These phishing campaigns are exploiting a Zimbra vulnerability and affecting internet-facing webmail companies. Learn to defend your group from this safety risk.

A brand new Proofpoint report signifies that in late 2022, risk actor TA473 focused elected officers and staffers within the U.S., in addition to consultants in European politics and economics. Proofpoint additionally states that “social engineering lures and impersonated organizations typically pertain to Ukraine within the context of armed battle” and notes that the e-mail mailboxes of NATO-aligned authorities entities have been focused in Europe.
SEE: Safety danger evaluation guidelines (TechRepublic Premium)
In older phishing campaigns from TA473, targets included Polish authorities businesses, Ukraine’s and Italy’s Ministries of Overseas Affairs, and people inside the Indian authorities.
Soar to:
Who’s TA473?
TA473 is a risk actor, identified since 2021, that has focused a number of nations aligned in opposition to the pursuits of Belarus and Russia; the group is also called Winter Vivern for some safety firms and governmental entities.
Though there isn’t any confirmed proof, just a few components assist the idea that the risk actor originates from Russia. As an example, a Russian phrase utilized in malware samples and paperwork has leaked. Past this leak, TA473’s frequent alignment with Russian pursuits makes it plausible that the risk actor would originate from that nation.
The risk actor largely creates phishing campaigns to ship payloads and harvest credentials. Payloads typically goal vulnerabilities in internet-facing webmail companies and permit attackers to get entry to electronic mail mailboxes.
Somewhat than growing instruments to automate elements of its assaults, the group invests time and assets to compromise particular entities with customized payloads for the focused webmail portal.
How TA473’s phishing campaigns work
TA473 typically sends emails from compromised electronic mail addresses, originating from unpatched or insecure WordPress-hosted domains. The emails include benign URLs from the focused group or a related peer group, whereas the sender electronic mail is spoofed to look as if it comes from the group. Then, they hyperlink this benign URL to both ship a first-stage payload or redirect victims to a credential-harvesting touchdown web page with actor-controlled or compromised infrastructure (Determine A).
Determine A
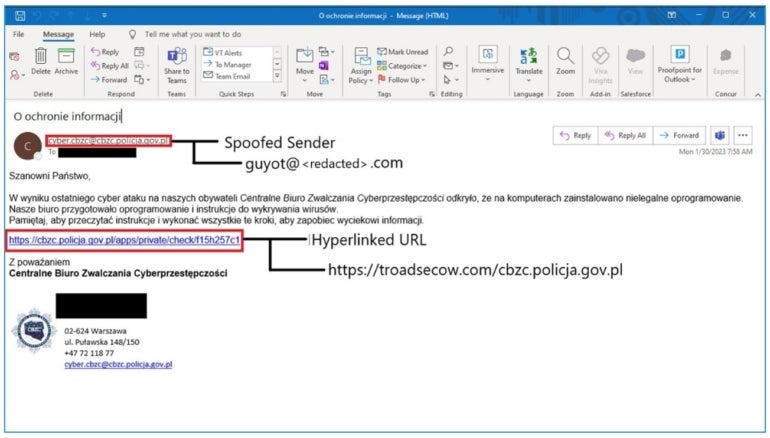
In some circumstances, TA473 makes use of structured URI paths that point out a hashed worth for the focused particular person, an unencoded indication of the focused group, and encoded or plaintext variations of the benign URL that was hyperlinked within the preliminary electronic mail to targets.
How TA473 exploits a Zimbra vulnerability
In early 2023, the risk actor began exploiting a identified vulnerability in Zimbra Collaboration variations 9.0.0 that was typically used to host internet-accessible webmail portals. To efficiently obtain that exploitation, the malicious hyperlink within the phishing electronic mail sends a hexadecimal-encoded JavaScript snippet to the Zimbra software program, which is executed as an error parameter (Determine B).
Determine B

As soon as the JavaScript snippet is decoded, it downloads the following stage payload that triggers cross-site request forgery to steal usernames, passwords and CSRF tokens from the person who clicked the malicious hyperlink (Determine C).
Determine C
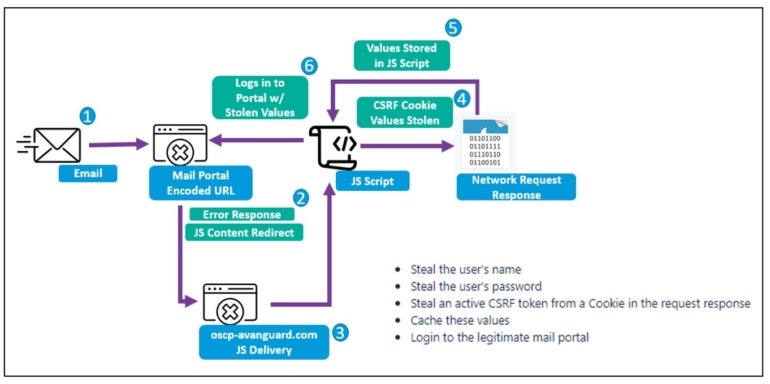
The JavaScript utilized by TA473 attackers additionally makes an attempt to log in to the respectable electronic mail portal with energetic tokens.
Proofpoint has noticed that the risk actor typically targets particular RoundCube webmail request tokens as effectively, which reveals that the risk actor has already completed reconnaissance on the goal previous to attacking it.
Tips on how to defend from this safety risk
- Patch Zimbra Collaboration, which is able to forestall attackers from exploiting the CVE-2022-27926 vulnerability.
- Guarantee multifactor authentication is enabled on internet-facing companies comparable to internet portals; even when an attacker owns legitimate credentials, they won’t be capable of use them. Sturdy password insurance policies additionally have to be enforced.
- Put community insurance policies in place in order that, despite the fact that the webmail portal faces the web, it ought to solely be accessible from a company VPN connection.
- Educate customers about phishing threats and social engineering methods that attackers would possibly make use of.
- Maintain working techniques and software program up to date and patched.
Disclosure: I work for Development Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.










