PSA: Hackers can steal your username and password for an internet site utilizing an embedded iframe. It is a weak point for all password managers, and most have addressed the flaw in numerous methods, together with issuing warnings when customers are on a login web page with an iframe or not trusting subdomains. Bitwarden is the only exception, having decided in 2018 that the menace was not vital sufficient to deal with.
In its assist pages concerning “Auto-fill,” Bitwarden advises customers to show off their browsers’ password autofill features as a result of they intrude with its password administration answer. It additionally mentions it’s a good suggestion as a result of “consultants usually agree that inbuilt [browser] password managers are extra weak than devoted options like Bitwarden,” which is usually true.
Sadly, its password filler won’t be a lot better than your browser’s. Safety researchers at Flashpoint found that Bitwarden’s autofill extension handles web sites with embedded iframes in an unsafe method. A fundamental understanding of iframes is required to know this vulnerability.
Web site builders use the inline body factor, or iframe, to embed a part of one other webpage into their web site. For instance, TechSpot makes use of iframes to embed YouTube movies into its articles. It may also be used to embed net types. Usually, iframes are secure to make use of so long as the embedded materials from the exterior web site has not been compromised, and that is the place managers have an issue.
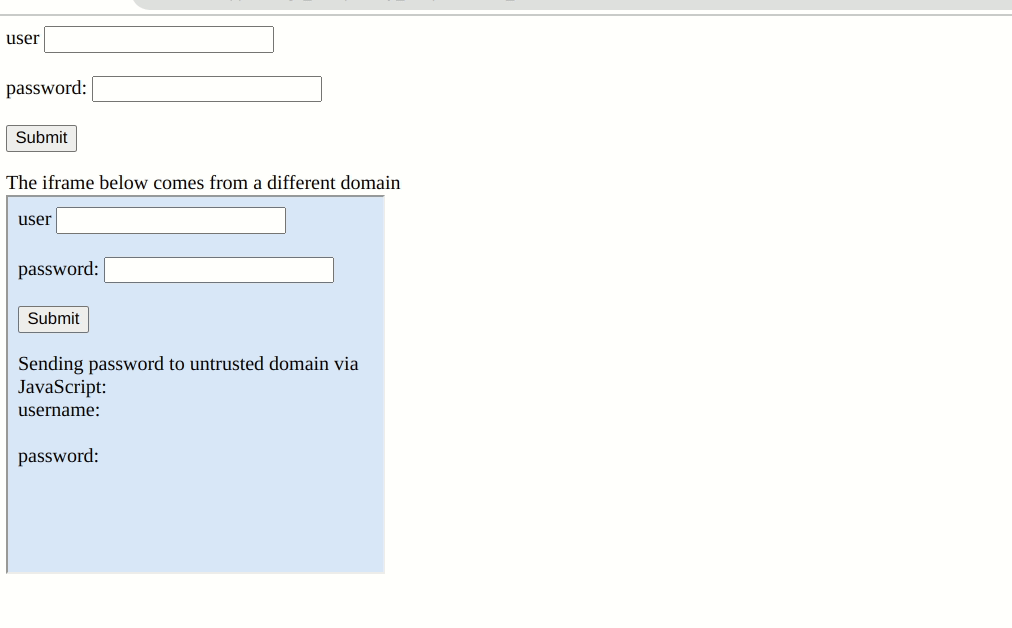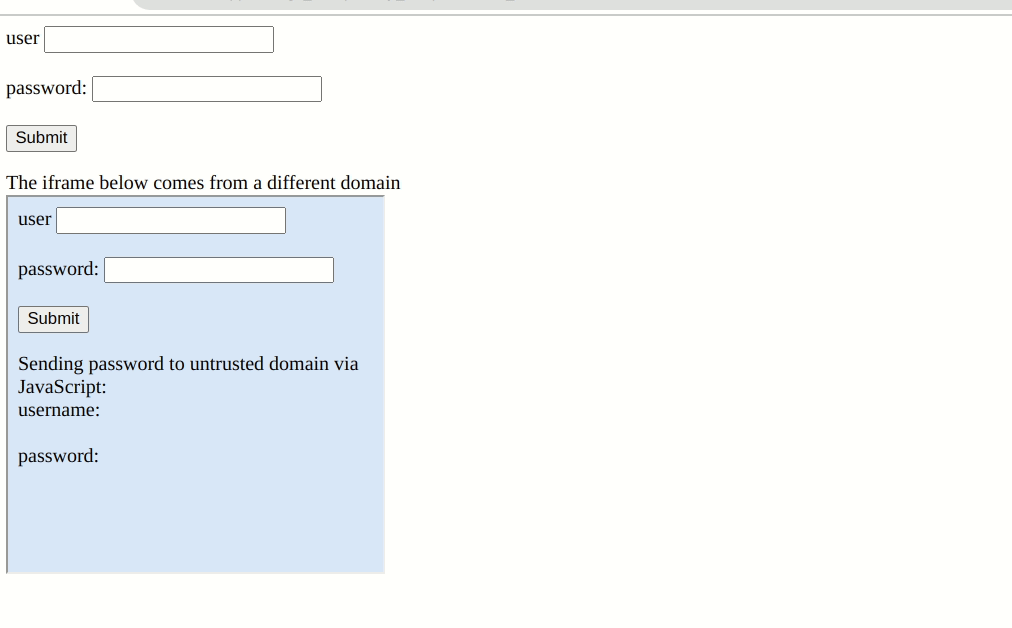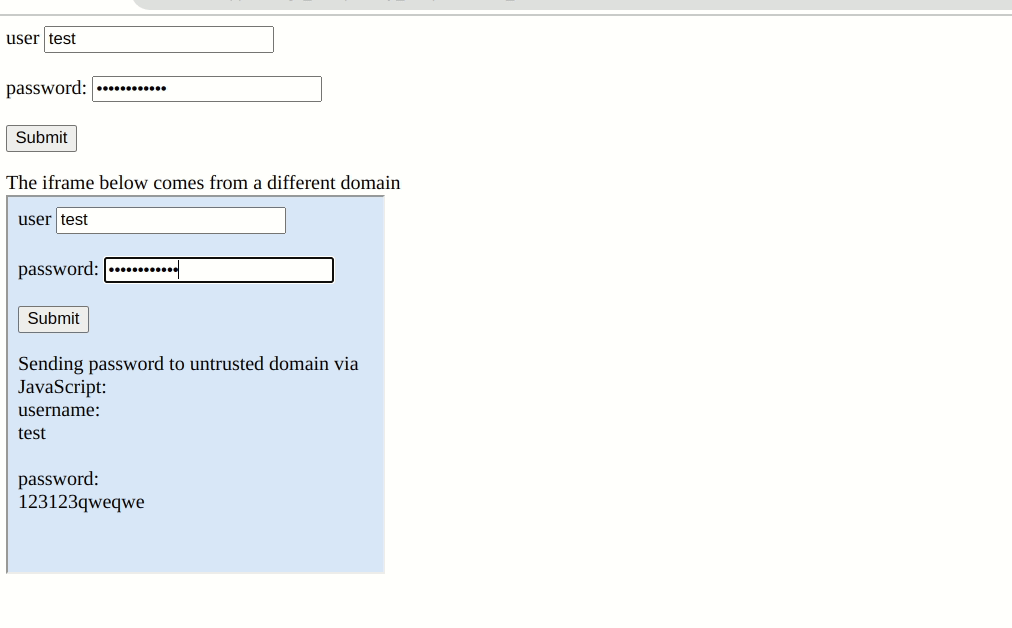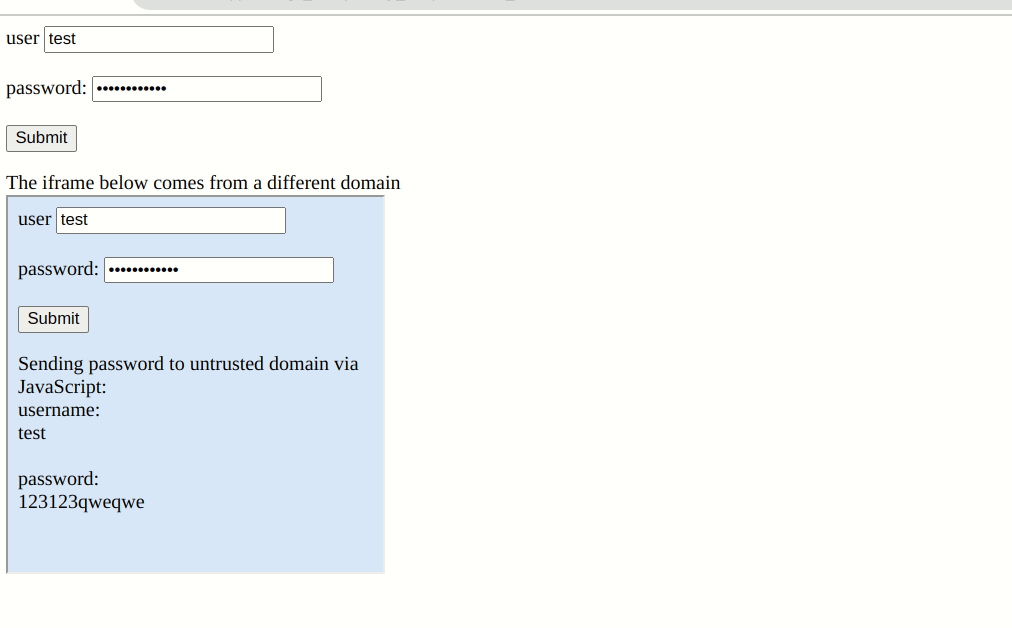
Password extensions autofill credentials on any webpage customers have saved their credentials by design. They’ll even fill out the login kind pre-emptively with out person interplay. In Bitwarden’s thesis a setting referred to as “Auto-fill on web page load.” Nevertheless, the extension will carry out this operate in an iframe with out performing a “Similar-origin Coverage” verify. So if a web page has a malicious iframe from a special area, the supervisor will unknowingly hand over your credentials for them to be despatched to a hacker’s server.
