As a reasonably commercially profitable writer as soon as wrote, “the evening is darkish and stuffed with terrors, the day shiny and exquisite and stuffed with hope.” It’s becoming imagery for AI, which like all tech has its upsides and drawbacks.
Artwork-generating fashions like Secure Diffusion, as an example, have led to unimaginable outpourings of creativity, powering apps and even completely new enterprise fashions. Alternatively, its open supply nature lets unhealthy actors to make use of it to create deepfakes at scale — all whereas artists protest that it’s profiting off of their work.
What’s on deck for AI in 2023? Will regulation rein within the worst of what AI brings, or are the floodgates open? Will highly effective, transformative new types of AI emerge, a la ChatGPT, disrupt industries as soon as thought secure from automation?
Anticipate extra (problematic) art-generating AI apps
With the success of Lensa, the AI-powered selfie app from Prisma Labs that went viral, you may anticipate lots of me-too apps alongside these traces. And anticipate them to even be able to being tricked into creating NSFW pictures, and to disproportionately sexualize and alter the looks of ladies.
Maximilian Gahntz, a senior coverage researcher on the Mozilla Basis, stated he anticipated integration of generative AI into shopper tech will amplify the consequences of such methods, each the nice and the unhealthy.
Secure Diffusion, for instance, was fed billions of pictures from the web till it “discovered” to affiliate sure phrases and ideas with sure imagery. Textual content-generating fashions have routinely been simply tricked into espousing offensive views or producing deceptive content material.
Mike Prepare dinner, a member of the Knives and Paintbrushes open analysis group, agrees with Gahntz that generative AI will proceed to show a serious — and problematic — drive for change. However he thinks that 2023 must be the yr that generative AI “lastly places its cash the place its mouth is.”

Immediate by TechCrunch, mannequin by Stability AI, generated within the free device Dream Studio.
“It’s not sufficient to encourage a neighborhood of specialists [to create new tech] — for know-how to change into a long-term a part of our lives, it has to both make somebody some huge cash, or have a significant affect on the each day lives of most people,” Prepare dinner stated. “So I predict we’ll see a severe push to make generative AI truly obtain one in all these two issues, with blended success.”
Artists lead the hassle to choose out of information units
DeviantArt launched an AI artwork generator constructed on Secure Diffusion and fine-tuned on art work from the DeviantArt neighborhood. The artwork generator was met with loud disapproval from DeviantArt’s longtime denizens, who criticized the platform’s lack of transparency in utilizing their uploaded artwork to coach the system.
The creators of the preferred methods — OpenAI and Stability AI — say that they’ve taken steps to restrict the quantity of dangerous content material their methods produce. However judging by lots of the generations on social media, it’s clear that there’s work to be achieved.
“The info units require energetic curation to deal with these issues and ought to be subjected to important scrutiny, together with from communities that are inclined to get the quick finish of the stick,” Gahntz stated, evaluating the method to ongoing controversies over content material moderation in social media.
Stability AI, which is basically funding the event of Secure Diffusion, not too long ago bowed to public strain, signaling that it will enable artists to choose out of the information set used to coach the next-generation Secure Diffusion mannequin. By means of the web site HaveIBeenTrained.com, rightsholders will have the ability to request opt-outs earlier than coaching begins in a couple of weeks’ time.
OpenAI gives no such opt-out mechanism, as an alternative preferring to companion with organizations like Shutterstock to license parts of their picture galleries. However given the authorized and sheer publicity headwinds it faces alongside Stability AI, it’s probably solely a matter of time earlier than it follows go well with.
The courts could in the end drive its hand. Within the U.S. Microsoft, GitHub and OpenAI are being sued in a category motion lawsuit that accuses them of violating copyright regulation by letting Copilot, GitHub’s service that intelligently suggests traces of code, regurgitate sections of licensed code with out offering credit score.
Maybe anticipating the authorized problem, GitHub not too long ago added settings to forestall public code from displaying up in Copilot’s ideas and plans to introduce a function that may reference the supply of code ideas. However they’re imperfect measures. In at the very least one occasion, the filter setting brought on Copilot to emit massive chunks of copyrighted code together with all attribution and license textual content.
Anticipate to see criticism ramp up within the coming yr, significantly because the U.Ok. mulls over guidelines that might that might take away the requirement that methods educated via public knowledge be used strictly non-commercially.
Open supply and decentralized efforts will proceed to develop
2022 noticed a handful of AI corporations dominate the stage, primarily OpenAI and Stability AI. However the pendulum could swing again in the direction of open supply in 2023 as the power to construct new methods strikes past “resource-rich and highly effective AI labs,” as Gahntz put it.
