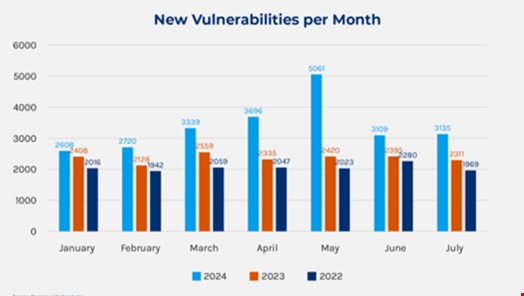
Printed vulnerabilities rose by 43% in H1 2024 in comparison with H1 2023, with attackers closely focusing on flaws in digital personal networks (VPNs) and different perimeter gadgets for preliminary entry, a brand new report from Forescout has discovered.
A complete of 23,668 vulnerabilities had been reported within the first six months of 2024, with a mean of 111 new CVEs per day.
The vast majority of printed vulnerabilities in H1 2024 had both a medium (39%) or low (25%) severity rating (CVSS), whereas simply 9% had a important rating.
That is in distinction to the identical interval final yr, the place round two-thirds of vulnerabilities had been both medium (39%) or excessive (27%).
The report additionally highlighted that 87 CVEs had been added to the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company’s (CISA) Recognized Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog in H1 2024, bringing the full to 1140 vulnerabilities. This represents a lower of 23% in comparison with the identical interval in 2023.
The brand new vulnerabilities printed within the catalog in H1 2024 affected 39 totally different distributors, a 17% lower from 47 in H1 2023. Essentially the most generally impacted firm was Microsoft (17%), adopted by Google (8%), Apple (6%), D-Hyperlink (6%), Ivanti (6%), Android (5%) and Cisco (5%).
Practically half (46%) of the vulnerabilities added this yr had been printed earlier than 2024. 5 of those flaws had been in end-of-life merchandise affecting Web Explorer, D-Hyperlink routers and community connected storage merchandise, that means no patches can be found for this gear.
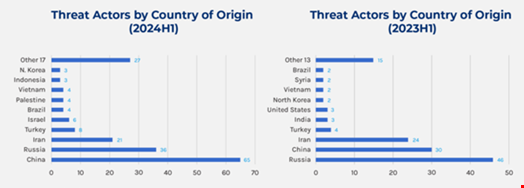
Most Risk Actors Originate from China, Russia and Iran
Forescout discovered that almost all menace actors lively in H1 2024 originated from China (65), Russia 36%) and Iran (21), with China overtaking Russia from H1 2023.
Half (50%) of those actors are designated as cybercriminals, adopted by state-sponsored actors (40%) and hacktivists (10%).
The researchers famous that there are more and more blurred traces between hacktivists and state-sponsored actors focusing on important infrastructure, with state-sponsored actors utilizing hacktivist personae to conduct a few of their assaults.
This shift could also be pushed by a number of components, comparable to elevated visibility of campaigns and believable deniability for the actors.
An instance of this kind of menace actor is the Cyber Military of Russia, believed to be linked to Sandworm, which launched an assault in opposition to a wastewater remedy plant within the US in April 2024.
One other is Predatory Sparrow, which poses as a hacktivist group rebelling in opposition to the Iranian state, however is believed to be affiliated with Israel.
Learn now: From Protests to Revenue: Why Hacktivists Are Becoming a member of the Ransomware Ranks
Ransomware Assaults Proceed to Rise
The report confirmed a 6% rise in ransomware assaults in H1 2024 in comparison with H1 2023, reaching 3085 assaults.
The ransomware panorama has considerably fragmented over this era – in H1 2023, the highest 10 teams accounted for 3 quarters of assaults, however in H1 2024 they represented 59%.
LockBit was essentially the most lively group on this interval, chargeable for 15% of assaults. That is regardless of the numerous regulation enforcement operation focusing on the group’s infrastructure in February 2024.
LockBit was adopted by Play (6%), RansomHub (6%), Cactus (5%), Akira (5%), Hunters (5%) and BlackBasta (5%).