch a cryptocurrency alternate.
By the second week of January, Russia had amassed greater than 100,000 troops alongside its southern border with Ukraine. The Kremlin breaks with all custom and broadcasts that — on the request of the USA — it has arrested 14 folks suspected of working for REvil, one of many extra ruthless and worthwhile Russian ransomware teams.
Safety and Russia consultants dismiss the low-level arrests as a type of “ransomware diplomacy,” a sign to the USA that if it doesn’t enact extreme sanctions towards Russia for invading Ukraine, Russia will proceed to cooperate on ransomware investigations.
The Jan. nineteenth story IRS Will Quickly Require Selfies For On-line Entry goes instantly viral for declaring one thing that apparently no person has observed on the U.S. Inner Income Service web site for months: Anybody looking for to create an account to view their tax data on-line would quickly be required to supply biometric information to a personal firm in Virginia — ID.me.
Going through a backlash from lawmakers and the general public, the IRS quickly reverses course, saying video selfies will probably be non-compulsory and that any biometric information collected will probably be destroyed after verification.
FEBRUARY
Tremendous Bowl Sunday watchers are handled to no fewer than a half-dozen commercials for cryptocurrency investing. Matt Damon sells his soul to Crypto.com, telling viewers that “fortune favors the courageous” — mainly, “solely cowards would fail to purchase cryptocurrency at this level.” In the meantime, Crypto.com is making an attempt to place area between it and up to date headlines {that a} breach led to $30 million being stolen from a whole bunch of buyer accounts. A single bitcoin is buying and selling at round $45,000.

Larry David, the comic who introduced us years of awkward hilarity with hits like Seinfeld and Curb Your Enthusiasm, performs the a part of the “doofus, crypto skeptic” in a prolonged Tremendous Bowl advert for FTX, a cryptocurrency alternate then valued at over $20 billion that’s pitched as a “protected and straightforward approach to get into crypto.” [Last month, FTX imploded and filed for bankruptcy; the company’s founder now faces civil and criminal charges from three different U.S. agencies].
On Feb. 24, Russia invades Ukraine, and fault strains rapidly start to look within the cybercrime underground. Cybercriminal syndicates that beforehand straddled Russia and Ukraine with ease are compelled to reevaluate many comrades who’re instantly working for The Different Facet.
Many cybercriminals who operated with impunity from Russia and Ukraine previous to the conflict selected to flee these international locations following the invasion, presenting worldwide legislation enforcement companies with uncommon alternatives to catch most-wanted cybercrooks. A type of is Mark Sokolovsky, a 26-year-old Ukrainian man who operated the favored “Raccoon” malware-as-a-service providing; Sokolovsky was busted in March after fleeing Ukraine’s obligatory navy service orders.
Additionally nabbed on the lam is Vyacheslav “Tank” Penchukov, a senior Ukrainian member of a transnational cybercrime group that stole tens of hundreds of thousands of {dollars} over practically a decade from numerous hacked companies. Penchukov was arrested after leaving Ukraine to satisfy up along with his spouse in Switzerland.

