In July 2023, the Affiliation of Southeast Asian Nations formally opened a joint cyber safety data sharing and analysis centre, or Cybersecurity and Data Centre of Excellence, in a bid to extend the area’s shared cyber risk defences.
The centre is a response to a altering risk panorama. On the opening of the ACICE, Singapore’s Ministry of Defence mentioned Singapore alone skilled a 174% enhance in phishing makes an attempt between 2021 and 2022, whereas Southeast Asia cyber crime had elevated 82%.
Recorded Future Chief Data Safety Officer Jason Steer instructed TechRepublic some prospects within the area felt digitisation was turning information from gold into uranium because of cyber threat. He named digital provide chains and AI as key threat issues for ASEAN CISOs.
Soar to:
Digitisation development in ASEAN causes rising threat consciousness
The ASEAN area, like different rising markets, is experiencing a speedy acceleration in digitisation. With the expansion of cloud suppliers like Microsoft and AWS, companies and governments are utilizing these providers to make operations extra scalable, whether or not that’s to digitise processes like invoicing and payroll or to higher handle distant work progress.

This digitisation development comes with threat. At risk intelligence agency Recorded Future’s native convention within the area, Steer mentioned CISOs in ASEAN had been extra acutely aware than ever now that, though they need numerous information about shoppers due to the worth it may drive for his or her companies, there’s a rising consciousness that the urge for food for information additionally brings dangers.
SEE: Australia’s cyber shields technique wants information science issues.
“Certainly one of our visitor CISOs made the purpose that, traditionally, information has been seen as gold,” Road mentioned. “However, when what organisations have skilled over the past 12 to 18 months, information is now seen extra like uranium: The extra information you may have, the extra threat, and the extra you need to do to guard and safe it. How do you handle that threat appropriately now?”
ASEAN nations feeling the warmth of extra cyber felony exercise
ASEAN CISOs are proper to be apprehensive. The Asia-Pacific area as an entire was probably the most attacked area on the earth in 2022, in line with a report from IBM (Determine A).
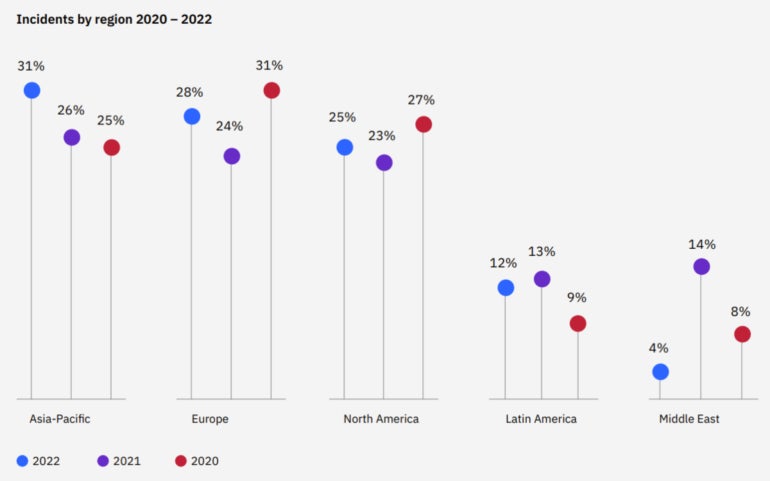
Additional, a July 2023 survey by Cloudflare of 4,000 cyber safety managers within the area discovered that 78% of these interviewed had skilled at the least one cyber safety incident within the earlier 12 months. Of these attacked, 80% reported 4 or extra incidents, and 50% had skilled 10 or extra.
ASEAN nations are keenly feeling this enhance in exercise. Cloudflare’s report discovered that, in Malaysia, Indonesia and The Philippines, the biggest problem for cyber safety leaders was defending towards cyber assaults within the type of phishing, net assaults and enterprise electronic mail compromise (Determine B). For CISOs in Singapore and Thailand, this threat was topped by the necessity to safe their distant workforces, an growing want in a cloud-driven working setting.