A neighborhood method could result in extra scrutiny of methods as they’re being constructed and deployed, he stated: “If fashions are open and if knowledge units are open, that’ll allow rather more of the vital analysis that has pointed to lots of the issues and harms linked to generative AI and that’s usually been far too troublesome to conduct.”
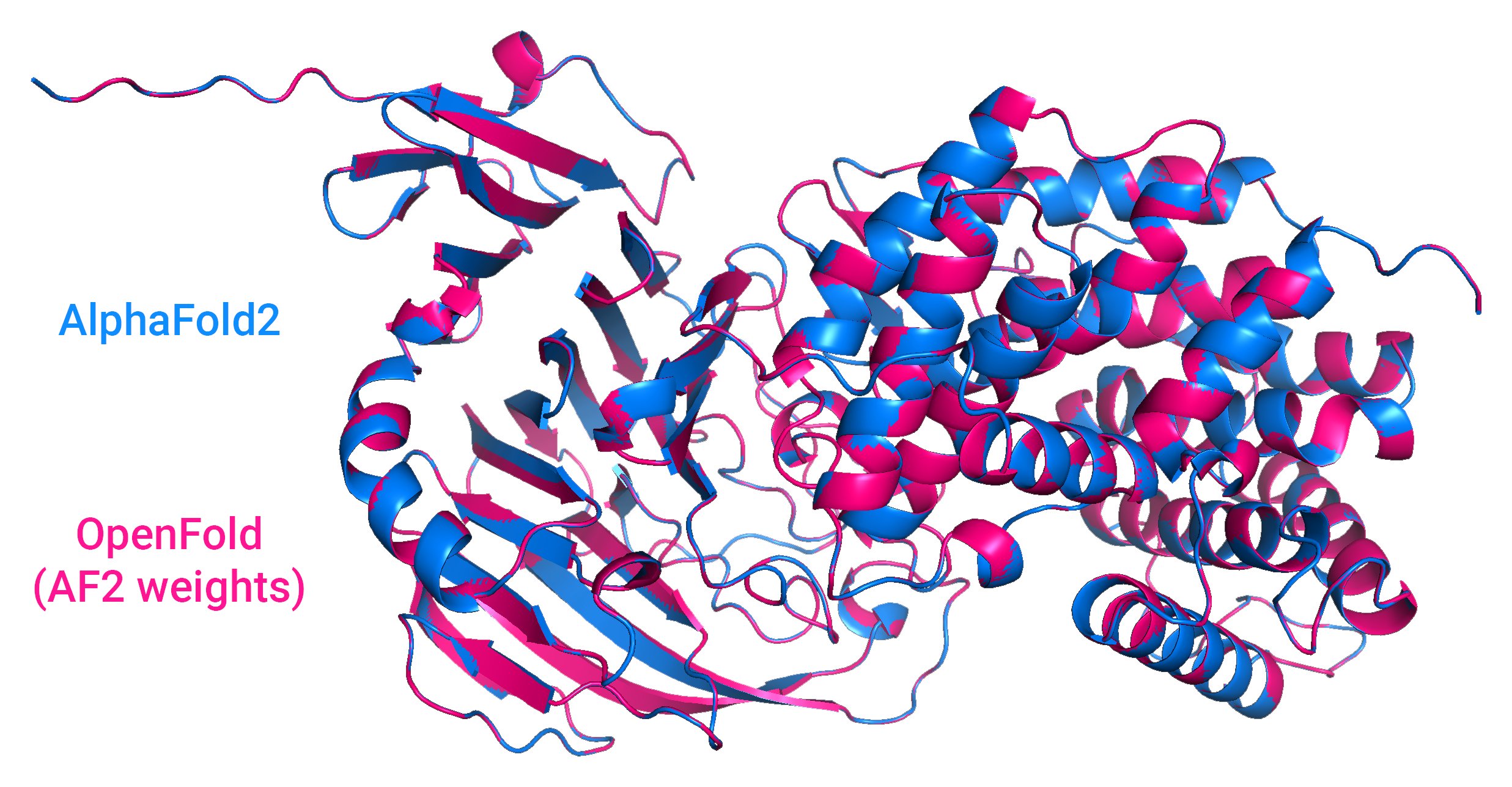
Picture Credit: Outcomes from OpenFold, an open supply AI system that predicts the shapes of proteins, in comparison with DeepMind’s AlphaFold2.
