CISOs know finest observe info safety administration comes right down to individuals as a lot as expertise. With out staff and a sturdy safety tradition in your aspect, tech deployment is not going to cease risk actors, who proceed to seek out their approach into organisations.
It seems Asia-Pacific staff aren’t getting the message. Cyber safety firm Proofpoint just lately surveyed 7,500 staff and 1,050 safety professionals in 15 international locations, together with Australia, Japan, South Korea and Singapore. The corporate discovered that within the Asia-Pacific, many staff confess to behaviours that improve the chance of compromise — like accessing inappropriate web sites — regardless of understanding what they’re doing is dangerous.
Many staff cite comfort and the necessity for pace as causes. A big proportion are additionally nonetheless not sure of their safety obligations or consider it’s another person’s job, regardless of the funding that has gone into cyber safety training and consciousness throughout the area.
What number of staff are taking dangerous actions?
63% of staff within the 4 surveyed international locations within the Asia-Pacific area take dangers with safety, in keeping with Proofpoint’s State of the Phish report. To make this discovering extra troubling, an enormous proportion of them (98%) knew what they have been doing was dangerous whereas they have been doing it however did it anyway.
SEE: Keep forward of those high cyber safety developments in Australia.
Nonetheless, Japanese staff take the fewest cybersecurity dangers. Over half (53%) of respondents from Japan say they by no means take dangerous motion, in contrast with a 29% world common. Proofpoint speculated that Japan’s cultural values and a concentrate on self-discipline could also be behind Japan’s comparatively higher efficiency on safety behaviour.
Asia-Pacific staff take much less dangers than these in world markets
Asia-Pacific staff are much less more likely to take dangers compared with the worldwide common however extra doubtless to take action after they know they need to not. Proofpoint’s world statistics present 71% of customers across the globe take dangerous actions, and 95% of worldwide staff who take dangerous actions are conscious of the dangers they’re taking.
What dangerous actions are staff taking?
Proofpoint discovered 4 of the highest 5 dangers cited by safety professionals are widespread behaviours amongst customers. For instance, the highest danger cited by cyber execs — accessing an inappropriate web site — was the fourth commonest dangerous behaviour amongst staff. (Determine A). Proofpoint prompt staff could also be unclear these are dangerous.

The most typical dangerous behaviour admitted to by staff surveyed within the area was the usage of a piece gadget for private actions. That is although this will improve susceptibility to phishing. For instance, staff might obtain and belief phishing emails they obtain in a private account, placing safety in danger.
Workers have been additionally actively reusing or sharing passwords, connecting their work gadget with out utilizing a VPN in a public place, and responding to e mail and SMS messages from somebody they didn’t know.
Why are staff taking dangerous actions?
Workers revealed the first the explanation why they interact in dangerous cyber safety behaviour:
- 54% took dangers as a result of it was extra handy.
- 38% had achieved so to avoid wasting time on their work.
- 23% had behaviour pushed by an pressing deadline.
Much less widespread the explanation why staff took dangers with cyber safety have been additionally unearthed:
- 19% took dangers to economize.
- 19% had minimize corners to fulfill efficiency aims.
- 11% have been making an attempt to fulfill a enterprise income goal.
PREMIUM: Shield your organisation with an info safety coverage.
Workers not sure about their safety accountability
Workers within the Asia-Pacific area have been the most certainly amongst world staff surveyed to say they have been not sure about their private accountability for cyber safety. Proofpoint discovered that 57% of staff surveyed within the area mentioned they have been not sure about their obligations, in contrast with 54% across the globe.
