A brand new report for cybersecurity agency WithSecure suggests that almost all firms are investing in safety options which are tactical and reactive, however not in keeping with strategic goals of a company.

A brand new report by cybersecurity agency WithSecure, primarily based on a survey of greater than 400 international cybersecurity and IT decision-makers carried out by Forrester Consulting, means that many organizations are reactive of their strategy to defending towards threats, and piecemeal in terms of cybersecurity investments.
The outcome? Safety objectives turn into indifferent from enterprise objectives, leading to organizations investing in defenses towards threats that aren’t related to their enterprise or objectives.
Consequence-based safety versus reactive safety
In line with Forrester, an outcome-based safety helps enterprise objectives reasonably than merely reacting to perceived vulnerabilities. It permits enterprise leaders to simplify cybersecurity by “Cultivating solely these capabilities that measurably ship their desired outcomes versus conventional menace, activity-based, or ROI-based strategies,” mentioned WithSecure’s report.
The report mentioned a extra holistic strategy to cybersecurity ought to try for outcomes associated to danger administration, buyer expertise, resilience, and visibility of the menace floor and dangers. The outcomes must also pertain to expertise, sources and response pace and agility (Determine A).
Determine A
Paul Brucciani, cybersecurity adviser and head of product advertising for options at WithSecure, mentioned that the idea of outcome-based cybersecurity constitutes each a method to make cybersecurity executions align with enterprise objectives, and to cut back litter and redundancy of safety options and techniques. This can be a Marie Kondo-esque effort to throw objects on the ground and discard these layers of management that don’t strategically help enterprise objectives.
SEE: Companies whose objectives embody extra clouds ought to anticipate rain.
“Consequence primarily based safety is a method to make selections about what you want to shield and the way. Nevertheless it’s a self-discipline: it’s very simple to purchase and implement a brand new device, far more troublesome to modify off legacy programs. To show issues off [that aren’t useful],” Brucciani mentioned.
Despite the fact that 83% of respondents to the survey mentioned they have been concerned about, planning to undertake, or increasing their adoption of outcome-based safety options and providers, 60% mentioned their organizations are reactive, not proactive; they reply to particular person cybersecurity issues as they come up.
One-fifth of firms align cybersecurity with enterprise priorities
The examine, which aimed to grasp organizational cybersecurity priorities and enterprise objectives, discovered:
- Solely 20% of respondents mentioned their group has full alignment between cybersecurity priorities and enterprise outcomes.
- 75% of respondents mentioned cyber-risk administration is receiving elevated consideration from the board of their organizations.
- 60% of companies are prepared to spend 6% or extra of their operational revenue to attain the advantages they see in adopting an outcome-based strategy for cybersecurity investments.
- 50% of companies battle to measure cybersecurity worth and have bother articulating the contribution of safety to enterprise outcomes.
‘Market of lemons’ paradigm complicates safety investments
Cybersecurity budgets are rising, however might the sheer dimension and scope of the cybersecurity service market be driving IT patrons to allocate budgets haphazardly?
SEE: On this Q&A, an IT professional and advisor talks about easy methods to prioritize safety in budgets.
Brucciani mentioned that is most likely the case, as the present marketplace for cybersecurity Software program as a Service itself constitutes a “marketplace for lemons,” a time period coined by economist George Akerlof to explain a circumstance through which the market is peppered by good and dangerous merchandise and the client is hobbled by an incapacity to discern which is which.
“Cybersecurity is an enormous enterprise; relying on the way you outline the market there are 10,000 cybersecurity firms on the planet which creates a loud market, and lots of of these firms are enterprise capital backed, so their job is to get to market as quick as attainable. As a consequence it creates a market that’s troublesome to navigate, with the added problem of measuring high quality: Consumers don’t have any method of assessing the standard of what they’re being offered,” Brucciani mentioned.
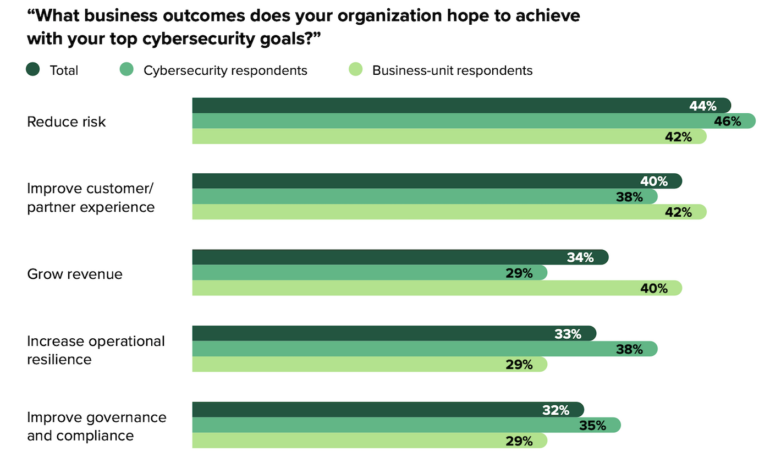
What companies search from cybersecurity instruments and providers
Survey respondents cited a number of the greatest safety challenges: visibility into cyber dangers, discovering the required expertise and sources, and responding shortly and successfully (Determine B).
Determine B
Outcomes that respondents mentioned they sought from cybersecurity efforts embody:
- 44% of these polled need to scale back danger.
- 40% need safety to enhance buyer expertise.
- 34% need safety to help income progress.
- 33% need to enhance operational resilience.
- 32% need safety to be geared toward governance and compliance.
Getting significant metrics tying safety to enterprise outcomes is one other problem
The executives polled by Forrester listed challenges to extracting helpful metrics that tie safety priorities to enterprise outcomes:
- 37% expressed difficulties in measuring cybersecurity worth.
- 36% mentioned they might not seize constant and significant knowledge.
- 28% discovered challenges in overcoming a paradox: funding in efficient safety ends in fewer alternatives to display worth.
- 23% encountered challenges in translating cybersecurity metrics into one thing significant to the board.
Moreover, 42% mentioned they’d an inadequate understanding of present and target-state maturity towards which safety worth ought to be assessed. Brucciani defined that concentrate on state, in a safety context, is an expression of an enterprise’s safety objectives and will depend on such components as:
- Affect of a cyber safety assault on the enterprise.
- Threat tolerance — the impression an enterprise can take in and performance.
- Willingness to take safety dangers.
- Safety that regulators and purchasers anticipate.
“Typically companies need a increased degree of safety than they’ve at current,” mentioned Brucciani. “The query is, how a lot safety is sufficient? Their cyber danger technique — whether it is coherent — can be pushed by these components.” He added that NIST presents a helpful framework to help safety decision-making.
The right way to construct enterprise outcomes into safety
The examine included suggestions on easy methods to convey cybersecurity investments into strategic alignment with enterprise objectives:
- Enterprise outcomes ought to be agreed on with stakeholders and mapped to your safety investments, menace mannequin, and safety controls.
- Safety outcomes ought to embody enterprise advantages (e.g. risk-based authentication in e-commerce improves CX by eliminating additional steps and friction from low-risk transactions).
- Safety priorities ought to correlate to enterprise outcomes, avoiding pointless investments in safety that enterprise outcomes don’t require.
- Procurement and authorized groups ought to be ready for outcome-based safety buying.

/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24402139/STK071_apple_K_Radtke_03.jpg)








