A joint cybersecurity advisory from the Federal Bureau of Investigation, Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company, Division of Well being and Human providers and Multi-State Info Sharing and Evaluation Middle was just lately launched to offer extra details about the Black Basta ransomware.
Black Basta associates have focused organizations within the U.S., Canada, Japan, U.Ok., Australia and New Zealand. As of Could 2024, these associates have impacted greater than 500 organizations globally and stolen knowledge from at the very least 12 out of 16 important infrastructure sectors, in keeping with the joint advisory.
Latest safety analysis signifies ransomware threats are nonetheless excessive, and extra firms are paying the ransom calls for to recuperate their knowledge.
What’s Black Basta?
Black Basta is ransomware-as-a-service whose first variants had been found in April 2022. In line with cybersecurity firm SentinelOne, Black Basta is extremely seemingly tied to FIN7, a menace actor also called “Carbanak,” lively since 2012 and affiliated with a number of ransomware operations.
Rumors have additionally unfold that Black Basta might need emerged from the older Conti ransomware construction, but cybersecurity firm Kaspersky analyzed each code and located no overlap. The rumors are principally based mostly on similarities within the modus operandi of Conti and Black Basta, but with out stable proof.
How do Black Basta associates function?
Black Basta associates use frequent methods to compromise their goal’s community: phishing, exploitation of identified vulnerabilities or the acquisition of legitimate credentials from Preliminary Entry Brokers. Black Basta was deployed on programs by way of the notorious QakBot.
As soon as contained in the community, the associates use quite a lot of instruments to maneuver laterally by way of the focused community to steal delicate content material after which deploy the ransomware (double-extortion mannequin). Frequent administration or penetration testing instruments — akin to Cobalt Strike, Mimikatz, PsExec or SoftPerfect, to call just a few — are used to attain this activity.
A variant of Black Basta additionally targets Linux-based VMware ESXi digital machines. The variant encrypts all of the information within the /vmfs/volumes folder that shops all of the information for ESXi’s digital machines, leaving a ransom be aware after the encryption.
As soon as the ransomware has been deployed, a ransom be aware is unfold on the programs. The ransom be aware accommodates a novel identifier the group must contact the cybercriminal by way of a Tor hyperlink.
A countdown begins on the Black Basta Tor website, exposing firm names and details about the info Black Basta owns. As soon as the timer will get to zero, the stolen knowledge is being shared.
The state of ransomware: Key developments, together with ransom funds
Black Basta ranked the twelfth most lively household of 2023
In line with Kaspersky in its newest findings concerning the state of ransomware in 2024, Black Basta is ranked the twelfth most lively ransomware household in 2023, with a 71% rise within the variety of victims in 2023 as in comparison with 2022.
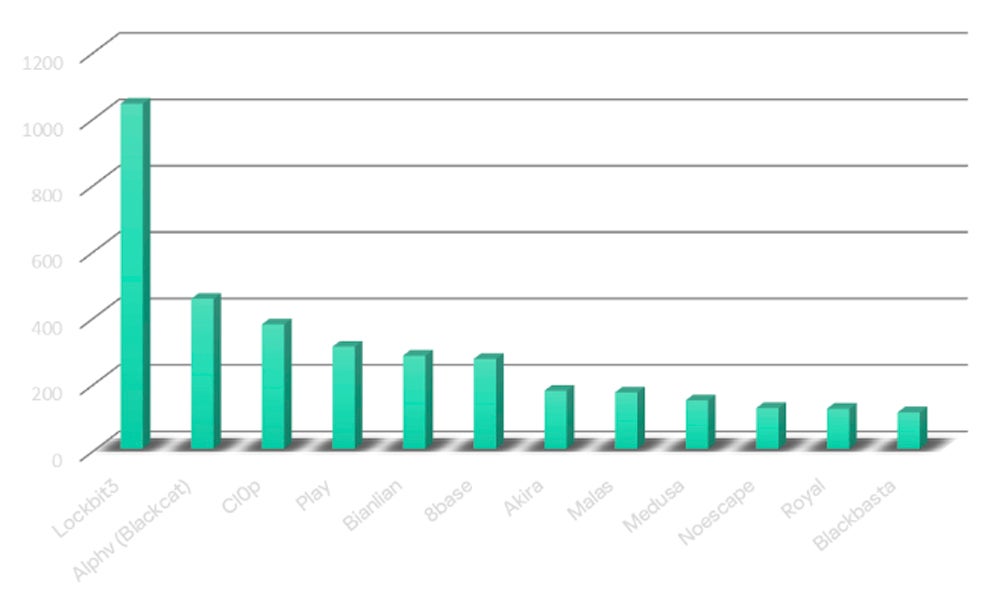
Kaspersky’s incident response staff studies that each third safety incident in 2023 was associated to ransomware.