Examples of such community-focused efforts embrace massive language fashions from EleutherAI and BigScience, an effort backed by AI startup Hugging Face. Stability AI is funding various communities itself, just like the music-generation-focused Harmonai and OpenBioML, a unfastened assortment of biotech experiments.
Cash and experience are nonetheless required to coach and run refined AI fashions, however decentralized computing could problem conventional knowledge facilities as open supply efforts mature.
BigScience took a step towards enabling decentralized improvement with the current launch of the open supply Petals mission. Petals lets individuals contribute their compute energy, just like Folding@residence, to run massive AI language fashions that might usually require an high-end GPU or server.
“Trendy generative fashions are computationally costly to coach and run. Some back-of-the-envelope estimates put each day ChatGPT expenditure to round $3 million,” Chandra Bhagavatula, a senior analysis scientist on the Allen Institute for AI, stated by way of e-mail. “To make this commercially viable and accessible extra extensively, it is going to be vital to deal with this.”
Chandra factors out, nevertheless, that that giant labs will proceed to have aggressive benefits so long as the strategies and knowledge stay proprietary. In a current instance, OpenAI launched Level-E, a mannequin that may generate 3D objects given a textual content immediate. However whereas OpenAI open sourced the mannequin, it didn’t disclose the sources of Level-E’s coaching knowledge or launch that knowledge.
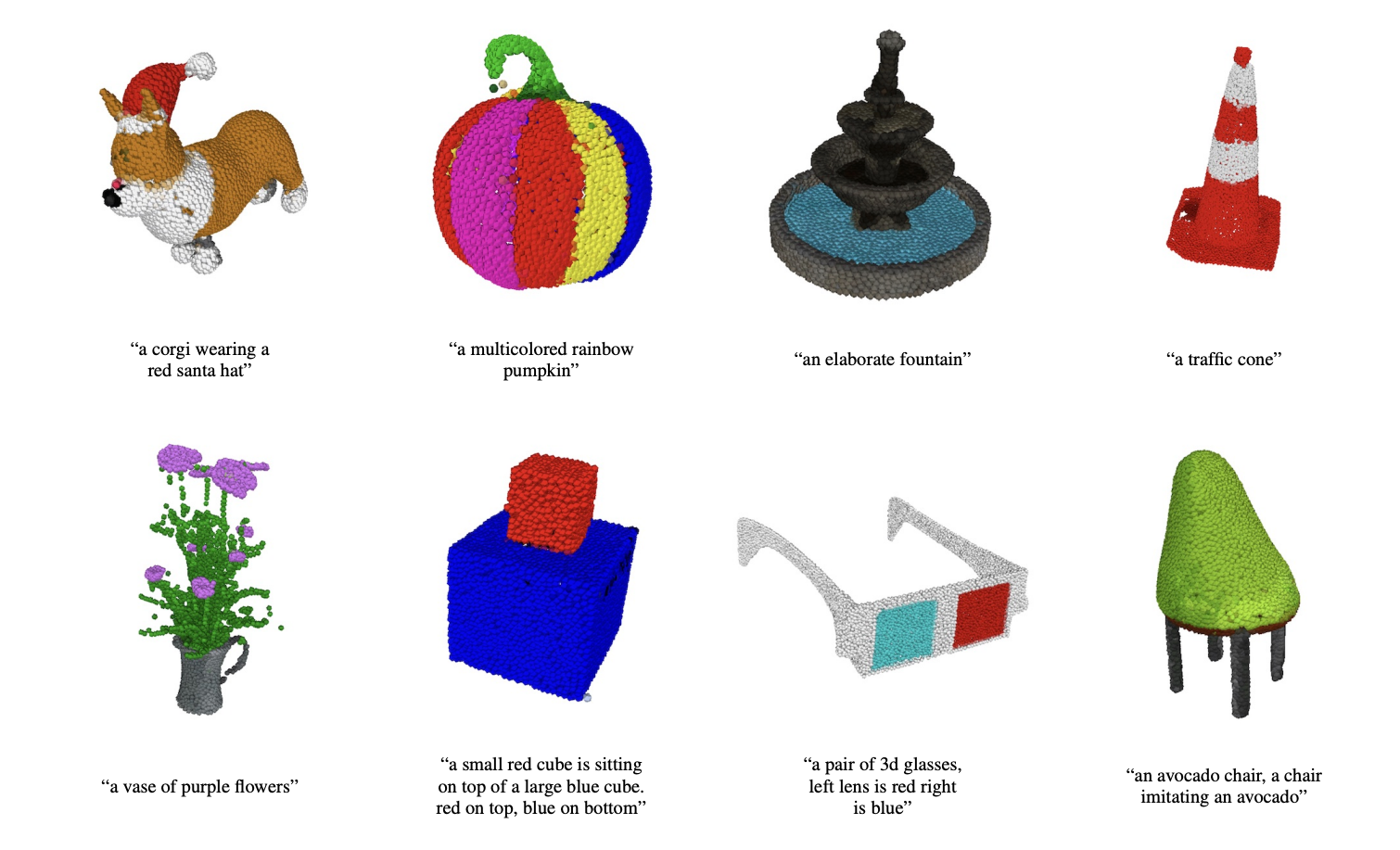
Level-E generates level clouds.
