The software program business is making headway in opposition to a bunch of pernicious vulnerabilities which can be liable for the overwhelming majority of vital, remotely exploitable, and in-the-wild assaults, software-security consultants stated this week.
The category of vulnerabilities — so-called memory-safety points — embody buffer overflows and use-after-free errors and have accounted for almost all of software safety points disclosed by software program firms. Now, the most recent information present that the rising use of memory-safe languages — reminiscent of Java, C#, and extra just lately, Rust — has resulted in a fast decline of the whole class of vulnerabilities.
Final week, for instance, Google revealed that the most recent model of the Android working system has extra new code written in memory-safe programing languages — reminiscent of Java, Rust, and Kotlin — than memory-unsafe languages reminiscent of C and C++, leading to a drop in memory-safety vulnerabilities from 223 to 85 over the previous three years.
“We’re persevering with to give attention to eliminating total courses of vulnerabilities, specializing in essentially the most extreme first,” says Jeffrey Vander Stoep, a software program engineer at Google. “As reminiscence security vulnerabilities turn out to be extra scarce, we anticipate the analysis neighborhood to focus their vulnerability-findings efforts on different courses of vulnerabilities.”
For many years, C and C++ have been the workhorse programming languages of the software program business. But they lack the reminiscence protections of extra trendy languages, reminiscent of C#, Go, Java, Python, Ruby, Rust, and Swift. The outcome? Fifty-nine % of purposes written in C++ have high-severity or critical-severity flaws, in comparison with 9% for JavaScript and 10% for Python, in line with application-security agency Veracode’s State of Software program Safety Vol. 11 report.
Buffer Overflows and Wormable Flaws
The convenience with which programmers can create flawed code has turn out to be a serious downside for giant software program firms. Microsoft, for instance, discovered that, up till 2018, memory-safety points accounted for 70% of the vulnerabilities found within the firm’s software program. General, reminiscence questions of safety have accounted for 60% to 70% of all vulnerabilities throughout all kinds of ecosystems, in line with 2020 analysis by software program resilience engineer Alex Gaynor.
And since the failings can simply be exploited to assault purposes, they’re the foundation causes behind a big variety of compromises, says Chris Wysopal, chief expertise officer of Veracode.
“Reminiscence corruption points are amongst the best severity flaws as they typically permit attackers to take advantage of with code execution which permits them to take full management of the applying,” he says. “Within the worst case situation this enables the creation of a worm exploit which might go on to assault different situations of the vulnerability.”
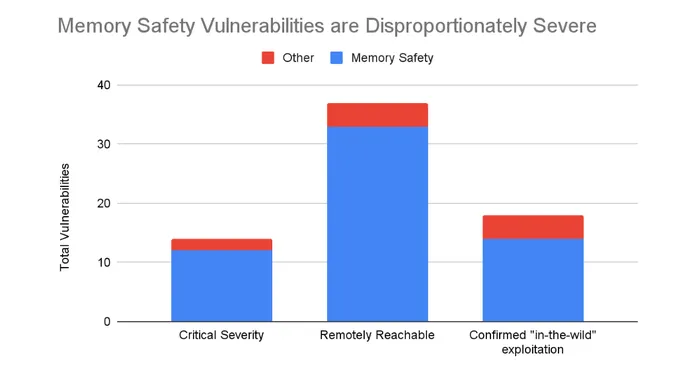
In its latest weblog publish on its shift to memory-safe languages for Android growth, Google famous that whereas memory-safety vulnerabilities now solely account for 36% of points disclosed in Android, they account for 86% of the vital safety vulnerabilities and 89% of remotely exploitable points.
Making the Swap to Protected Languages
For that motive, Google and others have urged builders to undertake memory-safe languages.
In Google’s case, C and C++ now account for simply lower than half of all new code. In reality, Android 13, the most recent model, is the primary the place the vast majority of code has been written in memory-safe languages, with Rust changing C and C++ for a lot of builders. Rust is an environment friendly programming language targeted on creating safe code.
Even the Nationwide Safety Company is urging firms to undertake memory-safe programming languages.
Switching to a memory-safe language is just not ample, nonetheless. Whereas the languages do make it more durable for programmers to jot down insecure code, each language has a distinct degree of safety. For that motive, the NSA has additionally really helpful that builders use quite a lot of application-security instruments — from compiler choices to static scanners to runtime evaluation — to harden purposes as a lot as doable.
“Software program evaluation instruments can detect many situations of reminiscence administration points and working atmosphere choices also can present some safety, however inherent protections supplied by reminiscence secure software program languages can forestall or mitigate most reminiscence administration points,” the NSA’s report said.
In the long run, whereas memory-safe programming languages will not be a standalone answer to the issue of software program vulnerabilities, they offer steering to builders who can then keep away from a few of the most extreme programming errors, says Veracode’s Wysopal.
“It is exhausting to generalize and say that there’s a decrease quantity of vulnerabilities in reminiscence secure languages for the reason that approach they’re used is totally different,” he says. “However if you happen to had been utilizing two totally different languages to perform the very same process, and one was reminiscence secure, you’d count on fewer vulnerabilities in that one and usually much less vital vulnerabilities.”










