After the failure of Silicon Valley Financial institution (SVB), a substantial amount of Individuals are beginning to notice the risks of fractional-reserve banking. Stories present that SVB suffered a big financial institution run after prospects tried to withdraw $42 billion from the financial institution on Thursday. The next is a take a look at what fractional-reserve banking is and why the follow can result in financial instability.
The Historical past and Risks of Fractional-Reserve Banking in america
For many years, individuals have warned concerning the risks of fractional-reserve banking, and the current ordeal of Silicon Valley Financial institution (SVB) has introduced renewed consideration to the problem. Basically, fractional-reserve banking is a system of financial institution administration that solely holds a fraction of financial institution deposits, with the remaining funds invested or loaned out to debtors. Fractional-reserve banking (FRB) operates in almost each nation worldwide, and within the U.S., it grew to become extensively outstanding through the nineteenth century. Previous to this time, banks operated with full reserves, which means they held 100% of their depositors’ funds in reserve.
Nonetheless, there’s appreciable debate on whether or not fractional lending happens lately, with some assuming that invested funds and loans are merely printed out of skinny air. The argument stems from a Financial institution of England paper known as “Cash Creation within the Trendy Economic system.” It’s typically used to dispel myths related to trendy banking. Economist Robert Murphy discusses these alleged myths in chapter 12 of his e-book, “Understanding Cash Mechanics.”
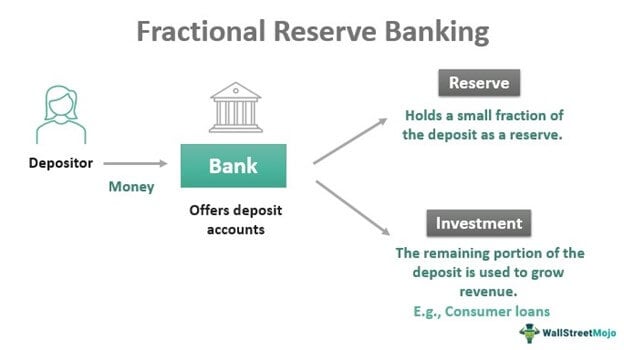
The FRB follow unfold considerably after the passage of the Nationwide Banking Act in 1863, which created America’s banking constitution system. Within the early 1900s, the fractional-reserve technique began to indicate cracks with the occasional financial institution failures and monetary crises. These grew to become extra outstanding after World Battle I, and financial institution runs, highlighted within the standard film “It’s a Great Life,” grew to become commonplace on the time. To repair the scenario, a cabal of bankers dubbed “The Cash Belief” or “Home of Morgan” labored with U.S. bureaucrats to create the Federal Reserve System.
After additional troubles with fractional reserves, the Nice Despair set in, and U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt initiated the Banking Act of 1933 to revive belief within the system. The Federal Deposit Insurance coverage Company (FDIC) was additionally created, which offers insurance coverage for depositors holding $250,000 or much less in a banking establishment. Since then, the follow of fractional-reserve banking continued to develop in recognition within the U.S. all through the twentieth century and stays the dominant type of banking as we speak. Regardless of its recognition and widespread use, fractional-reserve banking nonetheless poses a big menace to the financial system.
Historical past of FDIC deposit limits. pic.twitter.com/e0q1NkzW6n
— Lyn Alden (@LynAldenContact) March 12, 2023
The most important downside with fractional-reserve banking is the specter of a financial institution run as a result of the banks solely maintain a fraction of the deposits. If a lot of depositors concurrently demand their deposits again, the financial institution could not have sufficient money available to fulfill these calls for. This, in flip, causes a liquidity disaster as a result of the financial institution can’t appease depositors and it might be compelled to default on its obligations. One financial institution run may cause panic amongst different depositors banking at different areas. Main panic might have a ripple impact all through your entire monetary system, resulting in financial instability and doubtlessly inflicting a wider monetary disaster.
