Throughout a current investigation of a Qilin ransomware breach, the Sophos X-Ops workforce recognized attacker exercise resulting in en masse theft of credentials saved in Google Chrome browsers on a subset of the community’s endpoints – a credential-harvesting method with potential implications far past the unique sufferer’s group. That is an uncommon tactic, and one which might be a bonus multiplier for the chaos already inherent in ransomware conditions.
What’s Qilin?
The Qilin ransomware group has been in operation for simply over two years. It was within the information in June 2024 as a consequence of an assault on Synnovis, a governmental service supplier to numerous UK healthcare suppliers and hospitals. Previous to the exercise described on this put up, Qilin assaults have usually concerned “double extortion” – that’s, stealing the sufferer’s knowledge, encrypting their programs, after which threatening to disclose or promote the stolen knowledge if the sufferer gained’t pay for the encryption key, a tactic we’ve just lately mentioned in our “Turning the Screws” analysis
The Sophos IR workforce noticed the exercise described on this put up in July 2024. To offer some context, this exercise was noticed on a single area controller throughout the goal’s Lively Listing area; different area controllers in that AD area have been contaminated however affected in a different way by Qilin.
Opening maneuvers
The attacker obtained preliminary entry to the atmosphere by way of compromised credentials. Sadly, this technique of preliminary entry will not be new for Qilin (or different ransomware gangs for that matter). Our investigation indicated that the VPN portal lacked multifactor authentication (MFA) safety.
The attacker’s dwell time between preliminary entry to the community and additional motion was eighteen days, which can or might not point out that an Preliminary Entry Dealer (IAB) made the precise incursion. In any case, eighteen days after preliminary entry occurred, attacker exercise on the system elevated, with artifacts displaying lateral motion to a website controller utilizing compromised credentials.
As soon as the attacker reached the area controller in query, they edited the default area coverage to introduce a logon-based Group Coverage Object (GPO) containing two gadgets. The primary, a PowerShell script named IPScanner.ps1, was written to a brief listing throughout the SYSVOL (SYStem VOLume) share (the shared NTFS listing positioned on every area controller inside an Lively Listing area) on the precise area controller concerned. It contained a 19-line script that tried to reap credential knowledge saved throughout the Chrome browser.
The second merchandise, a batch script named logon.bat, contained the instructions to execute the primary script. This mix resulted in harvesting of credentials saved in Chrome browsers on machines linked to the community. Since these two scripts have been in a logon GPO, they’d execute on every consumer machine because it logged in.
On the endpoints
Every time a logon occurred on an endpoint, the logon.bat would launch the IPScanner.ps1 script, which in flip created two recordsdata – a SQLite database file named LD and a textual content file named temp.log, as seen in Determine 1.
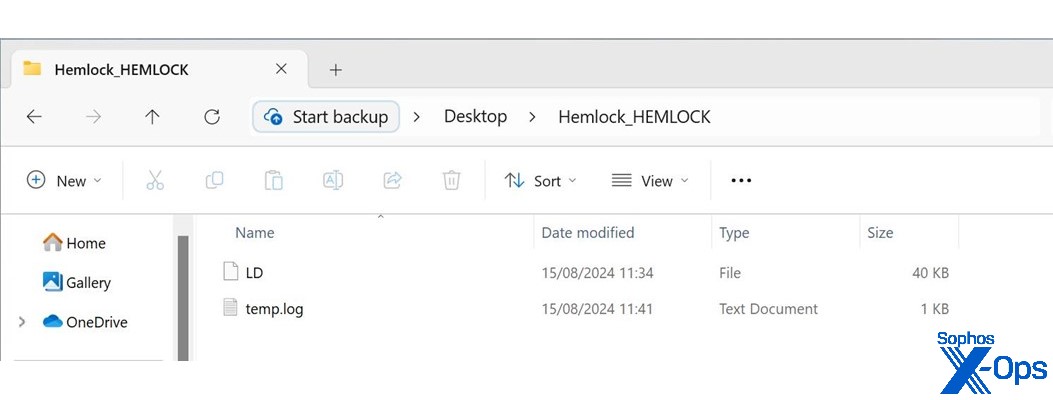
Determine 1: We name this demo gadget Hemlock as a result of it’s toxic: The 2 recordsdata created by the startup script on an contaminated machine
These recordsdata have been written again to a newly created listing on the area’s SYSVOL share and named after the hostname of the gadget(s) on which they have been executed (in our instance, Hemlock)
The LD database file incorporates the construction proven in Determine 2.
