Intel471’s new report reveals macOS is more and more focused by risk actors, who develop particular malware for the working system or use cross-platform languages to realize their objectives on macOS computer systems.
Extra macOS vulnerabilities are additionally being exploited within the wild. Malware and exploits may be used for each cybercrime and cyberespionage.
Extra malware than ever on macOS
Between January 2023 and July 2024, the researchers noticed greater than 40 risk actors concentrating on macOS programs with completely different malware varieties, the preferred being infostealers and trojans.
Infostealers
Data stealer malwares — aka infostealers — are more and more developed and deployed on all working programs, and macOS isn’t any exception.
In accordance with cloud safety firm Uptycs, incidents involving infostealers doubled within the first quarter of 2023 when put next with the identical interval in 2022. Cybersecurity firm Group-IB additionally studies a fivefold rise in underground gross sales associated to macOS infostealers.
Such software program is utilized by cybercriminals to steal log-in credentials, session cookies enabling authentication with out credentials, and extra information akin to bank card info or cryptocurrency wallets. The software program can also be broadly utilized by preliminary entry brokers, who acquire legitimate credentials, most frequently from firms somewhat than people, and promote them to different cybercriminals.
Atomic Stealer — additionally referred to as Atomic macOS Stealer or AMOS — is likely one of the hottest macOS infostealers since 2023. It’s designed to steal credentials and cryptocurrency pockets information from macOS units and browsers.
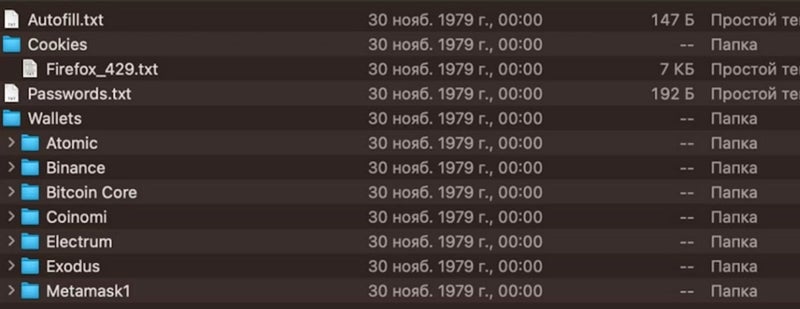
But a number of cybercriminals function or promote different infostealers concentrating on macOS. A risk actor nicknamed codehex marketed for a macOS infostealer dubbed ShadowVault, able to stealing information from numerous Chrome-based browsers, recordsdata saved on compromised computer systems, and information from cryptocurrency wallets.
The malware operators may additionally signal it with an Apple developer signature, making its detection tougher for safety software program. The malware was offered at a month-to-month value of $500 beneath a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) enterprise mannequin.
One other dearer infostealer, Quark Lab, with capabilities to steal keychain passwords from programs in addition to cryptocurrency wallets and well-liked browser info, was offered for $3,000 per thirty days.
Trojans
Distant entry trojans are one other well-liked class of malware more and more deployed on macOS.
RustDoor, a macOS malware developed in RUST and probably tied to a ransomware risk actor, offers a number of functionalities to its controller:
- Executes distant instructions.
- Manipulates recordsdata on compromised programs.
- Provides extra payloads.
- Collects system info.
This makes it a singular device for each cyberespionage and cybercrime risk actors. Rust programming language has turn into extra well-liked amongst malware builders, as it’s a cross-platform language that permits a developer to simply port code into any working system.
Ransomware
As written by Intel471, “the looks of macOS ransomware raises issues because it demonstrates risk actors searching for new avenues to compromise Apple customers.”
In April 2023, safety researchers found a brand new encryptor for the notorious LockBit ransomware, which focused macOS units, together with newer macOS programs working on Apple Silicon.
In late 2023 got here one other less-advanced ransomware, dubbed Turtle, and developed as soon as once more in a cross-platform programming language, Golang, aka Go. The malware was solely signed advert hoc and never notarized, making it detectable by Gatekeeper, as defined by professional safety researcher Patrick Wardle.
Vulnerabilities exploited
The variety of macOS vulnerabilities exploited in 2023 elevated by greater than 30%, in line with patch administration software program firm Action1.
Moreover, Intel471 discovered 69 vulnerabilities that impacted a number of variations of macOS from March 2020 to July 2024, with greater than 10 vulnerabilities ranked at a high-risk degree. A few of these vulnerabilities have been exploited by cyberespionage risk actors.
CVE-2023-41993, an unspecified vulnerability concentrating on a number of variations of macOS, was exploited to put in Cytrox’s Predator spyware and adware that was offered to a number of state-sponsored organizations worldwide.
Risk actors additionally exploited CVE-2023-41064, a buffer-overflow vulnerability. The cyberespionage risk actor offered its spyware and adware to state-sponsored organizations.
A cybercriminal nicknamed oDmC3oJrrSuZLhp provided to promote an exploit on an underground discussion board for $2.7 million for the CVE-2022-32893 vulnerability, which permits an attacker to execute arbitrary code on focused programs.
State-sponsored risk actors
Whereas completely different spyware and adware suppliers have offered their providers to state-sponsored risk actors, a few of these risk actors do develop malware and instruments aimed toward macOS.
North Korean risk actor BlueNoroff, for instance, has developed a malicious loader often known as RustBucket, developed for macOS and aimed toward concentrating on monetary establishments whose actions are associated to cryptocurrencies.
The group additionally targets people holding cryptocurrency property, with the last word aim of stealing all of the crypto cash from focused wallets.
Russian risk actors APT28, a part of the Russian Principal Directorate of the Common Employees of the Armed Forces, and APT29, a part of Russia’s International Intelligence Service, have additionally used macOS malware.
The XAgent modular backdoor utilized by APT28 has been round for a few years and included a macOS model, permitting it to steal information from compromised macOS programs, together with iOS backups containing messages, contacts, voicemail, name histories, notes, and calendars. APT29 used the no-longer-supported Empire cross-platform distant administration and post-exploitation framework, enabling concentrating on of macOS.
Vietnam-based risk actor APT32 additionally deployed a macOS backdoor used for concentrating on completely different organizations.
The way to guard towards this risk
macOS programs should at all times be updated and patched to keep away from being compromised by frequent vulnerabilities.
Safety software program needs to be deployed on the programs to detect malware and suspicious actions. E-mail safety options also needs to be used since a whole lot of the preliminary compromise is unfold by way of phishing emails.
Lastly, all workers should be skilled to detect potential social engineering strategies utilized in emails or on the spot messaging instruments.
Disclosure: I work for Pattern Micro, however the views expressed on this article are mine.