Most password managers have checks in place to at the least warn customers of potential risks. Nevertheless, Bitwarden doesn’t stop or warn that an iframe from a special area is probably stealing credentials. It assumes that each one iframes on a login web page are secure. It stated as a lot in a 2018 safety report, however extra on that later.
In fact, this might solely occur if the trusted web site is already compromised, proper? In response to Flashpoint, that is not essentially true.
Clearly, if hackers have gained sufficient of a foothold to embed an iframe on a legit web site, customers have larger issues than this weak point on their palms. There’s little that any password administration extension might do in that situation. Nevertheless, some legit web sites use types from one other area, embedding them with an iframe. If hackers can compromise the secondary supply, they’ve a proxy for stealing info from the trusted web site.
Flashpoint admits it is a uncommon situation and confirmed that with a spot-check of a number of websites utilizing iframes on their login pages. Nevertheless, there’s one other downside. Bitwarden’s default URI (Uniform Useful resource Identifier) matching is about to “Base area.” So the extension will present password autofill so long as the top-level and second-level domains match.
The issue is that a number of internet hosting companies permit customers to host “arbitrary content material” below a subdomain making it comparatively straightforward to spoof a login web page.
“For instance, ought to an organization have a login web page at https://logins.firm.tld and permit customers to serve content material below https://[clientname].firm.tld, these customers are capable of steal credentials from the Bitwarden extensions,” stated Flashpoint. “In our analysis, we confirmed that a few main web sites present this precise surroundings. If a person with a Bitwarden browser extension visits a specifically crafted web page hosted in these net companies, an attacker is ready to steal the credentials saved for the respective area.”
Oddly, when Flashpoint contacted Bitwarden about this weak point to coordinate disclosure, the corporate identified that it has recognized about it since 2018.
“Since Bitwarden doesn’t verify every iframe’s URL, it’s doable for an internet site to have a malicious iframe embedded, which Bitwarden will autofill with the ‘top-level’ web site credentials,” the corporate’s 2018 Safety Evaluation Report reads. “Sadly, there are legit instances the place web sites will embody iframe login types from a separate area than their ‘mum or dad’ web site’s area. No motion is deliberate right now.”
In different phrases, Bitwarden is conscious of the issue however deems the danger acceptable sufficient to not do something about it, even when it had been so simple as having the extension situation a warning when there’s an iframe on a web page. Flashpoint discovered this inexplicable since all of Bitwarden’s rivals have some type of mitigation for this exploit.
The researchers created a proof of idea utilizing the flaw as an assault vector and a “working exploit” they carried out privately on a “outstanding internet hosting surroundings.” They hope that builders at Bitwarden will change their minds in regards to the situation since no one had created such exploits in 2018 when the corporate initially assessed the weak point. Till Bitwarden addresses the vulnerability, you are able to do a few issues to mitigate it with out switching password managers.
First, flip off the extension’s “Auto-fill on web page load” setting. You’ll have to set off the autofill characteristic manually on a regular basis. Nevertheless, it provides you some respiration room to examine the login web page with out instantly handing your credentials over to an iframe. That’s really good recommendation for any password supervisor extension that includes preemptive autofill.
Second, use that pause to make sure you’re on a trusted area and that the web page is what it appears. Take a look at the URL to make sure you are on the proper area or subdomain and that nothing seems suspicious. For example, one thing like “login.wellsfargo.com” might be legit, whereas “credx257.wellsfargo.com” seemingly is not.
These steps will nonetheless not shield you from websites that use compromised exterior net types, however Flashpoint famous that these situations are uncommon. It is no motive to surrender utilizing a password supervisor, even Bitwarden. Managers are well-suited that can assist you hold your credentials straight. It is all the time higher to have tons of strong hard-to-remember passwords distinctive to each web site than to reuse weak ones.