Tank, seen right here performing as a DJ in Ukraine in an undated photograph from social media.
Ransomware group Conti chimes in shortly after the invasion, vowing to assault anybody who tries to face in Mom Russia’s approach. Inside hours of that declaration a number of years price of inside chat logs stolen from Conti had been leaked on-line. The candid worker conversations present a uncommon glimpse into the challenges of working a sprawling prison enterprise with greater than 100 salaried workers. The data additionally reveal how Conti handled its personal inside breaches and assaults from non-public safety corporations and international governments.
Confronted with an rising mind drain of sensible folks fleeing the nation, Russia floats a brand new technique to handle a worsening scarcity of certified data know-how consultants: Forcing tech-savvy folks throughout the nation’s jail inhabitants to carry out low-cost IT work for home firms.
Chipmaker NVIDIA says a cyberattack led to theft of knowledge on greater than 71,000 workers. Credit score for that intrusion is rapidly claimed by LAPSUS$, a gaggle of 14-18 year-old cyber hooligans largely from the UK who specialised in low-tech however extremely profitable strategies of breaking into firms: Concentrating on workers straight over their cellphones.
LAPSUS$ quickly employs these abilities to efficiently siphon supply code and different information from among the world’s largest know-how corporations, together with Microsoft, Okta, Samsung, T-Cell and Uber, amongst many others.
MARCH
We be taught that prison hackers are compromising electronic mail accounts and web sites for police departments worldwide, in order that they will impersonate police and ship authorized requests to acquire delicate buyer information from cell suppliers, ISPs and social media firms. That story prompts revelations that a number of firms — together with Apple, Discord and Meta/Fb — have complied with the faux requests, and attracts the eye of Congress to the issue.
APRIL
It emerges that electronic mail advertising and marketing large Mailchimp acquired hacked. The unknown intruders gained entry to inside Mailchimp instruments and buyer information by social engineering workers on the firm, after which began sending focused phishing assaults to homeowners of Trezor {hardware} cryptocurrency wallets.
The FBI warns a few large surge in victims from “pig butchering” scams, during which flirtatious strangers on-line lure folks into investing in cryptocurrency scams. Investigative stories reveal pig butchering’s hyperlink to organized crime gangs in Asia that entice younger job seekers with the promise of customer support jobs. As a substitute, those that present up on the appointed time and place are kidnapped, trafficked throughout the border into neighboring international locations like Cambodia, and pressed into a lifetime of indentured servitude scamming others on-line.
The now-defunct and at all times phony cryptocurrency buying and selling platform xtb-market[.]com, which was fed by pig butchering scams.
MAY
KrebsOnSecurity stories that hackers who specialise in submitting faux police requests for subscriber information gained entry to a U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) portal that faucets into 16 completely different federal legislation enforcement databases.
The federal government of Costa Rica is compelled to declare a state of emergency after a ransomware assault by Conti cripples authorities methods. Conti publishes practically 700 GB price of presidency data after the nation’s leaders decline to pay a $20 million ransom demand.
JUNE
KrebsOnSecurity identifies Russian nationwide Denis Emelyantsev because the doubtless proprietor of the RSOCKS botnet, a group of hundreds of thousands of hacked units that had been offered as “proxies” to cybercriminals on the lookout for methods to route their malicious site visitors via another person’s pc. Emelyantsev was arrested that very same month at a resort in Bulgaria, the place he requested and was granted extradition to the USA — reportedly telling the decide, “America is on the lookout for me as a result of I’ve huge data they usually want it.”

The staff who stored issues working for RSOCKS, circa 2016. Discover that no person appears to be carrying footwear.
JULY
Huge-three shopper credit score bureau Experian comes underneath scrutiny after KrebsOnSecurity reveals identification thieves are reliably seizing management over shopper credit score information by merely re-registering utilizing the goal’s private data and an electronic mail deal with tied to the crooks. Two months later, Experian could be hit with a class-action lawsuit over these safety and privateness failures.
Twitter acknowledges that it was relieved of cellphone numbers and electronic mail addresses for five.4 million customers. The safety weak point that allowed the information to be collected was patched in January 2022.
AUGUST
Messaging behemoth Twilio confirms that information on 125 prospects was accessed by intruders, who tricked workers into handing over their login credentials by posing as workers of the corporate’s IT division.
Among the many Twilio prospects focused was encrypted messaging service Sign, which relied on Twilio to supply cellphone quantity verification providers. Sign mentioned that with their entry to Twilio’s inside instruments, the attackers had been capable of re-register these customers’ cellphone numbers to a different system.
Meals supply service DoorDash discloses {that a} “subtle phishing assault” on a third-party vendor allowed attackers to achieve entry to a few of DoorDash’s inside firm instruments. Because of information left uncovered on-line by the intruders, it turns into clear that DoorDash was victimized by the identical group that snookered workers at Twilio, Mailchimp, CloudFlare, and dozens of different main firms all through 2022.