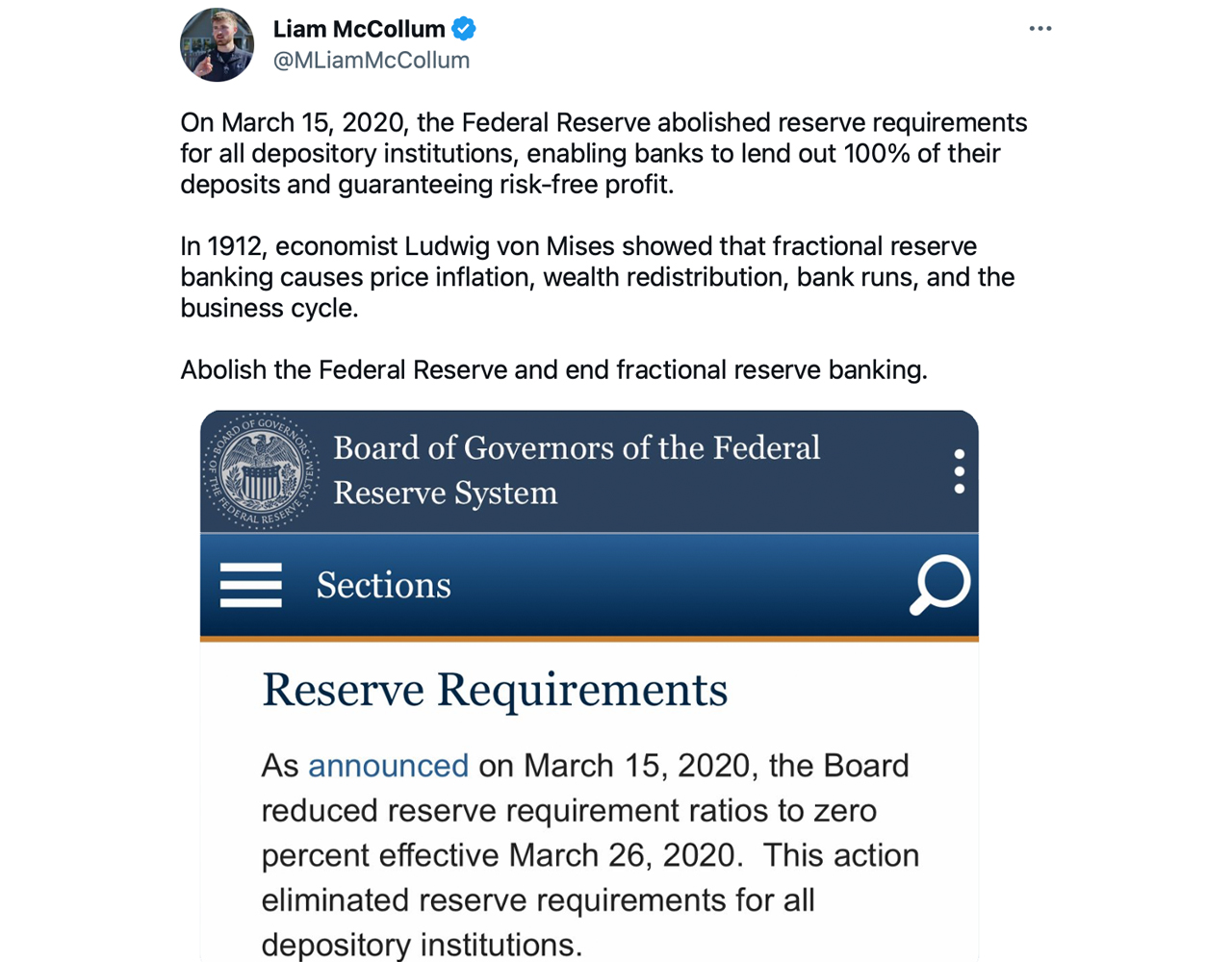
“so it is known as fractional reserve banking”
“what is the fraction?”