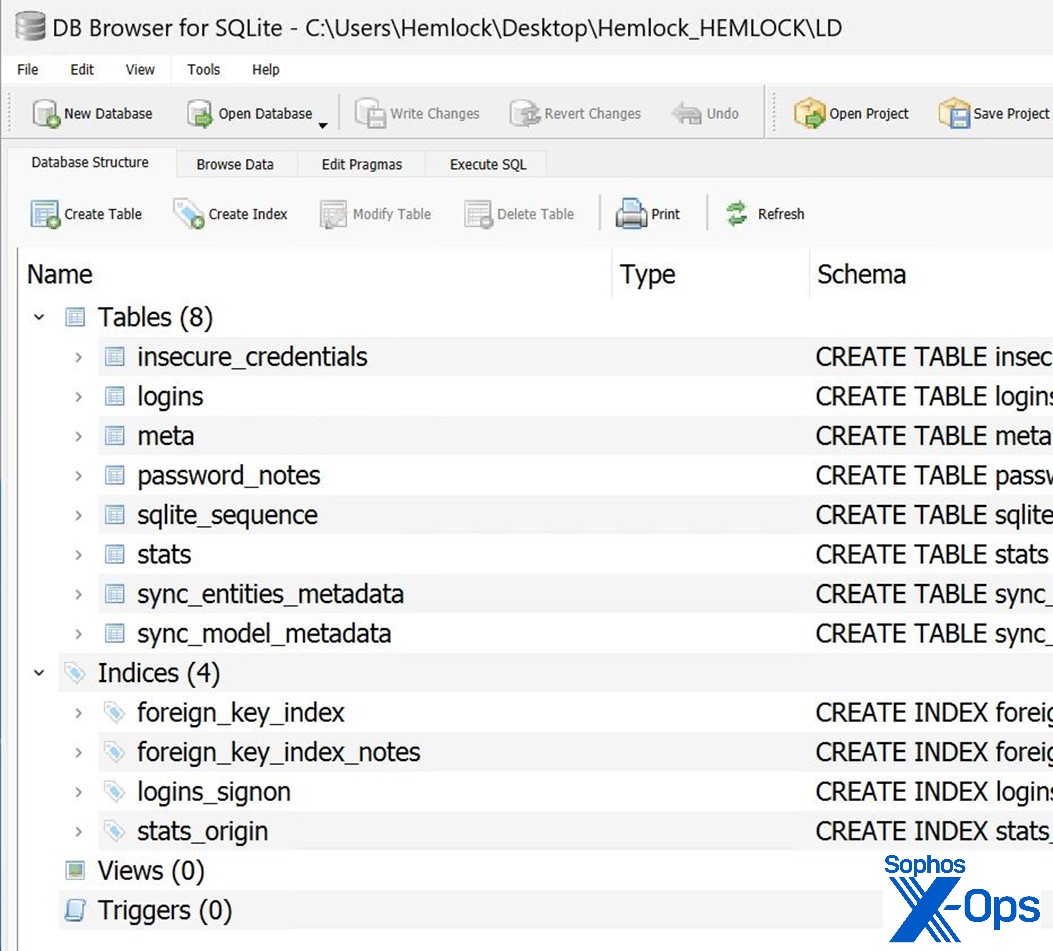
Determine 2: Inside LD, the SQLite database file dropped into SYSVOL
In a show of confidence that they’d not be caught or lose their entry to the community, the attacker left this GPO energetic on the community for over three days. This offered ample alternative for customers to go browsing to their units and, unbeknownst to them, set off the credential-harvesting script on their programs. Once more, since this was all achieved utilizing a logon GPO, every consumer would expertise this credential-scarfing every time they logged in.
To make it harder to evaluate the extent of the compromise, as soon as the recordsdata containing the harvested credentials have been stolen and exfiltrated, the attacker deleted all of the recordsdata and cleared the occasion logs for each the area controller and the contaminated machines. After deleting the proof, they proceeded to encrypt recordsdata and drop the ransom notice, as proven in Determine 3. This ransomware leaves a duplicate of the notice in each listing on the gadget on which it runs.