Provide chain dangers a key think about a related digital world
The dangers of digitisation are amplified by organisations who now depend on their digital provide chain. For instance, 48% of Singapore-based respondents to Cloudflare’s survey who had been score the highest points with their cyber safety structure named restricted oversight over their IT provide chain as a difficulty, simply behind their purposes and information being saved on the general public cloud (50%).
Steer mentioned that every one organisations in ASEAN, and for that matter world wide, had been shopping for digital options from product distributors however weren’t essentially monitoring the cyber safety postures of this prolonged ecosystem. If a kind of important instruments within the provide chain is down, the affect can be felt on the enterprise as a result of a cog within the enterprise course of has gone down.
“At Recorded Future, if AWS goes down for 20 minutes, that will be the entire platform down till we transition to the subsequent area,” Steer mentioned. “You’ll be able to mitigate a few of these provide chain points to some extent, however it is crucial for organisations to ask what their plan is to recuperate and restore operations and the way lengthy they are often down till it impacts their skill to service shoppers.
“The availability chain in massive organisations is getting longer and larger; it isn’t simply third events, however their suppliers. This can be a onerous factor to consider, notably while you don’t signal contracts with a provider’s suppliers. Whereas there could also be little you are able to do, you must at the least begin to consider what that appears like and the right way to handle dangers higher.”
Geopolitical conflicts one other threat to digital provide chains
The affect of battle or geopolitical stress is of concern in ASEAN, as it’s a area that depends on commerce. Steer mentioned tensions corresponding to these between China and The Philippines within the South China Sea, an necessary delivery lane, was on the minds of CISOs in organisations. This battle has the potential to affect digital provide chains in addition to enhance uncertainty round cyber threats dealing with organisations, governments or infrastructure.
Synthetic intelligence may additionally affect organisations and CISOs
ASEAN CISOs are contemplating the optimistic and unfavourable impacts that the explosion in synthetic intelligence instruments might have on cyber defences and assault traits within the area. One of many key discussions, in line with Steer, is the governance of organisational information.
PREMIUM: Keep compliant with this information governance guidelines.
CISOs are strolling the road between outright banning AI instruments like ChatGPT to make sure organisational information is protected against leaks or going all in on AI to understand the potential enterprise benefits.
AI may have an effect on regional elections in ASEAN
Steer mentioned a dialogue level round AI within the area was election manipulation, notably from state actors. With quite a lot of precedents world wide from earlier current elections, he mentioned risk actors, empowered by the benefit of making content material utilizing AI instruments, now had the power to create extra convincing faux disinformation campaigns. This might affect the likes of Indonesia’s election developing in February 2024, which might affect enterprise and politics.
AI may assist to safe information within the area extra successfully
The chance to struggle fraud and enhance safety may enhance with AI. Steer mentioned customers authenticating to a banking software would usually use their username, password and robust multi-factor authentication. In a world of AI, extra information may add layers of safety to accounts, corresponding to the place log-ins happen, what time log-ins sometimes occur and the IP deal with they often come from.
“With much more information factors, there’s not solely the prospect to create a greater consumer expertise, however higher stop fraud and account takeover as properly,” Steer mentioned.
ASEAN nations setting sights on cyber safety collectively
The launch of the ACICE confirmed ASEAN nations are persevering with to work extra intently collectively on cyber safety. The area has additionally developed a joint cyber safety technique and information safety framework and is engaged on making a unified ASEAN safety emergency response workforce. Skilling up ASEAN workforces is on the agenda; Malaysia has dedicated to coaching and certifying 20,000 cyber safety professionals by 2025 as a part of its cyber safety technique.
SEE: Microsoft invests in Australia’s cyber safety and expertise abilities priorities.
Steer mentioned Singapore and Malaysia stand out within the area for superior cyber safety practices. The massive variety of world firms utilizing it as a base has boosted the native expertise pool and infrastructure. Different nations, like The Philippines, are elevating the bar in addition to regional cyber safety requirements rise, partly due to the provision chain governance and threat frameworks they’re being compelled to observe to maintain up with opponents within the area.








/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25841912/Silo_Photo_021008.jpg)

