Latest investigations into the cyber safety preparedness of Australian Federal Authorities businesses have discovered gaps within the public sector’s readiness for cyber safety assaults or main information breaches, contributing to a spotlight in 2024 on enhancing their cyber readiness.
An audit of two authorities businesses, Providers Australia and AUSTRAC, launched in 2024, revealed these businesses should not well-prepared to get better from a big cyber assault, whereas a earlier whole-of-government survey discovered gaps in some areas of company cyber maturity.
The Australian Authorities’s Cyber Safety Technique 2023-2030 mentioned the Federal Authorities ought to “maintain itself to the identical commonplace it expects of trade.” In 2024, a spotlight of the Australian Indicators Directorate is to uplift cybersecurity abilities in authorities businesses.
Australian authorities entities unfit for heightened cyber risk surroundings
Australian public sector businesses are prime targets for cybercriminals due to the information they maintain. For example, the Australian Taxation Workplace revealed in 2024 that it faces 4.7 million assaults per thirty days because of the 50 petabytes of information it holds, whereas information on a big variety of individuals was accessed when South Australian tremendous fund operator Tremendous SA was compromised in 2023.
Assaults confronted by Australian authorities entities in 2022-23
Official statistics based mostly on incidents reported to the ASD present that authorities entities proceed to show enticing targets for cybercriminals, with a powerful quantity of assaults. In 2022-2023:
- Roughly 31% of cyber safety incidents reported to the Australian Indicators Directorate have been from Australian Authorities entities.
- Over 40% of those have been coordinated low-level malicious cyberattacks directed on the federal authorities, government-shared providers or regulated essential infrastructure.
- Ransomware is probably the most vital cybercrime risk, posing appreciable danger to Australian Authorities entities in addition to companies and people.
SEE: Will Australia ever dig itself out of the cyber safety abilities scarcity?
The present cyber safety posture of presidency entities
The ASD’s 2023 Cyber Safety Posture Report, assessing the maturity stage of all authorities businesses, indicated that “the general maturity stage throughout entities remained low in 2023.” The report discovered:
- 25% of entities self-assessed at Maturity Degree Two throughout the ASD’s Important Eight mitigation methods. The Important Eight framework contains 4 maturity ranges, with Maturity Degree Zero the bottom and Degree Three thought-about greatest apply.
- Most public sector entities — 71% — self-assessed at Maturity Degree Two for the Important Eight mitigation technique “Common backups.” This indicated a possible drawback with the flexibility to get better from a big cyberattack.
- Simply 82% had an incident response plan, although this was an enchancment from 2022. Of those, 90% mentioned that their plan had been final up to date inside the final two years, and 69% indicated it had been enacted a minimum of each two years.
Earlier audits of public sector our bodies, together with the Australian Federal Police, Australian Taxation Workplace and Division of International Affairs and Commerce, carried out by the Australian Nationwide Audit Workplace, had additionally “recognized low ranges of cyber resilience in entities.”
AUSTRAC, Providers Australia present cyber safety deficiencies
An ANAO report on cyber safety incident administration at Providers Australia and AUSTRAC in June 2024 discovered their measures solely “partially efficient,” with neither effectively positioned to make sure enterprise continuity or catastrophe restoration after a big cyber safety incident.
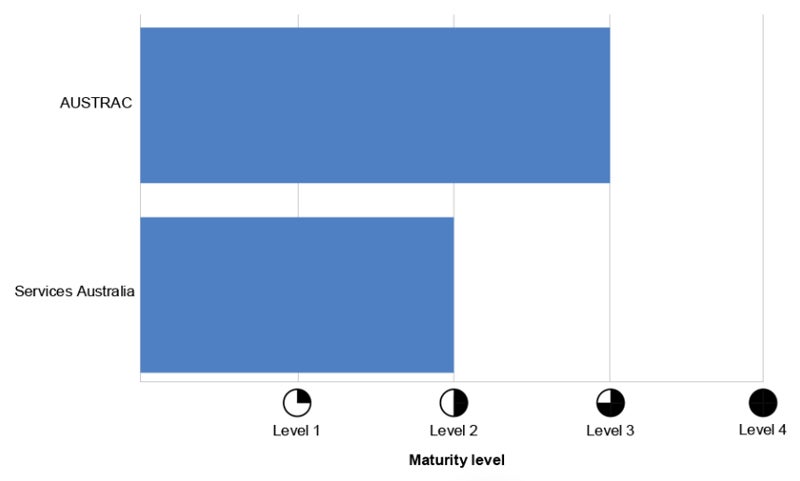
Providers Australia, delivering providers and funds to residents, and AUSTRAC, chargeable for stopping prison abuse of the monetary system, are each custodians of financial or industrial data and private data, and are classed as nationwide safety or essential infrastructure.
AUSTRAC
The ANAO report discovered that AUSTRAC’s procedures supporting incident restoration processes didn’t embrace the safety and testing of backup options, nor did they element the techniques, functions and servers supporting essential enterprise processes.
As well as, it didn’t element CISO tasks — its steady monitoring and enchancment reporting method — or outline timeframes for reporting. Additional, the organisation didn’t have an occasion logging coverage or doc its evaluation of all cyber safety occasions, violating ASD pointers.
SEE: CISOs in Australia urged to take a better have a look at information breach dangers
Providers Australia
Providers Australia is barely “partly efficient” within the design of cyber safety incident administration procedures, with no documented method to risk and vulnerability assessments. It additionally had no timeframe for triage and escalation, and no outlined method for investigations.
The company had “partly applied efficient restoration processes,” together with common backups. Nonetheless, its plans didn’t embrace all techniques and functions supporting essential enterprise processes, and the company doesn’t take a look at the recoverability of backups.
What’s the Australian nationwide cyber safety technique?
The Australian authorities is conscious of the necessity for businesses to enhance their stage of cyber safety preparedness and resilience. Within the Cyber Safety Technique 2023-2030, for instance, the federal government writes that, as an proprietor and operator of essential infrastructure and being chargeable for holding among the most delicate information about Australia’s individuals, economic system and nationwide safety, “the federal government wants to carry itself to the identical commonplace it imposes on trade.”
As a part of the technique, the federal government has dedicated to:
- Strengthening the cyber maturity of presidency departments and businesses.
- Figuring out and defending essential techniques throughout authorities.
- Uplifting the cyber abilities of the Australian Public Service.
The ASD mentioned it’s enjoying a job in stepping up safety at authorities businesses in 2024 utilizing additional funding. This contains introducing extra technical capabilities to departments and offering extra specialists to assist businesses fortify their networks towards cyber criminals.
Personal sector calls for rise in public sector safety requirements
The non-public sector will welcome strikes to enhance cyber safety within the public sector.
In a latest submission to authorities on proposed cyber safety legislative reforms, The Know-how Council of Australia, representing the know-how trade, urged the Australian authorities to uplift and safeguard its personal data safety practices and strategies. That is to make sure that any data supplied to it by non-public sector organisations, as a part of necessary cyber incident data sharing proposals, happens in safe switch environments and channels.
Amazon Internet Providers prompt the federal government ought to formally embrace its personal essential infrastructure and “Programs of Authorities Significance” underneath the remit of the Safety of Crucial Infrastructure Act, or different legislative framework.
“Doing so would set essential enforceable benchmarks for presidency,” AWS wrote, “and ship an essential sign to trade that authorities actually sees itself as an equal accomplice within the nation’s cyber uplift.”