“was once 10%. however now it is 0” pic.twitter.com/iBbH6yxDXn
— foobar (@0xfoobar) March 12, 2023
Digital Banking and the Pace of Info Can Gasoline the Menace of Monetary Contagion
Within the film “It’s a Great Life,” the information of insolvency unfold via the city like wildfire, however financial institution run information lately might be an entire lot quicker attributable to a number of components associated to advances in expertise and the pace of data. First, the web made it simpler for info to unfold shortly, and information of a financial institution’s monetary instability might be disseminated quickly via social media, information web sites, and different on-line platforms.
Fractional reserve banking does NOT work, particularly within the web and social media age.
Info and worry unfold far too quick for an establishment to react.
What used to take weeks takes minutes.
A weak establishment might be uncovered and crash in a matter of hours.
— The Wolf Of All Streets (@scottmelker) March 12, 2023
Second, digital banking has made transactions quicker, and individuals who need to withdraw can accomplish that with out bodily going to the department. The pace of on-line banking can result in a quicker and extra widespread run on a financial institution if depositors understand that there’s a danger of their funds changing into unavailable.
Lastly, and perhaps crucial a part of as we speak’s variations, is the interconnectedness of the worldwide monetary system implies that a financial institution run in a single nation can shortly unfold to different areas. The pace of data, digital banking, and the linked monetary system might very effectively result in a a lot quicker and extra widespread contagion impact than was attainable prior to now. Whereas the advances in expertise have made banking much more environment friendly and simpler, these schemes have elevated the potential for monetary contagion and the pace at which a financial institution run can happen.
Deception and ‘Waves of Credit score Bubbles With Barely a Fraction in Reserve’
As beforehand talked about, many market observers, analysts, and famend economists have warned concerning the points with fractional reserve banking. Even the creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, wrote concerning the risks within the seminal white paper: “The central financial institution have to be trusted to not debase the forex, however the historical past of fiat currencies is filled with breaches of that belief. Banks have to be trusted to carry our cash and switch it electronically, however they lend it out in waves of credit score bubbles with barely a fraction in reserve,” Nakamoto wrote. This assertion highlights the chance related to fractional reserve banking, the place banks lend out extra money than they’ve in reserves.
Murray Rothbard, an Austrian economist and libertarian, was a powerful critic of fractional reserve banking. “Fractional reserve banking is inherently fraudulent, and if it weren’t backed and privileged by the federal government, it couldn’t lengthy exist,” Rothbard as soon as mentioned. The Austrian economist believed that the fractional reserve system relied on deception and that banks created a synthetic enlargement of credit score that might result in financial booms adopted by busts. The Nice Recession in 2008 was a reminder of the risks of fractional reserve banking, and it was the identical yr that Bitcoin was launched as an alternative choice to conventional banking that doesn’t depend on the trustworthiness of centralized establishments.
So bizarre how America instantly awakened and realized what fractional reserve banking is
— Erik Voorhees (@ErikVoorhees) March 12, 2023
The issues with SVB have proven that individuals have loads to find out about these points and about fractional banking as an entire. At the moment, some Individuals are calling on the Fed to bail out Silicon Valley Financial institution, hoping the federal authorities will step in to help. Nonetheless, even when the Fed saves the day concerning SVB, the risks of fractional reserve banking nonetheless exist, and plenty of are utilizing the SVB failure for example of why one shouldn’t belief the banking system working on this method.
What steps do you assume people and monetary establishments ought to take to organize for and mitigate the potential menace of monetary contagion in as we speak’s quickly evolving digital panorama? Share your ideas within the feedback part beneath.
Picture Credit: Shutterstock, Pixabay, Wiki Commons, Wall Avenue Mojo, It is a Great Life, Twitter
Disclaimer: This text is for informational functions solely. It isn’t a direct supply or solicitation of a suggestion to purchase or promote, or a advice or endorsement of any merchandise, providers, or corporations. Bitcoin.com doesn’t present funding, tax, authorized, or accounting recommendation. Neither the corporate nor the writer is accountable, instantly or not directly, for any harm or loss precipitated or alleged to be brought on by or in reference to the usage of or reliance on any content material, items or providers talked about on this article.