Mailchimp discloses one other intrusion involving focused phishing assaults towards workers, whereby hackers stole information on greater than 200 Mailchimp prospects. Website hosting large DigitalOcean discloses it was one of many victims, and that the intruders used their entry to ship password reset emails to a variety of DigitalOcean prospects concerned in cryptocurrency and blockchain applied sciences. DigitalOcean severs ties with Mailchimp after that incident, which briefly prevented the internet hosting agency from speaking with its prospects or processing password reset requests.
Password supervisor service LastPass discloses that its software program improvement atmosphere was breached, and that intruders made off with supply code and a few proprietary LastPass information. LastPass emphasizes the intruders weren’t capable of entry any buyer information or encrypted password vaults, and that “there isn’t any proof of any menace actor exercise past the established timeline,” and “no proof that this incident concerned any entry to buyer information or encrypted password vaults.”
SEPTEMBER
Uber discloses one other breach, forcing the corporate to take a number of of its inside communications and engineering methods offline because it investigates. The intrusion solely involves mild when the hacker makes use of the corporate’s inside Slack channel to boast about their entry, itemizing a number of inside databases they claimed had been compromised. The intruder instructed The New York Occasions they acquired in by sending a textual content message to an worker whereas posing as an worker from Uber’s IT division. Uber blames LAPSUS$ for the intrusion.
Australian telecommunications large Optus suffers an information breach involving practically 10 million prospects, together with passport or license numbers on nearly three million folks. The incident dominates headlines and politics in Australia for weeks, because the hacker calls for one million {dollars} in cryptocurrency to not publish the data on-line. Optus’s CEO calls the intrusion a “subtle assault,” however interviews with the hacker reveal they merely enumerated and scraped the information from the Optus web site with out authentication. After briefly posting 10,000 data from the intrusion, the hacker broadcasts they made a mistake, and deletes the public sale.
OCTOBER
A report commissioned by Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.) reveals that the majority massive U.S. banks are stiffing account takeover victims. Though U.S. monetary establishments are legally obligated to reverse any unauthorized transactions so long as the sufferer stories the fraud in a well timed method, the report cited figures exhibiting that 4 of the nation’s largest banks collectively reimbursed solely 47 % of the greenback quantity of claims they acquired.

Joe Sullivan, the previous chief safety officer for Uber, is discovered responsible of two felonies after a four-week trial. In 2016, whereas the U.S. Federal Commerce Fee was already investigating a 2014 breach at Uber, one other safety breach affected 57 million Uber account holders and drivers. The intruders demand $100,000, however Sullivan and his crew paid the ransom underneath the corporate’s bug bounty program, made the hackers signal a non-disclosure settlement, and hid the incident from customers and buyers. The 2 hackers concerned pleaded responsible in 2019; by this time, it has turn out to be a virtually on a regular basis incidence for sufferer firms to pay to maintain a ransomware assault quiet.
NOVEMBER
A ransomware group with ties to REvil begins publishing names, delivery dates, passport numbers and knowledge on medical claims on practically 10 million present and former prospects of Australian well being insurer Medibank. The information is printed after Medibank reportedly declines to pay a US$10 million ransom demand.
DECEMBER
KrebsOnSecurity breaks the information that InfraGard, a program run by the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) to construct cyber and bodily menace data sharing partnerships with the non-public sector, noticed its database of contact data on greater than 80,000 members put up on the market on an English-language cybercrime discussion board. In the meantime, the hackers accountable had been speaking straight with members via the InfraGard portal on-line — utilizing a brand new account underneath the assumed identification of a monetary trade CEO that was vetted by the FBI itself.
A cybercriminal begins promoting account information scraped from 400 million Twitter customers, together with electronic mail addresses and in lots of circumstances cellphone numbers. The vendor claims their information was scraped in late December 2021 utilizing the identical vulnerability that Twitter patched in January 2022, and that led Twitter to acknowledge the information scraping of 5.4 million consumer accounts earlier this 12 months. Twitter now not has a press workplace, and the corporate’s Chief Twit has remained silent in regards to the 400 million declare up to now, regardless of many indications that the information is professional.
Two days earlier than Christmas, LastPass posted an replace on its investigation into the August information breach, saying the intruder was in a position to make use of information stolen within the August breach to return again and duplicate a backup of buyer vault information from the encrypted storage container. LastPass’s lackadaisical disclosure timeline and failure to reply follow-up questions has accomplished little to assuage the fears of many customers, leaving Wired.com to advocate customers abandon the platform in favor of the password managers 1Password and Bitwarden.
Additionally two days earlier than Christmas, KrebsOnSecurity notifies Experian that anybody can bypass safety questions of their software for a free credit score report, that means identification thieves can entry your full credit score file with simply your identify, deal with, date of delivery and Social Safety quantity. Sadly, this static information on most People has been on the market within the cybercrime underground for years. Experian has but to say whether or not it has mounted the issue, however anticipate to see a full report about this early within the New 12 months.










