B-SIDES LAS VEGAS – Las Vegas – Wednesday, Aug. 7 – Organizations that use the Identified Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog to prioritize patching are probably lacking silent adjustments to the listing that might point out that a difficulty’s severity has modified, in response to an evaluation introduced on the BSides Las Vegas convention on Aug. 7.
The KEV catalog — which at present consists of greater than 1,140 vulnerabilities which are identified to have been exploited within the wild — tracks software program flaws by their Widespread Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) identifier, information the date when the vulnerability was confirmed within the wild and has a flag that signifies whether or not ransomware teams are utilizing the safety points.
But, particular adjustments to the information — reminiscent of uncommonly brief instances to remediate vulnerabilities and adjustments to the ransomware standing — may give safety groups worthwhile info, the evaluation acknowledged.
Sadly, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA), which manages the listing, doesn’t usually name out these adjustments and outliers, says Glenn Thorpe, senior director of safety analysis and detection engineering at GreyNoise Intelligence.
“We who aren’t certain by its directives neglect that that is really a to-do listing,” he says, including: “So, if people are literally utilizing this to prioritize remediation or some type of course of, they should know [when] it’s up to date silently.”
The KEV catalog, launched in November 2021 with 290 exploited vulnerabilities, is maintained by CISA and offers organizations the knowledge essential to prioritize patching flaws which are at present beneath assault. The listing, nevertheless, doesn’t rank the severity of points, and vulnerabilities are sometimes not added till nicely after the preliminary proof of exploitation involves gentle.
Surge From a Cyber Battle
Whereas lower than 3 years previous, the KEV catalog has already handed via three durations, Thorpe says. The unique catalog had 287 vulnerabilities, which had a mean age — the time between the discharge of the CVE and the vulnerability’s addition to the KEV listing — of 591 days. Then, throughout a 109-day interval in early 2022 and the preliminary months of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, a large stockpile of vulnerabilities was exploited, encompassing 396 points with a mean age of 1,898 days.
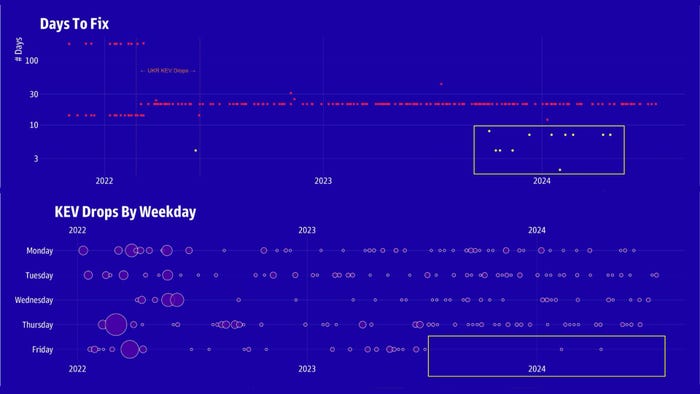
Beginning in mid- to late 2023, CISA began altering its insurance policies on the KEV catalog, offering extra indicators as to the severity of a vulnerability. Supply: GreyNoise Intelligence
Since mid-2022, 453 newly exploited vulnerabilities have been found, with a mean age of 567 days.
“There’s this thought that possibly the numbers have gone down, as a result of the Russia-Ukraine battle has dragged on so lengthy,” he says. “However I [feel that] when it ends, all sides will in search of vulnerabilities and stockpiling as soon as once more.”
5 organizations — Microsoft, Apple, Cisco, Adobe, and Google — account for about half of all vulnerabilities on the listing, demonstrating cyberattackers’ penchant for main software program platforms.
Pay Consideration to Friday Updates
Whereas any vulnerability within the KEV catalog ought to probably be patched as quickly as doable, firms could need to prioritize these being utilized in ransomware campaigns. The listing has a flag designating whether or not CISA has confirmed use of a selected flaw by ransomware gangs. Nonetheless, a minimum of 41 instances, that flag has been modified to “identified” — indicating ransomware use — after the vulnerability’s addition to the listing with out express notification.
Maybe extra important for prioritization is the “due date” for fixing a vulnerability, which informs federal companies of the date by which the problem should be remediated. Whereas the overwhelming majority of vulnerabilities have a 21-day requirement, since late 2023, CISA has set shorter remediation deadlines for particular vulnerabilities. The shorter patching deadlines are usually for extra important home equipment which are linked to a networks, such because the extreme Ivanti vulnerabilities, in addition to points in Juniper routers and Cisco gadgets and Atlassian’s Confluence server, GreyNoise’s Thorpe says.
In truth, one other knowledge level means that CISA made different adjustments to the way it handles KEV-catalog bulletins in late 2023. Across the similar time that CISA had assigned shorter deadlines, the company additionally started foregoing the discharge of any listing updates on Fridays, besides in two particular instances, the evaluation discovered.
“Both there was a call made to prioritize these a bit of in a different way, or they … have been type of determining the way to prioritize these in a different way, as a result of the listing is getting large,” Thorpe says.
Organizations can use the coverage adjustments inferred from the way in which CISA updates the KEV catalog to grasp which points the company considers most crucial. A KEV replace launched on a Friday needs to be thought of important, as ought to a vulnerability with a due date lower than 21 days away. Lastly, Thorpe says, updates to the identified ransomware utilization subject are one other sign that safety groups ought to take note of.