“I do assume the open supply efforts and decentralization efforts are completely worthwhile and are to the advantage of a bigger variety of researchers, practitioners and customers,” Chandra stated. “Nonetheless, regardless of being open-sourced, one of the best fashions are nonetheless inaccessible to a lot of researchers and practitioners resulting from their useful resource constraints.”
AI corporations buckle down for incoming laws
Regulation just like the EU’s AI Act could change how corporations develop and deploy AI methods transferring ahead. So might extra native efforts like New York Metropolis’s AI hiring statute, which requires that AI and algorithm-based tech for recruiting, hiring or promotion be audited for bias earlier than getting used.
Chandra sees these laws as crucial particularly in mild of generative AI’s more and more obvious technical flaws, like its tendency to spout factually unsuitable information.
“This makes generative AI troublesome to use for a lot of areas the place errors can have very excessive prices — e.g. healthcare. As well as, the benefit of producing incorrect info creates challenges surrounding misinformation and disinformation,” she stated. “[And yet] AI methods are already making selections loaded with ethical and moral implications.”
Subsequent yr will solely carry the specter of regulation, although — anticipate rather more quibbling over guidelines and court docket circumstances earlier than anybody will get fined or charged. However corporations should jockey for place in essentially the most advantageous classes of upcoming legal guidelines, just like the AI Act’s threat classes.
The rule as at the moment written divides AI methods into one in all 4 threat classes, every with various necessities and ranges of scrutiny. Methods within the highest threat class, “high-risk” AI (e.g. credit score scoring algorithms, robotic surgical procedure apps), have to satisfy sure authorized, moral and technical requirements earlier than they’re allowed to enter the European market. The bottom threat class, “minimal or no threat” AI (e.g. spam filters, AI-enabled video video games), imposes solely transparency obligations like making customers conscious that they’re interacting with an AI system.
Os Keyes, a Ph.D. Candidate on the College of Washington, expressed fear that corporations will intention for the bottom threat stage with a purpose to decrease their very own duties and visibility to regulators.
“That concern apart, [the AI Act] actually essentially the most constructive factor I see on the desk,” they stated. “I haven’t seen a lot of something out of Congress.”
However investments aren’t a certain factor
Gahntz argues that, even when an AI system works nicely sufficient for most individuals however is deeply dangerous to some, there’s “nonetheless lots of homework left” earlier than an organization ought to make it extensively accessible. “There’s additionally a enterprise case for all this. In case your mannequin generates lots of tousled stuff, customers aren’t going to love it,” he added. “However clearly that is additionally about equity.”
It’s unclear whether or not corporations will probably be persuaded by that argument going into subsequent yr, significantly as buyers appear keen to place their cash past any promising generative AI.
Within the midst of the Secure Diffusion controversies, Stability AI raised $101 million at an over-$1 billion valuation from outstanding backers together with Coatue and Lightspeed Enterprise Companions. OpenAI is alleged to be valued at $20 billion because it enters superior talks to lift extra funding from Microsoft. (Microsoft beforehand invested $1 billion in OpenAI in 2019.)
In fact, these could possibly be exceptions to the rule.

Picture Credit: Jasper
Outdoors of self-driving corporations Cruise, Wayve and WeRide and robotics agency MegaRobo, the top-performing AI corporations by way of cash raised this yr had been software-based, in line with Crunchbase. Contentsquare, which sells a service that gives AI-driven suggestions for net content material, closed a $600 million spherical in July. Uniphore, which sells software program for “conversational analytics” (assume name middle metrics) and conversational assistants, landed $400 million in February. In the meantime, Highspot, whose AI-powered platform supplies gross sales reps and entrepreneurs with real-time and data-driven suggestions, nabbed $248 million in January.
Traders could nicely chase safer bets like automating evaluation of buyer complaints or producing gross sales leads, even when these aren’t as “attractive” as generative AI. That’s to not counsel there received’t be large attention-grabbing investments, however they’ll be reserved for gamers with clout.