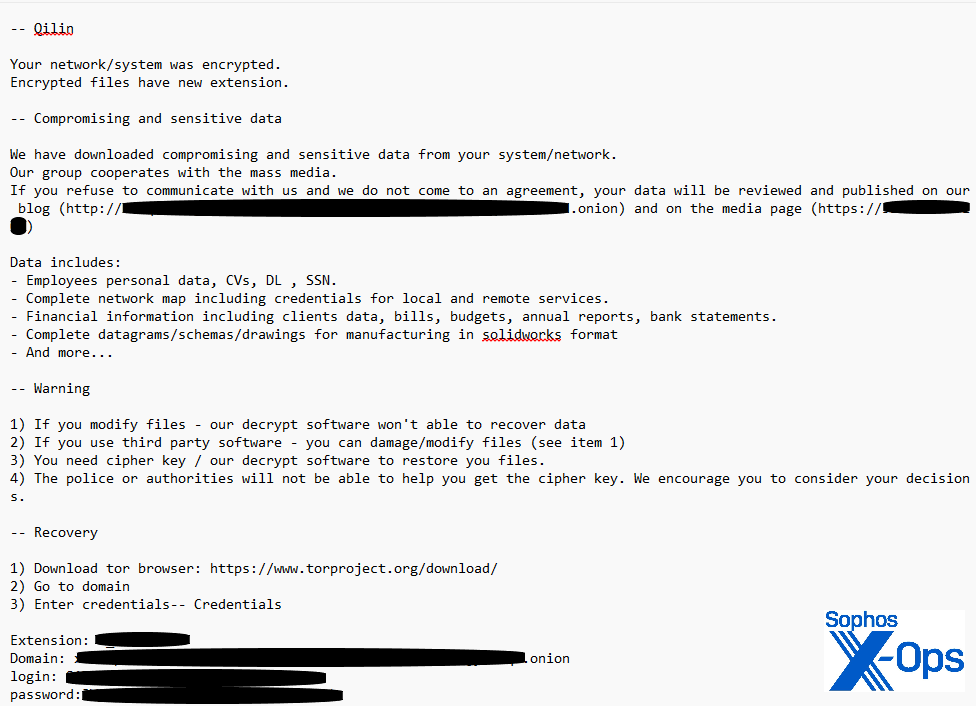
Determine 3: A Qilin ransom notice
The Qilin group used GPO once more because the mechanism for affecting the community by having it create a scheduled process to run a batch file named run.bat, which downloaded and executed the ransomware.
Affect
On this assault, the IPScanner.ps1 script focused Chrome browsers – statistically the selection most certainly to return a bountiful password harvest, since Chrome presently holds simply over 65 % of the browser market. The success of every try would rely upon precisely what credentials every consumer was storing within the browser. (As for what number of passwords is perhaps acquired from every contaminated machine, a current survey signifies that the typical consumer has 87 work-related passwords, and round twice as many private passwords.)
A profitable compromise of this kind would imply that not solely should defenders change all Lively Listing passwords; they need to additionally (in concept) request that finish customers change their passwords for dozens, probably a whole lot, of third-party websites for which the customers have saved their username-password mixtures within the Chrome browser. The defenders in fact would don’t have any method of creating customers do this. As for the end-user expertise, although nearly each web consumer at this level has acquired not less than one “your data has been breached” discover from a web site that has misplaced management of their customers’ knowledge, on this scenario it’s reversed – one consumer, dozens or a whole lot of separate breaches.
It’s maybe attention-grabbing that, on this particular assault, different area controllers in the identical Lively Listing area have been encrypted, however the area controller the place this particular GPO was initially configured was left unencrypted by the ransomware. What this might need been – a misfire, an oversight, attacker A/B testing – is past the scope of our investigation (and this put up).
Conclusion
Predictably, ransomware teams proceed to vary ways and develop their repertoire of methods. The Qilin ransomware group might have determined that, by merely concentrating on the community belongings of their goal organizations, they have been lacking out.
In the event that they, or different attackers, have determined to additionally mine for endpoint-stored credentials – which may present a foot within the door at a subsequent goal, or troves of details about high-value targets to be exploited by different means – a darkish new chapter might have opened within the ongoing story of cybercrime.
Acknowledgements
Anand Ajjan of SophosLabs, in addition to Ollie Jones and Alexander Giles from the Incident Response workforce, contributed to this evaluation.
Response and remediation
Organizations and people ought to depend on password managers functions that make use of business finest practices for software program improvement, and that are frequently examined by an unbiased third occasion. The usage of a browser-based password supervisor has been confirmed to be insecure again and again, with this text being the latest proof.
Multifactor authentication would have been an efficient preventative measure on this scenario, as we’ve mentioned elsewhere. Although use of MFA continues to rise, a 2024 Lastpass examine signifies that although MFA adoption at firms with over 10,000 workers is a not-terrible 87%, that adoption stage drops precipitously – from 78% for firms with 1,001-1000 workers all the best way all the way down to a 27% adoption fee for companies with 25 workers or much less. Talking bluntly, companies should do higher, for their very own security – and on this case, the protection of different firms as effectively.
Our personal Powershell.01 question was instrumental in figuring out suspicious PowerShell commends executed in the middle of the assault. That question is freely accessible from our Github, together with many others.
Sophos detects Qilin ransomware as Troj/Qilin-B and with behavioral detections corresponding to Impact_6a & Lateral_8a. The script described above is detected as Troj/Ransom-HDV.