It’s official — we’re smarter than the dinosaurs.
NASA has efficiently slammed a spacecraft into an asteroid in a historic mission that might sooner or later save Earth from hazardous house rocks noticed coming our method.
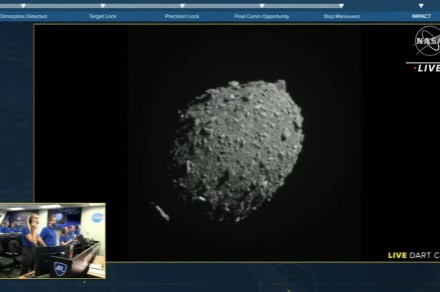
Monday’s Double Asteroid Redirection Take a look at (DART) mission was precisely that — a take a look at — focusing on a innocent asteroid, known as Dimorphos, some seven million miles from Earth.
Focusing on the 530-feet-wide rock after which crashing DART into it at 4,000 miles per second is already a significant achievement, however the mission will solely be thought-about a complete success if the influence has succeeded in altering the course of the asteroid’s orbit round a bigger asteroid, Didymos.
If it has, it means now we have the know-how to alter the trail of an incoming asteroid outlined as hazardous, directing it away from Earth and probably saving us from the identical destiny because the dinosaurs.
So when will we all know if the DART mission has been a whole success?
First, DART’s staff on the Johns Hopkins Utilized Physics Laboratory (APL) and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) might want to look at information from ground-based observatories which are tasked with monitoring Dimorphos’ path.
Based on APL and JPL representatives talking at a press conference held shortly after Monday’s asteroid influence, we’re going to have to attend “about two months” for “the complete quantitative reply.” Nonetheless, “some items of the reply” are more likely to trickle out quickly, presumably as early as this week.
“The vast majority of near-Earth objects have orbits that don’t convey them very near Earth, and due to this fact pose no danger of influence, however a small fraction of them — known as probably hazardous asteroids — require extra consideration,” JPL says on its web site. “These objects are outlined as asteroids which are greater than about 460 ft (140 meters) in measurement with orbits that convey them as shut as inside 4.6 million miles (7.5 million kilometers) of Earth’s orbit across the solar.”
NASA’s Heart for Close to Earth Object Research is consistently monitoring all identified near-Earth objects to find out the extent of influence danger. And if DART has totally succeeded in its mission targets, we now have the means to ship a hazardous asteroid packing.
Editors’ Suggestions