SEE: In 2022, Black Basta was thought of probably the most harmful and damaging ransomware teams
As well as, the researchers famous one other essential pattern noticed in 2023: Assaults by way of contractors and repair suppliers, together with IT providers, grew to become one of many high three assault vectors for the primary time. These sorts of assaults permit cybercriminals to spend much less effort on the preliminary compromise and lateral actions and sometimes keep undetected till encryption of the programs is finished.
Extra organizations paid the ransom in 2023
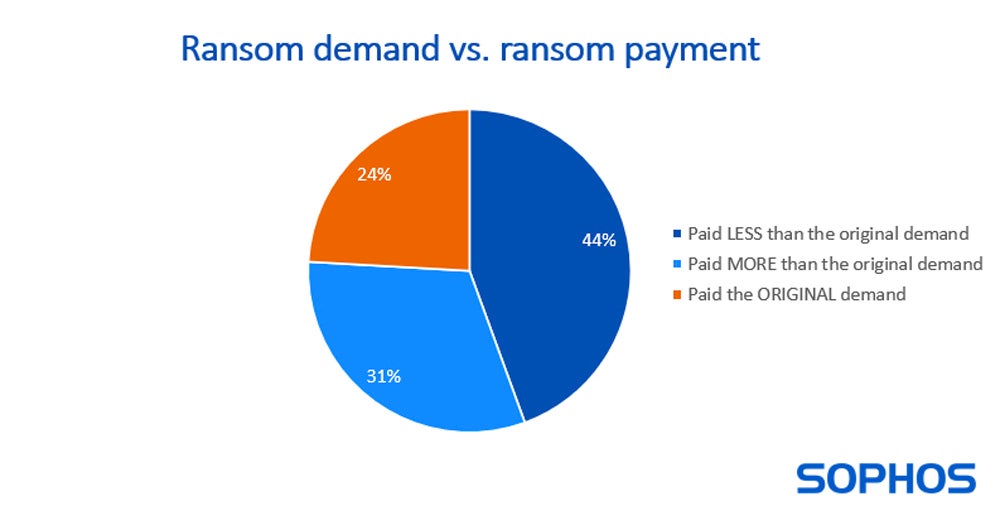
Cybersecurity firm Sophos in its yearly state of ransomware survey famous that, for the primary time, greater than half (56%) of the organizations that had fallen to ransomware admitted they paid the ransom to recuperate their knowledge in 2023.
For the organizations that determined to pay, 44% paid lower than the unique ransom quantity, whereas 31% paid extra.
How one can mitigate this Black Basta ransomware menace
Suggestions from CISA to all important infrastructure organizations are the next:
- Updates for working programs, software program and firmware needs to be put in as quickly as they’re launched.
- Phishing-resistant multifactor authentication have to be required for as many providers as potential.
- Consciousness needs to be raised; customers needs to be educated to acknowledge and report phishing makes an attempt.
- Distant entry software program have to be secured and monitored. Particularly, community directors and defenders should have the ability to acknowledge irregular conduct and detect malicious use of these software program.
- Zero-trust options have to be used when potential. The precept of the least-privilege use needs to be utilized when not potential.
- Inactive or out of date accounts within the Lively Listing needs to be audited.
- Safeguards for mass scripting have to be used, along with a script approval course of. An account attempting to push instructions on a number of gadgets inside a sure time frame ought to see its safety protocols being retriggered, akin to MFA, to make sure the supply is professional.
- Backups of important programs and system configuration have to be finished often to allow gadgets to be repaired and restored.
- Fashionable antimalware software program have to be used, with automated updates of the signatures the place potential.
- Exercising, testing and validating the group’s safety program in opposition to menace behaviors mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK for Enterprise framework within the joint advisory is extremely beneficial.
Extra mitigation methods can be found within the #StopRansomware Information from CISA.
Disclosure: I work for Pattern Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.