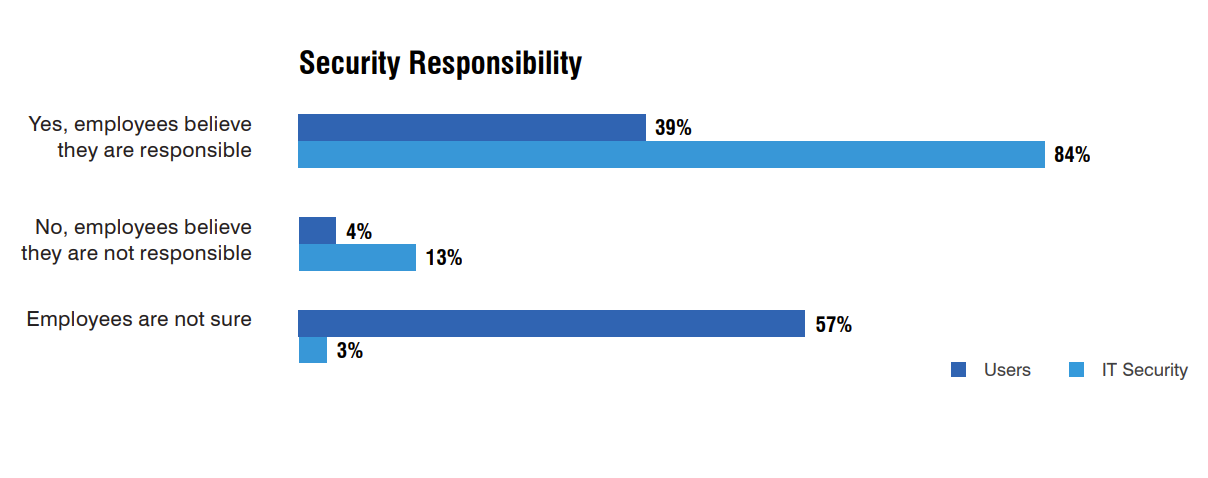
The survey additionally revealed IT safety groups are overconfident about staff’ stage of accountability consciousness. Whereas 84% of IT safety people surveyed mentioned their staff believed they have been chargeable for safety, solely 39% of staff themselves mentioned they counted this as a part of their obligations (Determine B).
What can Asia-Pacific organisations do in regards to the worker downside?
There is no such thing as a doubt that cyber professionals in APAC want staff to achieve readability over their obligations in the case of cybersecurity. In any case, APAC was named ‘floor zero’ for cyber crime progress in 2023, when it skilled the best year-over-year improve in weekly cyberattacks in the course of the first quarter of 2023.
Make following cyber safety finest practices simple
Proofpoint’s survey makes clear staff are taking dangers the place it’s extra handy or saves them time. Cyber safety professionals can solely scale back this danger in the event that they endeavour to make following safe practices so simple as doable and take away any obstacles staff might face to doing the fitting factor.
PREMIUM: Think about using e mail templates for safety alerts.
For instance, this may increasingly contain working with IT groups to make sure one thing so simple as streamlined entry to an environment friendly IT assist desk. This is able to guarantee streamlined entry to a VPN, keep away from them connecting to unsecured networks and cope with account or password points to take away the temptation of sharing passwords.
“Work with enterprise stakeholders and prioritise ease-of-use when implementing safety insurance policies,” Proofpoint mentioned in its survey. “Customers shall be much less inclined to avoid programs if safety aligns with their objectives. And they’re extra doubtless to make use of a management whether it is intuitive and doesn’t require any coaching.”
Educate to construct cyber safety consciousness and tradition
Schooling and elevating consciousness will proceed to play a essential position. If staff within the area are nonetheless not sure in lots of instances about their position in info safety administration, it solely is smart to spice up funding in delivering participating cyber safety coaching assets that may help an uplift in understanding of threats.
This might embrace coaching assets that target the highest dangers of cyber safety professionals. Workers may very well be higher knowledgeable about practices like clicking on hyperlinks or downloading attachments that would improve phishing or malware danger, whereas being supported with instruments that flag emails as coming from outdoors the organisation.
Constructing a robust cyber safety tradition is the endgame. Organisations which have success with participating staff in cyber safety typically enrol staff in serving to the organisation spot points. For instance, a phish reporting Slack or communications channel can act as a automobile for reporting, wholesome competitors and workers reward.










